Deploying CI/CD Pipeline project without Docker-file using Build-packs
 PrithishG
PrithishG
let’s get started :
What is build-packs ?
How Buildpacks Work:
Detection: Buildpacks first detect the language and framework of your application. Based on this, they determine the specific Buildpacks to apply.
Compilation: They then automatically install the necessary dependencies, configure the environment, and compile the application.
Packaging: Once compiled, Buildpacks package the application along with the runtime environment into a container image, ready for deployment.
Why Buildpacks Are Useful:
No Dockerfile Needed: Buildpacks remove the need for developers to manually write and maintain Dockerfiles. They handle dependencies and environment setup automatically.
Security: Since Buildpacks create images with the latest security patches and dependencies, they ensure your app is running in a secure environment.
Portability: Applications packaged with Buildpacks can be deployed to various cloud platforms (e.g., Heroku, Cloud Foundry, Google Cloud Run, etc.), providing flexibility and ease of scaling.
Consistent Builds: Buildpacks ensure that builds are repeatable and consistent across different environments (development, staging, and production).
When to Use Buildpacks:
If you want a simplified build process that requires minimal configuration.
If your project needs a faster, automated containerization process.
If you're aiming for greater security by leveraging community-maintained Buildpacks that update dependencies automatically.
How to Install Buildpacks ?
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker.io -y
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER && newgrp docker
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:cncf-buildpacks/pack-cli
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install pack-cli
Project Implementation :
Step 1: we will be using AWS for that let’s launch ec2 instance obviously we will be using t2.micro with default configuration free tier instance and install docker and build-packs (for reference you can use above commands)
Step 2 : clone the todo application in ec2 using the below :
git clone <followed_by_the_url_of_your_project>
Step 3 : from the app directory hit the below command :
pack build suggest
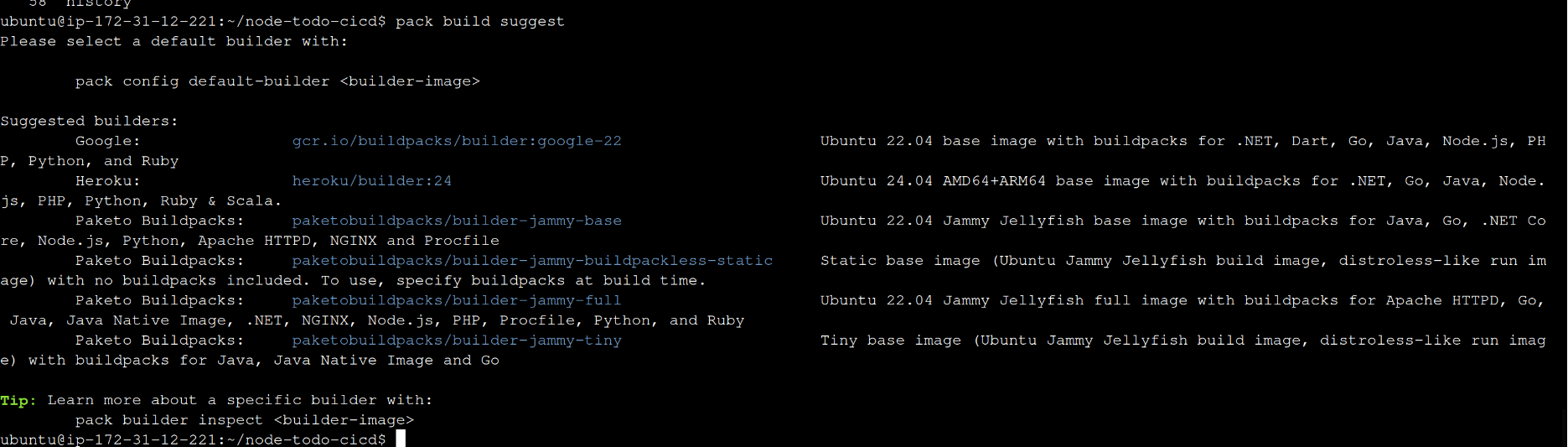
what is pack build ?
