End-to-End CI/CD Implementation using Jenkins, Docker, Argo CD, Kubernetes
 Radhika's Blog
Radhika's BlogImplementing an end-to-end Java-based application using Jenkins, Docker, SonarQube, Argo CD, and Kubernetes involves several steps.
Here's a comprehensive guide to help you set up the entire pipeline, from development to deployment:
Prerequisites
1. Version Control System (VCS)
- Git: Ensure Git is installed and configured. Your codebase should be hosted on a platform like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket.
2. CI/CD Tool
Jenkins: Install Jenkins for managing your CI/CD pipeline. Other options include GitLab CI, CircleCI, or Travis CI.
Java is the prerequisite for the Jenkins.
Jenkins is used as the CI server to build the application. Whenever there is a new code commit, Jenkins automatically pulls the code from GitHub, builds it using Maven, and runs automated tests. If the tests fail, the build is marked as failed and the team is notified.
3. Static Code Analysis
SonarQube: Set up SonarQube for static code analysis. This can be installed locally or on a server.
SonarQube is used to analyze the code and report on code quality issues such as bugs, vulnerabilities, and code smells. The SonarQube analysis is triggered as part of the Jenkins build pipeline.
4. Containerization
Docker: Install Docker to create and manage application containers.
Docker is used to containerizing the Java application. The Docker file is stored in the Git repository along with the source code. The Docker file specifies the environment and dependencies required to run the application.
Docker Hub: A container registry is a repository for storing Docker images. It serves as a centralized location for developers to push, store, and pull images..
5. Continuous Deployment
Argo CD is used to automate the deployment of the containerized application to Kubernetes. Whenever a new version of the application image is pushed to the Git repository, Argo CD will automatically deploy it to the Kubernetes cluster.
Overall, this project demonstrates how to integrate various tools commonly used in software development to streamline the development process, improve code quality, and automate deployment.
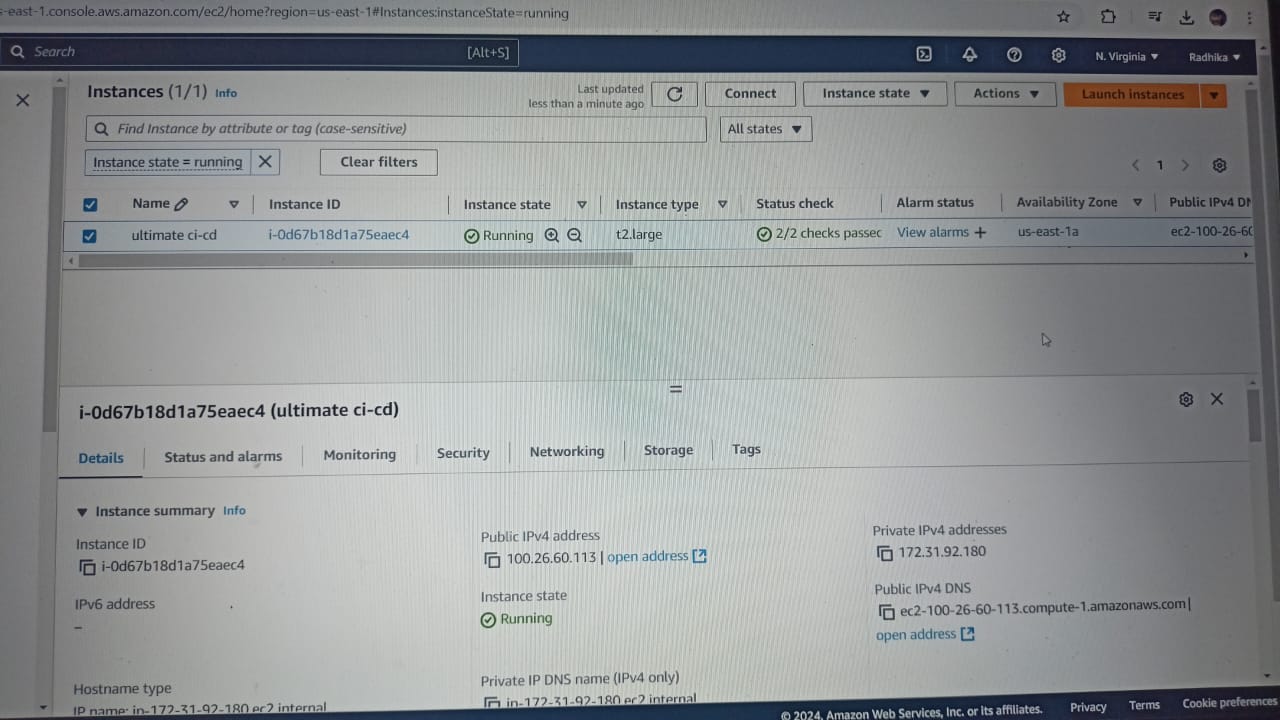
Launch AWS EC2 Instance: Login to an AWS account using a user with admin privileges and ensure your region is set to us-east-1 N. Virginia.(You can choose any region)
Move to the EC2 console. Click Launch Instance.
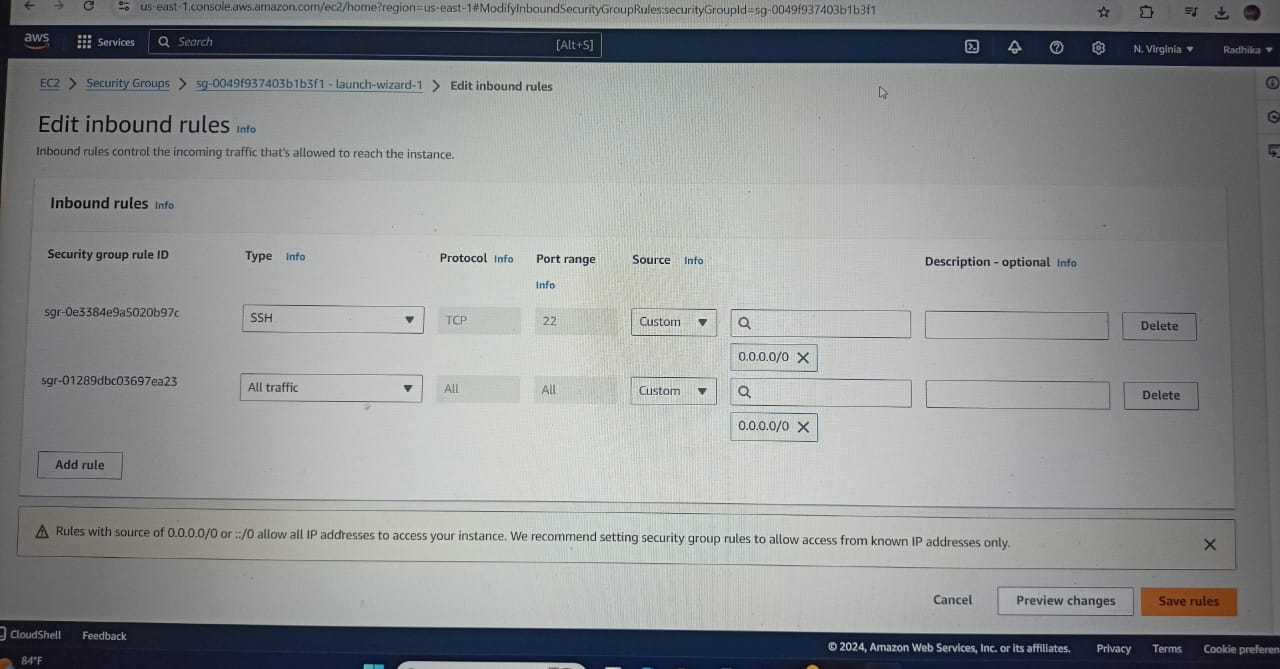
Give name as ultimate ci-cd (as your wish).Select AMIs as Ubuntu and select Instance Type as t2.large. Create new Key Pair and configure security group and click Inbound rules→ add rule → Type as All traffic → source as anywhere IP4 → save rules.
