Selecting Element Using JavaScript
 dheeraj koranga
dheeraj koranga1. getElementById()
The getElementById() method is used to select and return a single HTML element by its unique id attribute. Since an id should be unique within a document, this method will only return one element.
If you enters a wrong id name then it will return a null value
Syntax:
document.getElementById("idName");
Example : we wil change the heading using getElementById("idName")
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1 id="title">Hello World</h1>
<button onclick="changeTitle()">Change Title</button>
</body>
</html>
function changeTitle() {
let newTitle = document.getElementById("title"); // object
newTitle.innerText = "new title"; // object property -> innerText
}
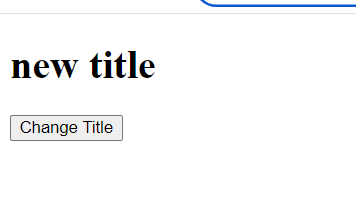
- In this example,
document.getElementById("title")selects the<h1>element, and we change its content to "New Title!" when the button is clicked.
2. getElementsByClassName()
The getElementsByClassName() method is used to select all elements with a given class name. It returns an HTMLCollection (a list of elements) that can be looped through, but it doesn't return an array.
If you enters a wrong class name then it will return a HTML collection with 0 length
Syntax:
document.getElementsByClassName("className");
Example : we wil change the paragraph content using getElementByClassName("")using for loop
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p class="text">First Paragraph</p>
<p class="text">Second Paragraph</p>
<p class="text">Third Paragraph</p>
<p class="text">Fourth Paragraph</p>
<button onclick="ChangeText()">Change Text</button>
<script src="index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
function ChangeText() {
const textObj = document.getElementsByClassName("text");
for (let i = 0; i < textObj.length; i++) {
textObj[i].textContent = "Updated para" + [i + 1];
}
}
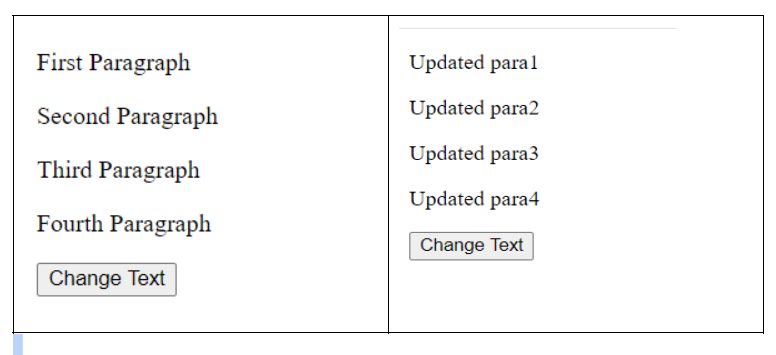
- Here, all elements with the class
"text"are selected and updated with new content using a loop.
3. getElementsByTagName()
The getElementsByTagName() method selects all elements with a specified tag name (like p, div, h1, etc.). It also returns an HTMLCollection of all matching elements.
Syntax:
document.getElementsByTagName("tagName");
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p class="text">First Paragraph</p>
<p class="text">Second Paragraph</p>
<p class="text">Third Paragraph</p>
<p class="text">Fourth Paragraph</p>
<button onclick="ChangeColor()">Change Text</button>
<script src="index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
let col = ["red", "blue", "teal", "Yellow"];
function ChangeColor() {
const tagObj = document.getElementsByTagName("p");
for (let i = 0; i < tagObj.length; i++) {
tagObj[i].style.color = col[i];
}
}
- Here, all
<p>tags are selected and their text color is changed to blue.

4. querySelector()
The querySelector() method selects the first element that matches a specified CSS selector (like class, id, tag name, or more complex nested queries). It returns the first matching element or null if no match is found.
Example (Selecting by ID):
document.querySelector("#myID");
Example (Selecting Nested Elements):
document.querySelector("div > p");
- This example selects a
<p>that is a direct child of a<div>element.
5. querySelectorAll()
The querySelectorAll() method selects all elements that match the given CSS selector. It returns a NodeList, which is similar to an array and can be looped over.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p class="text">First Paragraph</p>
<p class="text">Second Paragraph</p>
<p class="text">Third Paragraph</p>
<p class="text">Fourth Paragraph</p>
<button onclick="highlightAll()">Change Text</button>
<script src="index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
function highlightAll() {
const allPara = document.querySelectorAll(".text");
allPara.forEach((element) => {
element.style.backgroundColor = "teal";
element.style.color = "yellow";
});
}

- Here,
document.querySelectorAll(".text")selects all elements with the class"text"and changes their background color to teal.
Summary of Differences:
getElementById(): Selects one element by its unique ID.getElementsByClassName(): Selects all elements with a specific class name.getElementsByTagName(): Selects all elements of a specific tag type.querySelector(): Selects the first element that matches a given CSS selector.querySelectorAll(): Selects all elements that match a given CSS selector.
These methods are crucial for DOM manipulation in JavaScript, enabling dynamic interaction with HTML elements on a page.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from dheeraj koranga directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