pack build command automatically detects the language and framework your app uses. It then selects and applies the appropriate Buildpacks for your app. For example, if you have a Node.js app, it will apply Node.js-specific Buildpacks.Step 4 : let’s choose the first image and create our container without dockerfile :
pack build --builder=gcr.io/buildpacks/builder:google-22 pg_node_app
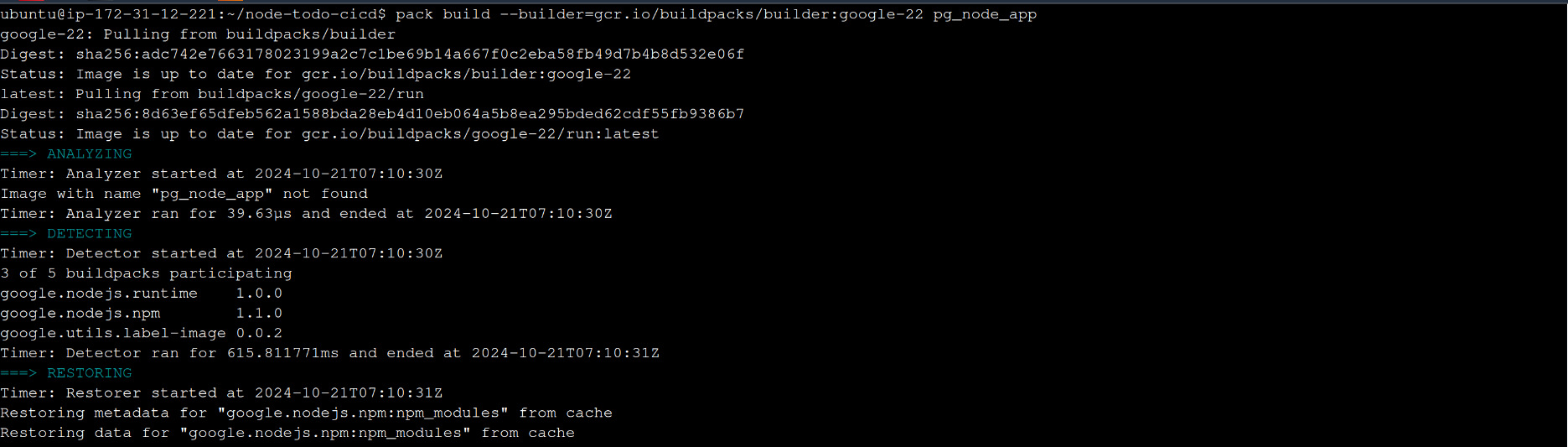
we need to check whether image has been created or not :
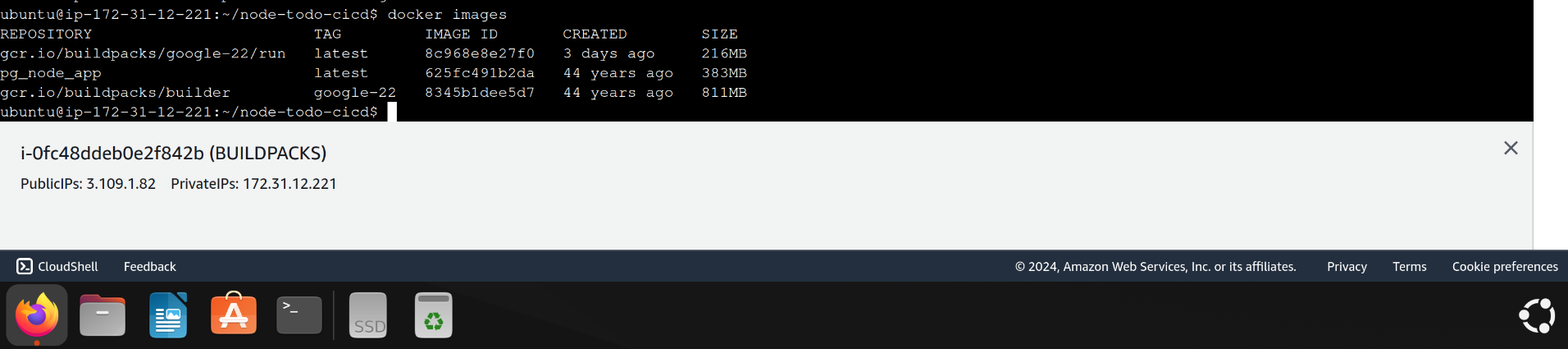
docker images
output :
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