Note: your not supposed to allow All Traffic in Real Time Scenario.
This is a simple Spring Boot-based Java application that can be built using Maven.
git clone
cd Jenkins-Zero-To-Hero/java-maven-sonar-argocd-helm-k8s/spring-boot-app
sudo apt update
sudo apt install maven
mvn clean package
mvn -v
sudo apt update

Now we are going to deploy this application on Kubernetes by CICD pipeline.
Continuous Integration
Install and Setup Jenkins
Step 1: Install Jenkins
Follow the steps for installing Jenkins on the EC2 instance.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jre -y
java --version
Install Jenkins
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee \
/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian binary/ | sudo tee \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
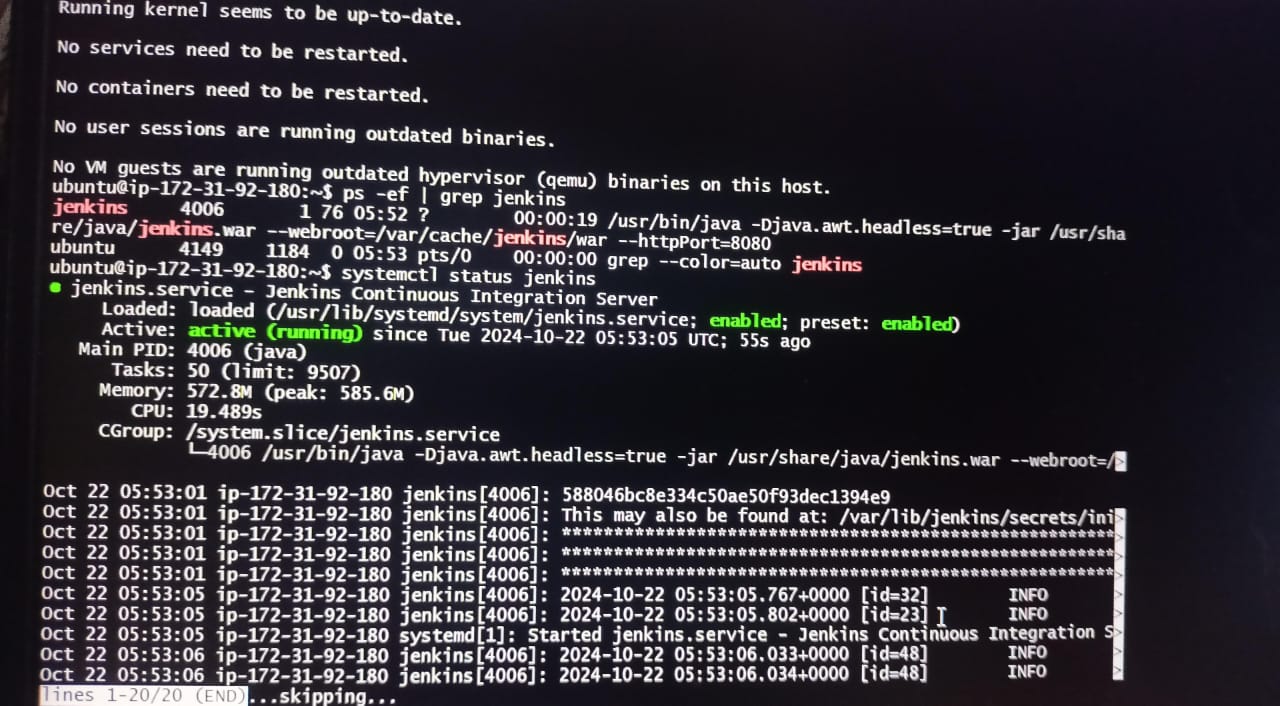
ps -ef | grep jenkins
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Step 2: Setup Jenkins
You can get the ec2-instance-public-ip-address from your AWS EC2 console page.
Jenkins will run the port 8080 by default.
http://<ec2-instance-public-ip-address>:8080/
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
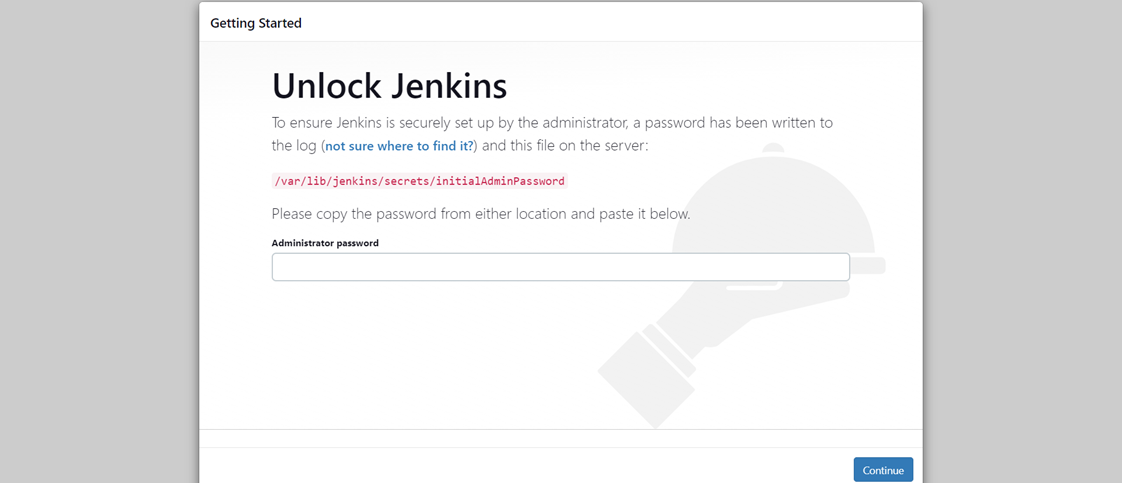

After completing the installation of the suggested plugin you need to set theFirst Admin User for Jenkins.