gcr.io/buildpacks/google-22/run latest 8c968e8e27f0 3 days ago 216MB
pg_node_app latest 625fc491b2da 44 years ago 383MB
gcr.io/buildpacks/builder google-22 8345b1dee5d7 44 years ago 811MB
Step 5 : let’s run the image and add the 8000 port in our inbound rules as gthe application works on 8000
docker run -d -p 8000:8000 pg_node_app
checking my ec2 instance http://IP:<followed_by_port_number> should our application up and running
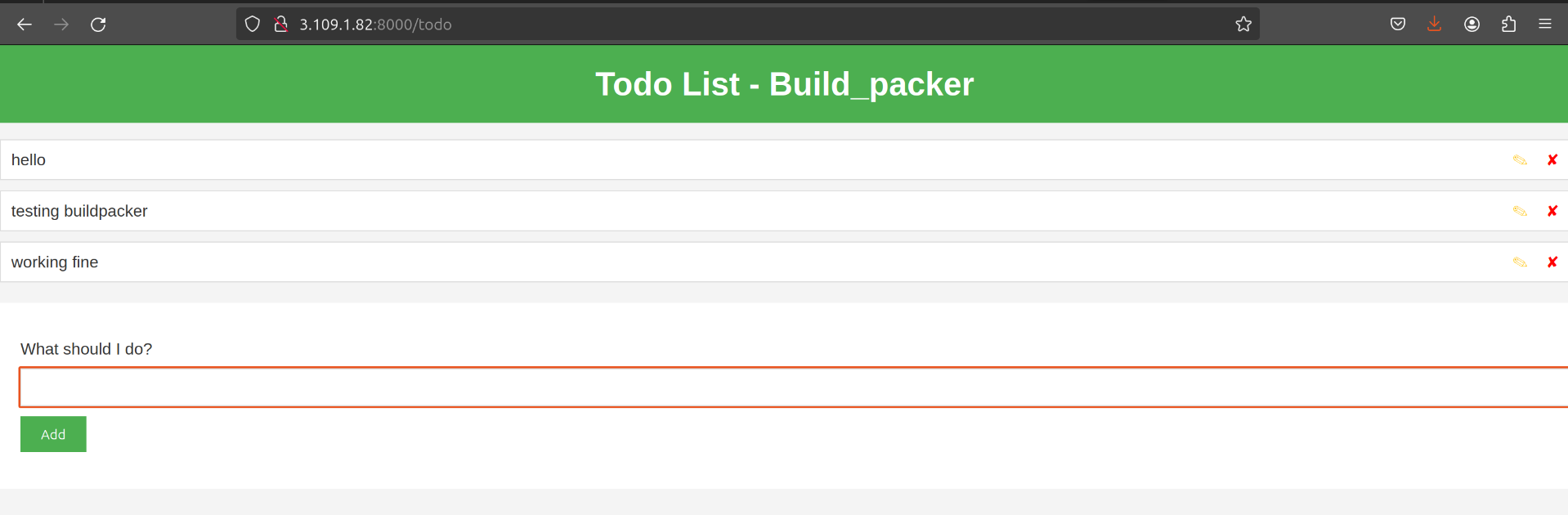
as you can see it is up and running perfectly.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from PrithishG directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