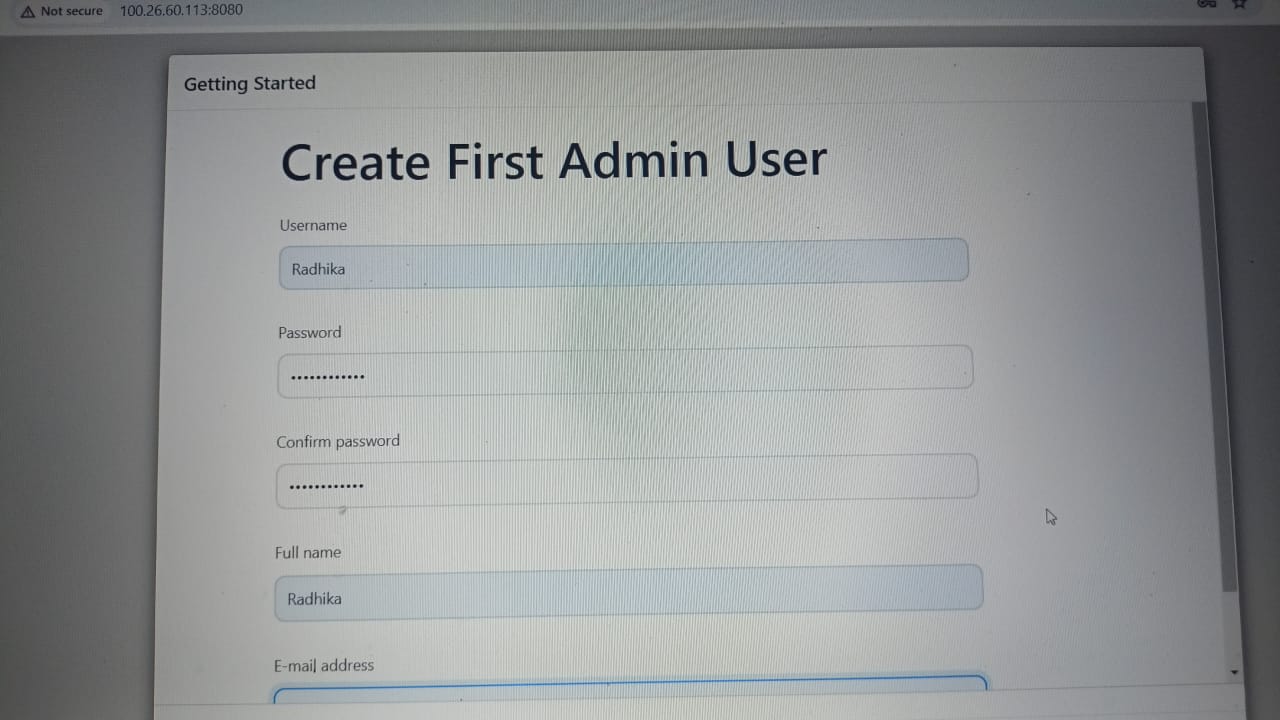
Click Save and Continue.
Click Save and Finish.
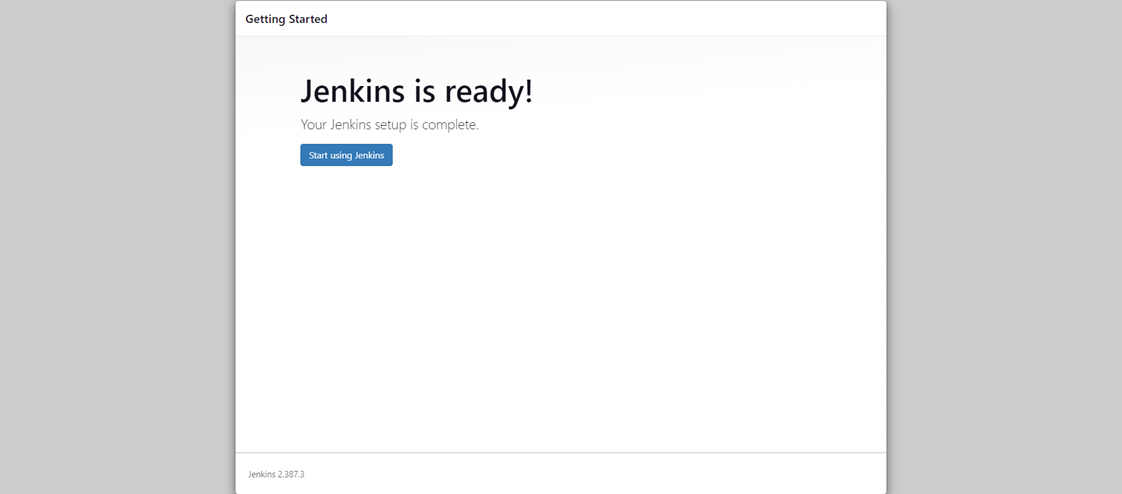
And now your Jenkins is ready for use.
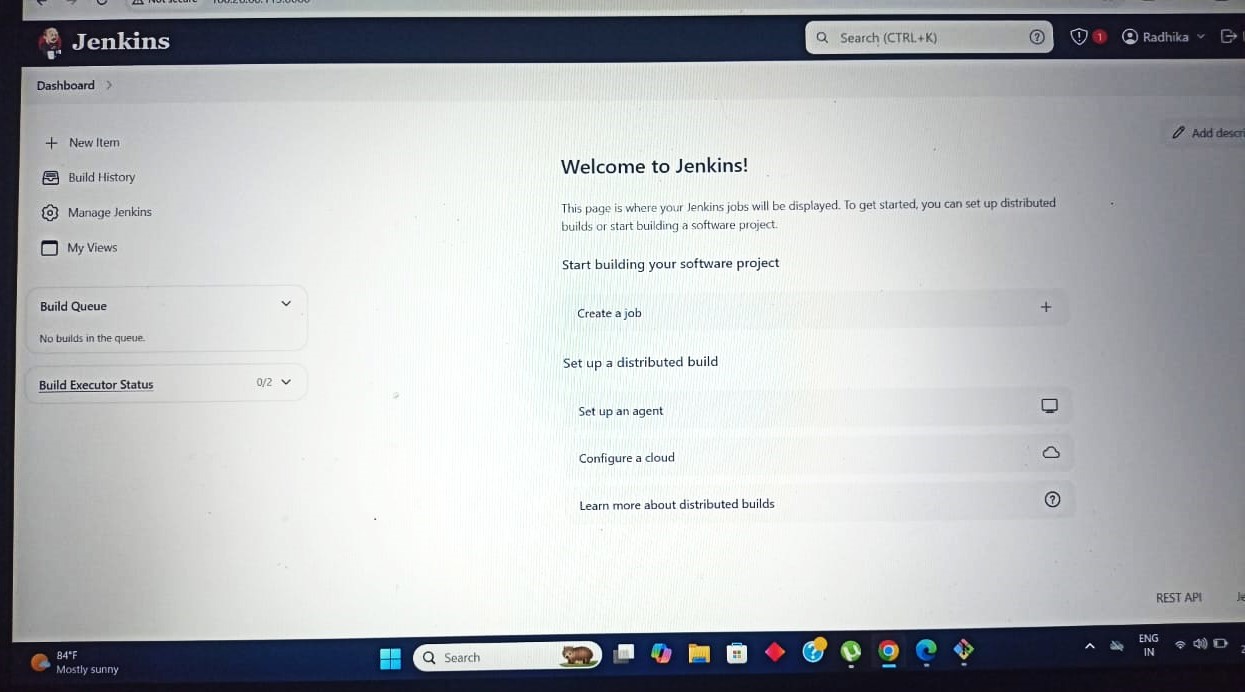
Start Using Jenkins
Create a new Jenkins pipeline
Github: github.com/radhikajessy/Jenkins-Zero-To-Hero
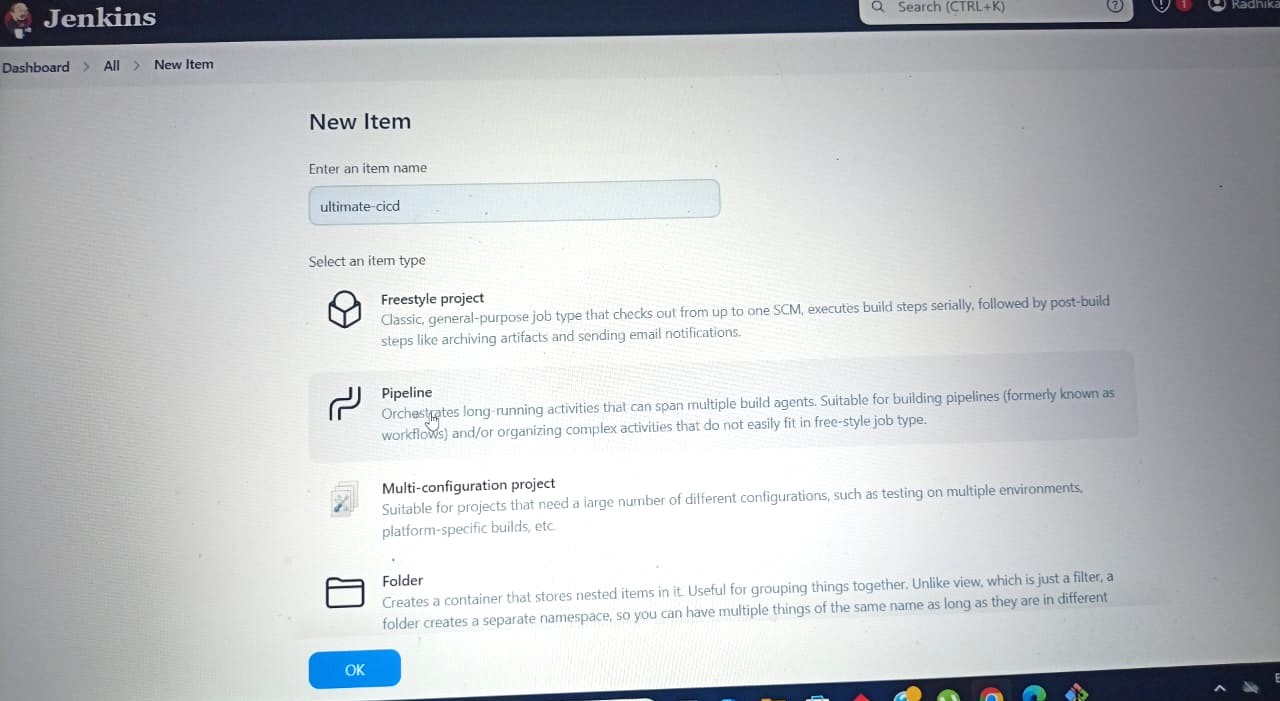
✅Click on New Item. Select Pipeline and Enter an Item name.
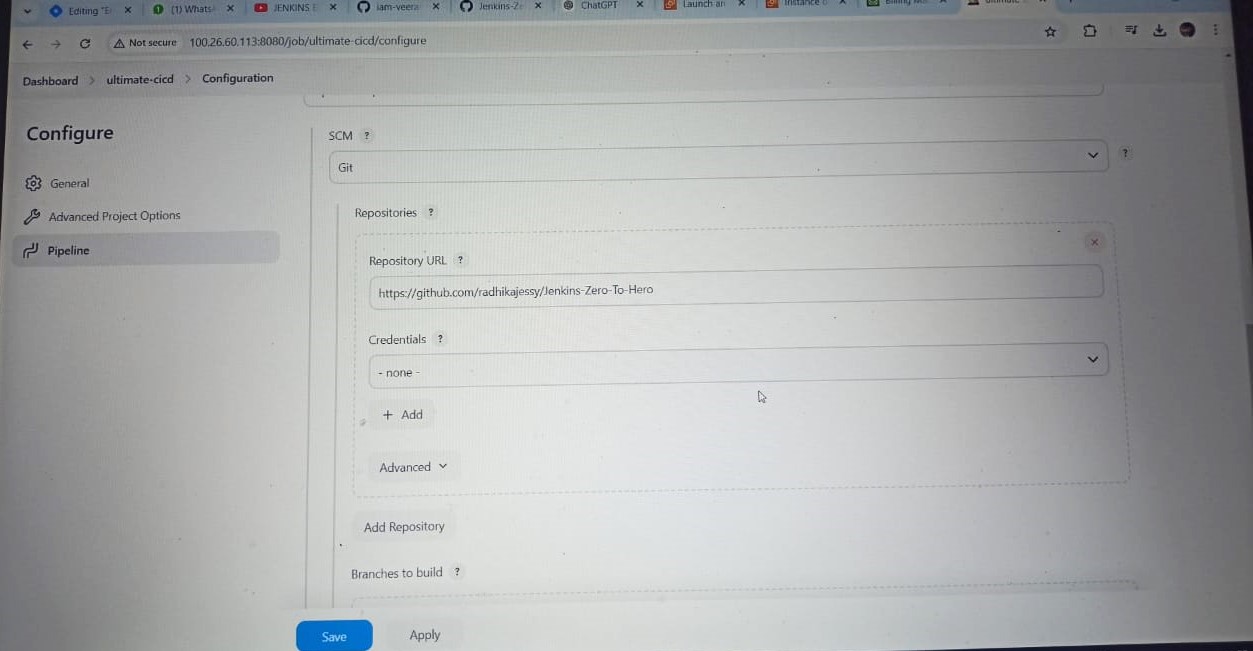
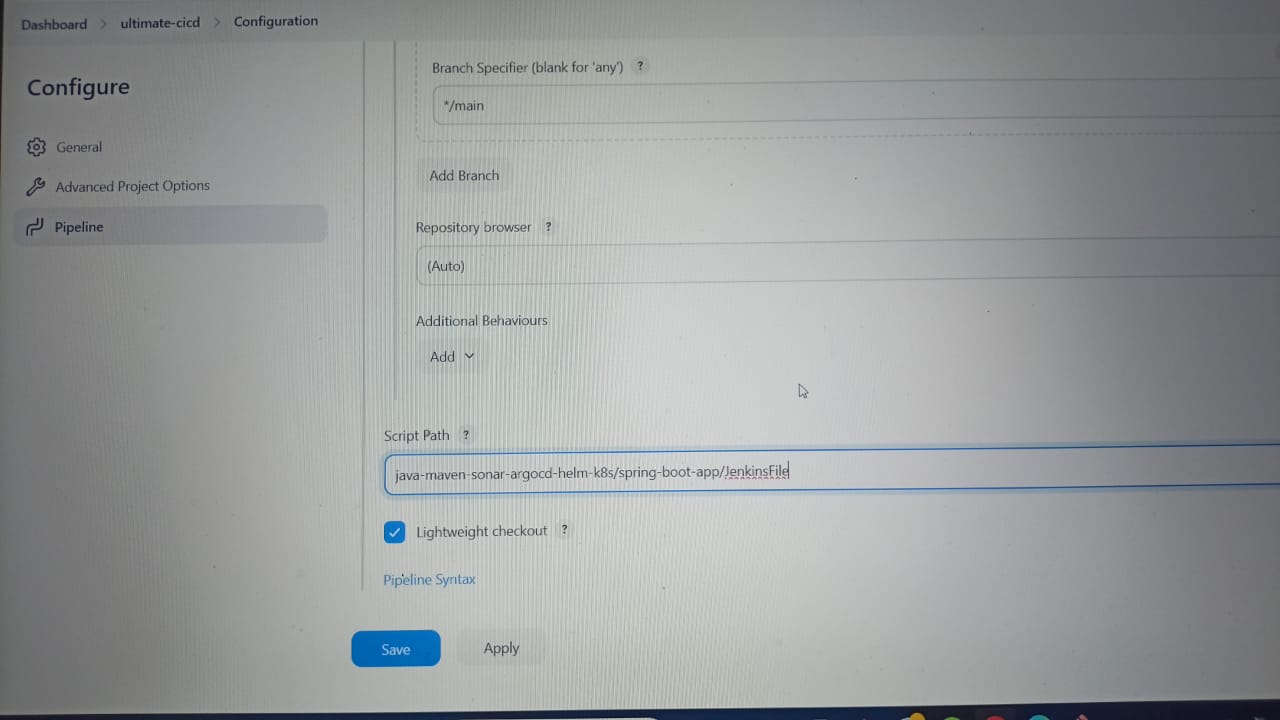
✅Select your repository where your Java application code is present. Make changes in Repository according to your Docker Hub Id and GitHub Id in spring-boot-app/Jenkins File and spring-boot-app-manifest/deployment.yml
✅Update this URL in spring-boot-app/Jenkins File with your SonarQubeURL(EC2 server)
Install the necessary Jenkins plugins.
Goto Jenkins Dashboard ==>Manage Jenkins ==>Plugins ==>Available plugins
Docker Pipeline
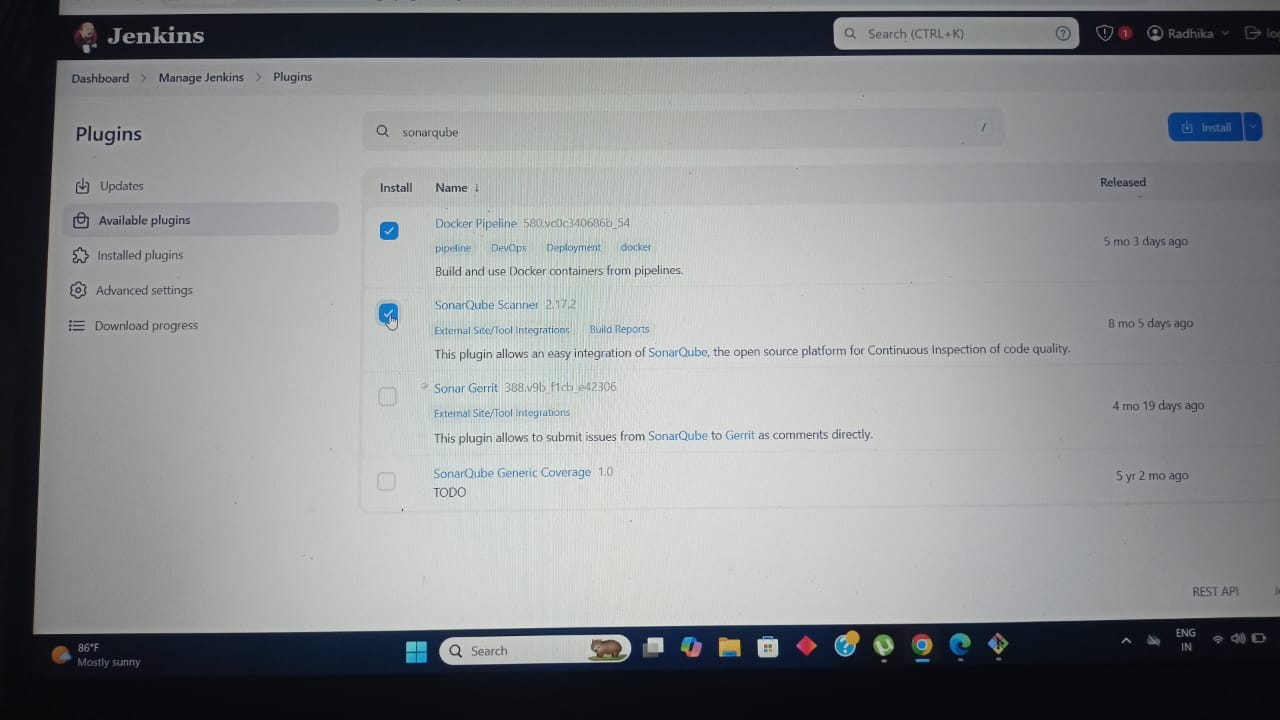
SonarQube Scanner
Configure a Sonar Server locally
SonarQube is used as part of the build process (Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery) in all Java services to ensure high-quality code and remove bugs that can be found during static analysis.
sudo apt install unzip
sudo adduser sonarqube
sudo su – sonarqube
wget https://binaries.sonarsource.com/Distribution/sonarqube/sonarqube-9.4.0.54424.zip
unzip *
chmod -R 755 /home/sonarqube/sonarqube-9.4.0.54424
chown -R sonarqube:sonarqube /home/sonarqube/sonarqube-9.4.0.54424
cd sonarqube-9.4.0.54424/bin/linux-x86-64/
./sonar.sh start

http://<ec2-instance-public-ip-address>:9000/
Enter Login as admin and password as admin.
Change with a new Password.
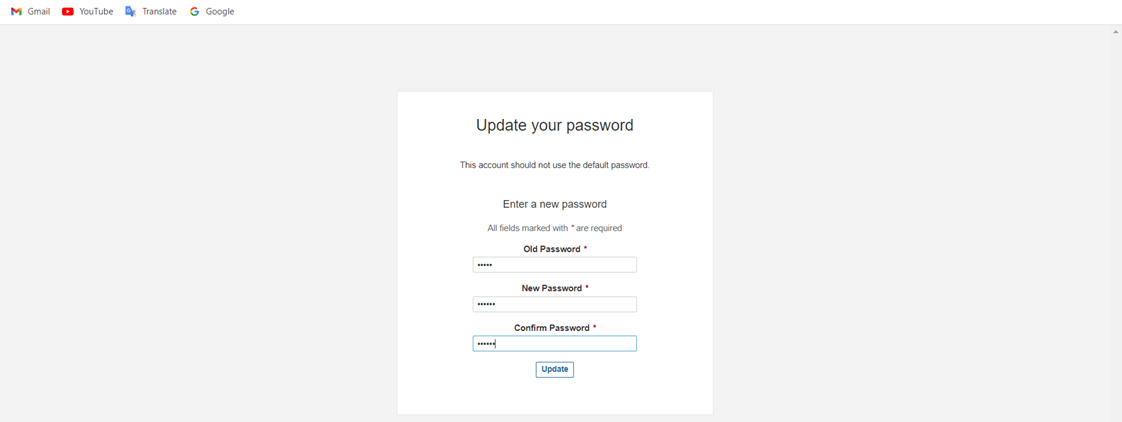
Create Credentials in Jenkins.
Please keep the below credentials ID name (sonarqube, docker-cred, github) as it is. Else according to your credentials, you need to make changes in Jenkinsfile.
Step 1: Credential for SonarQube
Go to the right-hand corner A then click on My Account ==>Security
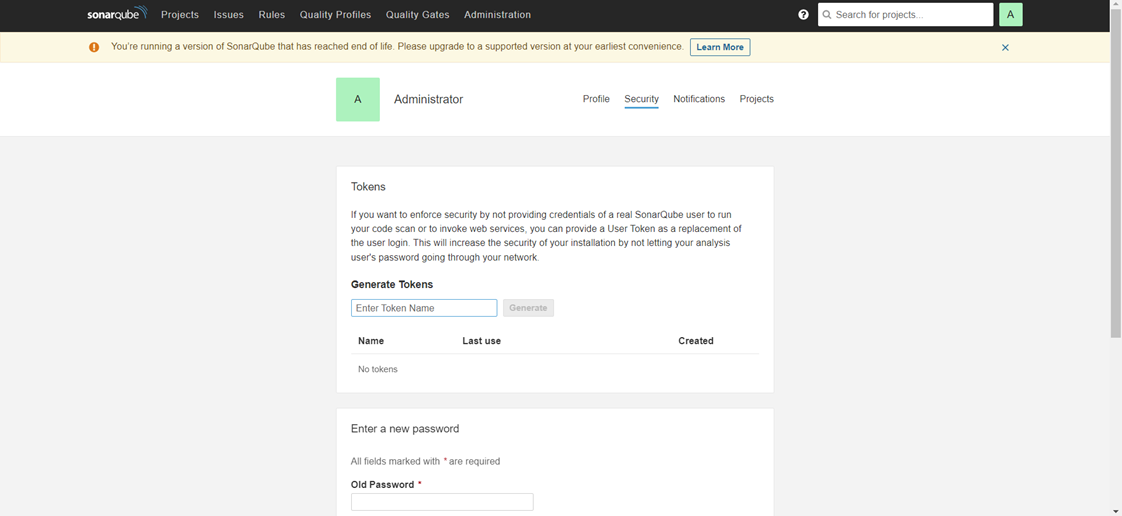
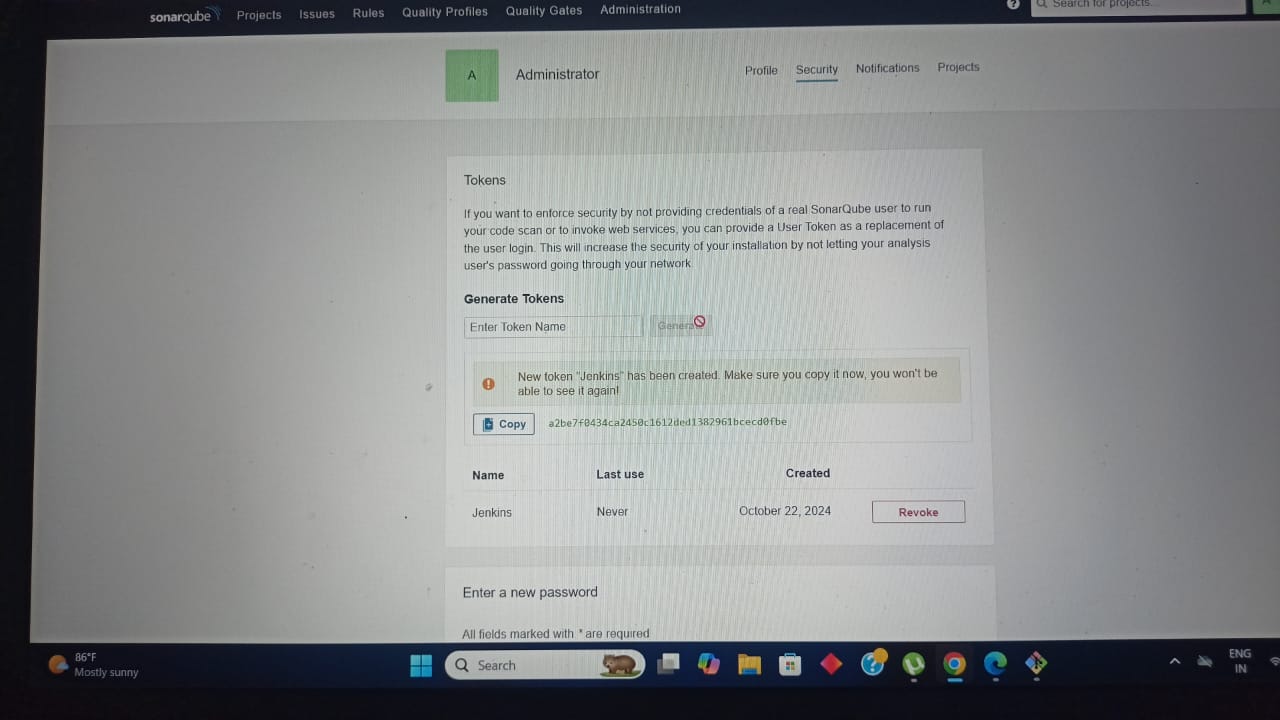
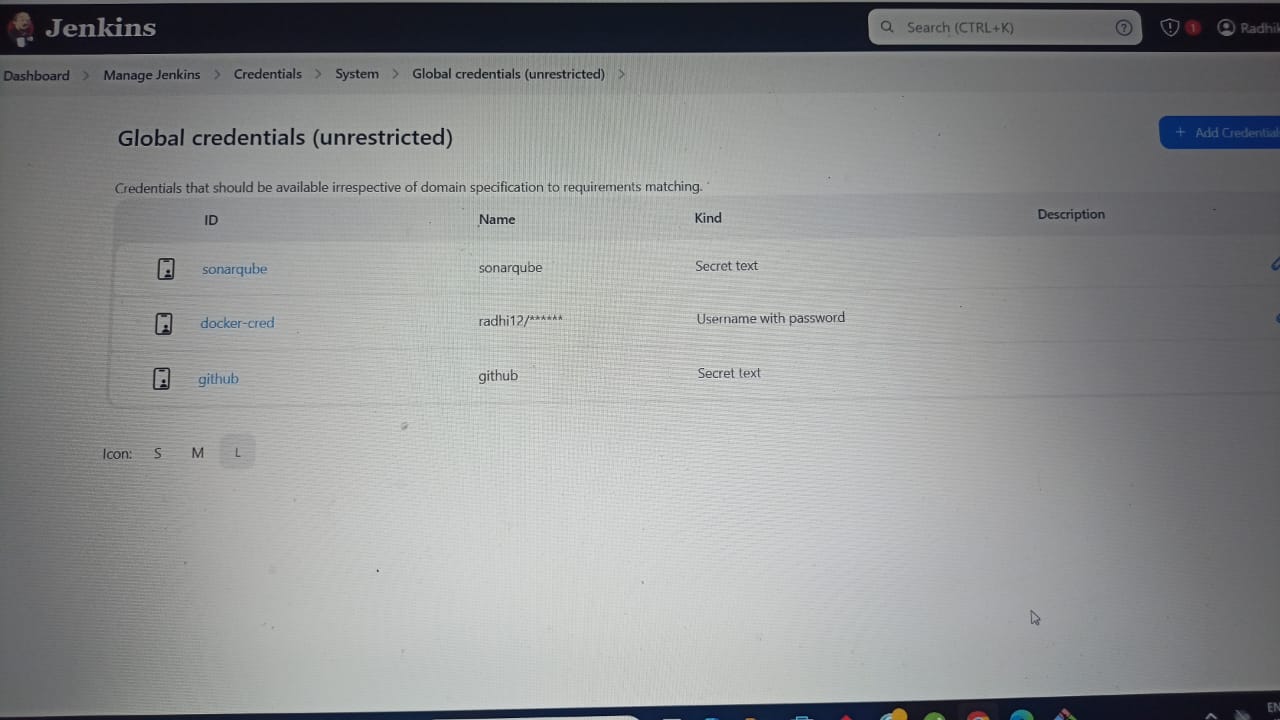
Step 2: Create Docker Hub Credential in Jenkins
Step 1: Setup Docker Hub Secret Text in Jenkins
You can set the docker credentials by going into –
Goto ->Jenkins ->Manage Jenkins ->Manage Credentials ->Stored scoped to jenkins ->global ->Add Credentials
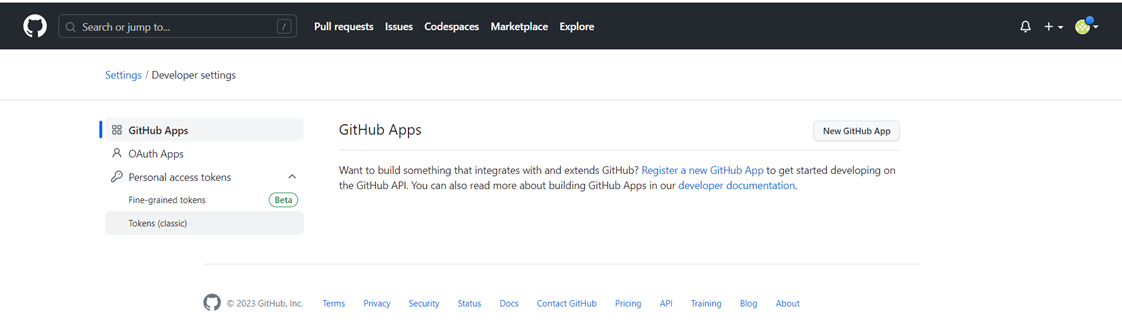
Step 3: Create GitHub credential in Jenkins
Goto GitHub ==>Setting ==>Developer Settings ==>Personal access tokens ==>Tokens(Classic) ==>Generate new token
Install Docker
If you have not performed step 1 and docker is not installed on your machine then please follow the below steps:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker.io
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
sudo usermod -aG docker Jenkins
sudo systemctl restart docker
Do jenkins Restart.
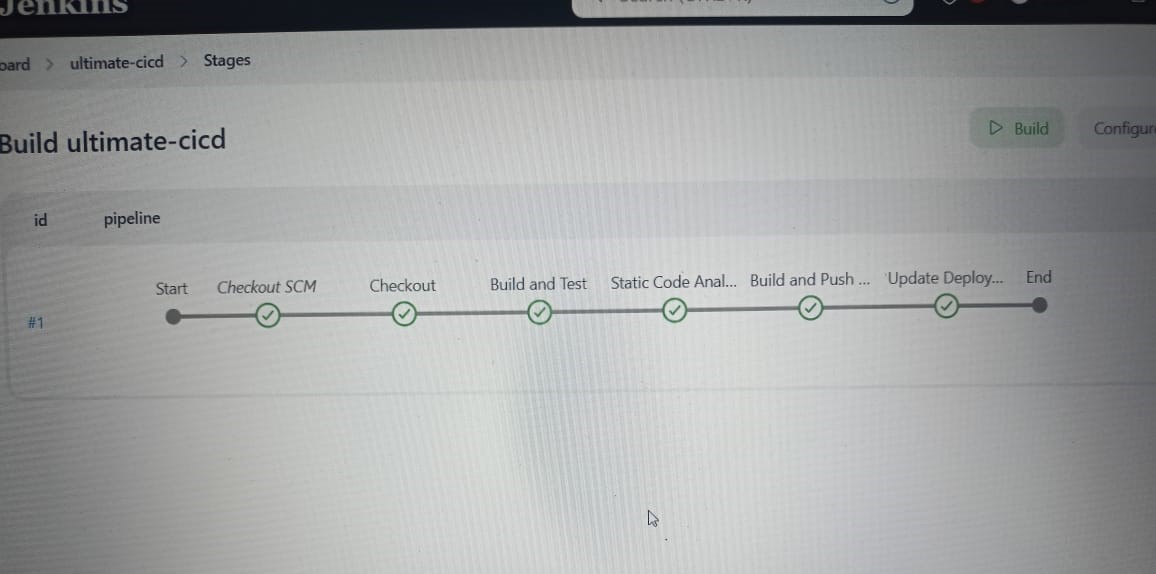
Run Pipeline
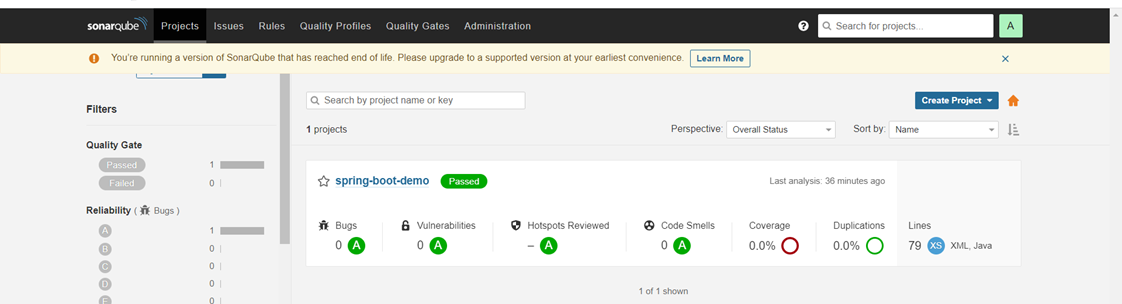
SonarQube Output will be as shown in the following image.
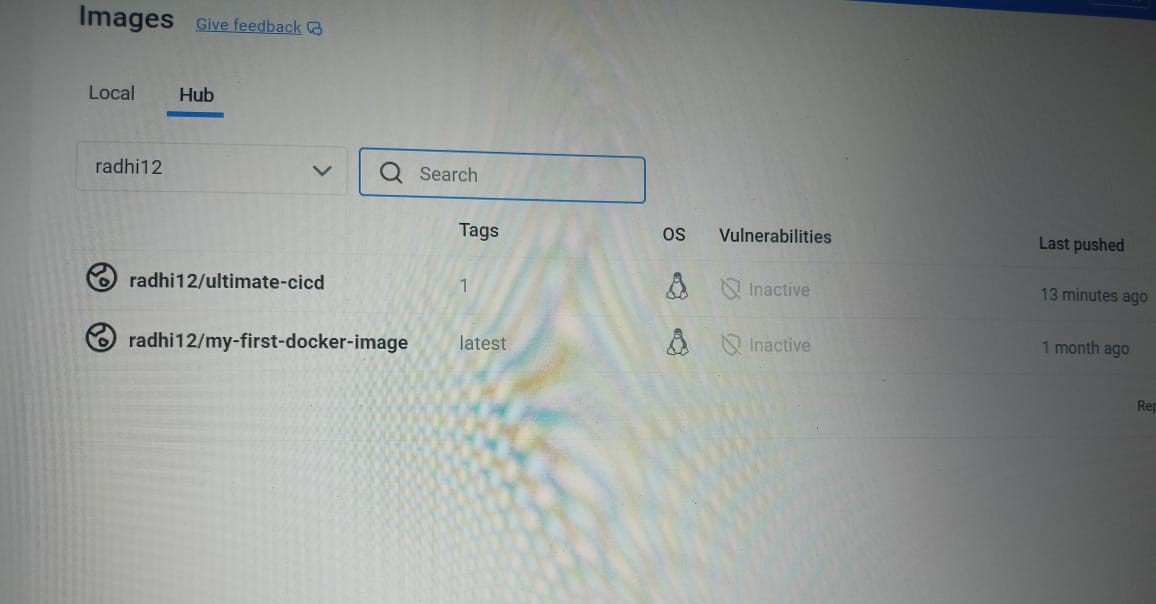
Check Docker Hub, that a new image is created for your Java application.
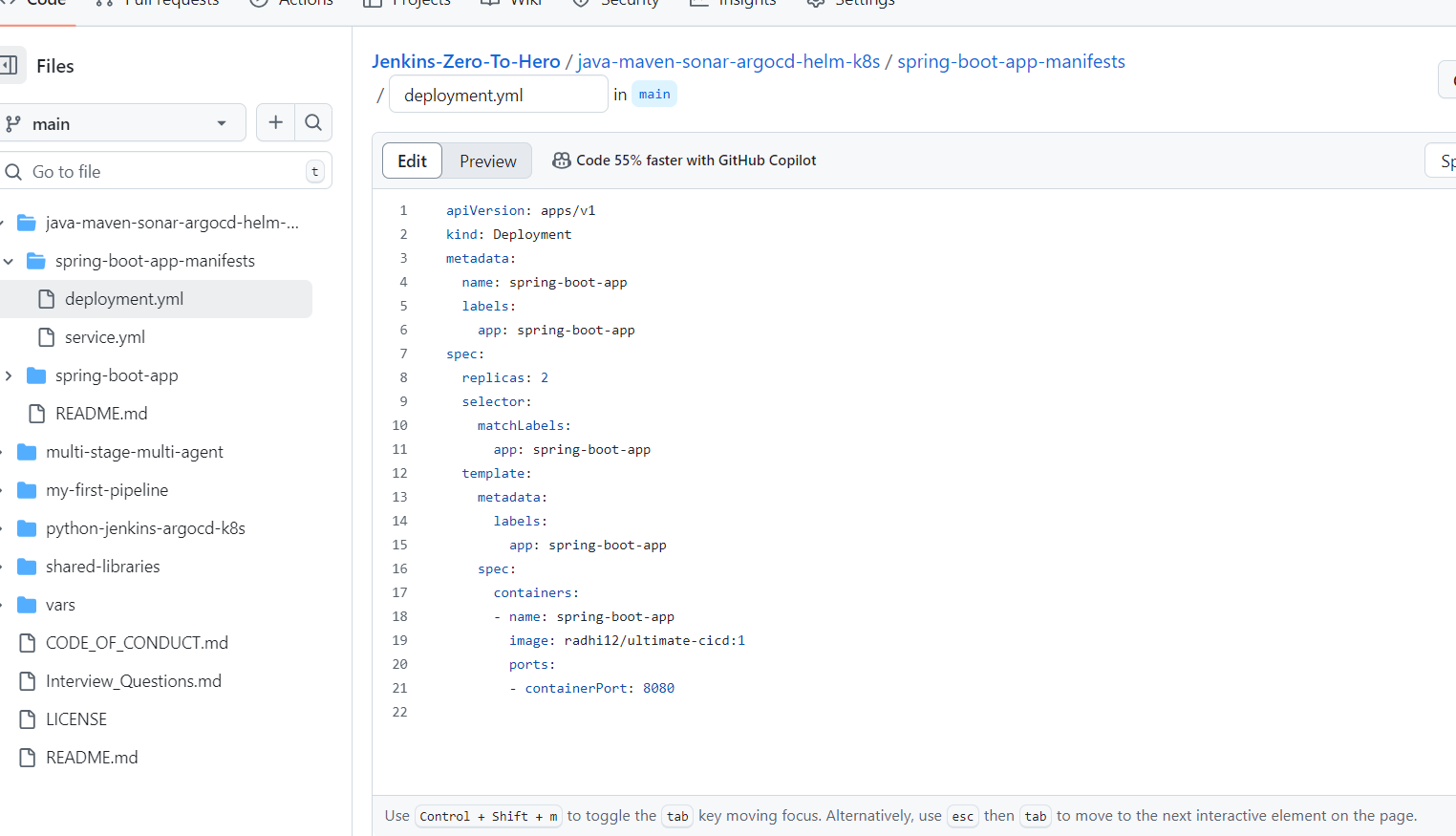
goto deployement.yml file gets updated with the latest image.
This way, we completed CI (Continuous Integration) Part. Java application is built, SonarQube completed static code analysis and the latest image is created, push to DockerHub and updated Manifest repository with the latest image.
Continuous Delivery Part
ArgoCD is utilized in Kubernetes to establish a completely automated continuous delivery pipeline for the configuration of Kubernetes. This tool follows the Git Ops approach and operates in a declarative manner to deliver Kubernetes deployments seamlessly.
Argo CD Setup
Argo CD is a very simple and efficient way to have declarative and version-controlled application deployments with its automatic monitoring and pulling of manifest changes in the Git repo, but it also has easy rollback and reverts to the previous state, not manually reverting every update in the cluster.
Setup Minikube
Minikube is a tool that enables users to set up and run a single-node Kubernetes cluster on their local machine. It is useful for developers who want to test their applications in a local Kubernetes environment before deploying them to a production cluster. Minikube provides an easy way to learn and experiment with Kubernetes without the need for a complex setup
After performing the steps we install Minikube and start it.
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-l
sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
minikube start --driver=docker
Install kubectl
Kubectl is a command-line interface (CLI)tool that is used to interact with Kubernetes clusters. It allows users to deploy, inspect, and manage Kubernetes resources such as pods, deployments, services, and more. Kubectl enables users to perform operations such as creating, updating, deleting, and scaling Kubernetes resources.
Run the following steps to install kubectl
curl -LO "https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl
chmod +x ./kubectl
sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin
kubectl version
Install Argo CD operator
ArgoCD is a widely-used GitOps continuous delivery tool that automates application deployment and management on Kubernetes clusters, leveraging Git repositories as the source of truth. It offers a web-based UI and a CLI for managing deployments, and it integrates with other tools. ArgoCD streamlines the deployment process on Kubernetes clusters and is a popular tool in the Kubernetes ecosystem.
The Argo CD Operator manages the full lifecycle of Argo CD and its components. The operator’s goal is to automate the tasks required when operating an Argo CD cluster.
curl -sL https://github.com/operator-framework/operator-lifecycle-manager/re
kubectl create -f https://operatorhub.io/install/argocd-operator.yaml
kubectl get csv -n operators
kubectl get pods -n operators
The following example shows the most minimal valid manifest to create a new Argo CD cluster with the default configuration.
Create argocd-basic.yml with the following content.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1kind
kind: ArgoCD
metadata:
name: example-argocd
labels:
example: basic
spec: {}
NodePort services are useful for exposing pods to external traffic where clients have network access to the Kubernetes nodes.
kubectl edit svc example-argocd-server And change from ClusterIP to NodePort. Save it.
minikube service argocd-server
minikube service list
Argo CD Configuration
Username : admin
Password : admin
We will use the Argo CD web interface to run sprint-boot-app.
Password for Argo CD
Find out password for Argo CD, so that, we can access Argo CD web interface.
Copy admin. password
kubectl get secret
kubectl edit secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -n argocd
echo <admin.password> | base64 -d
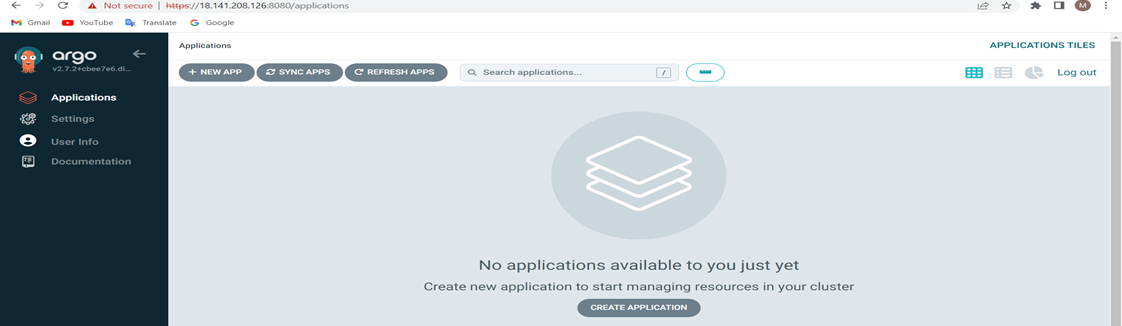
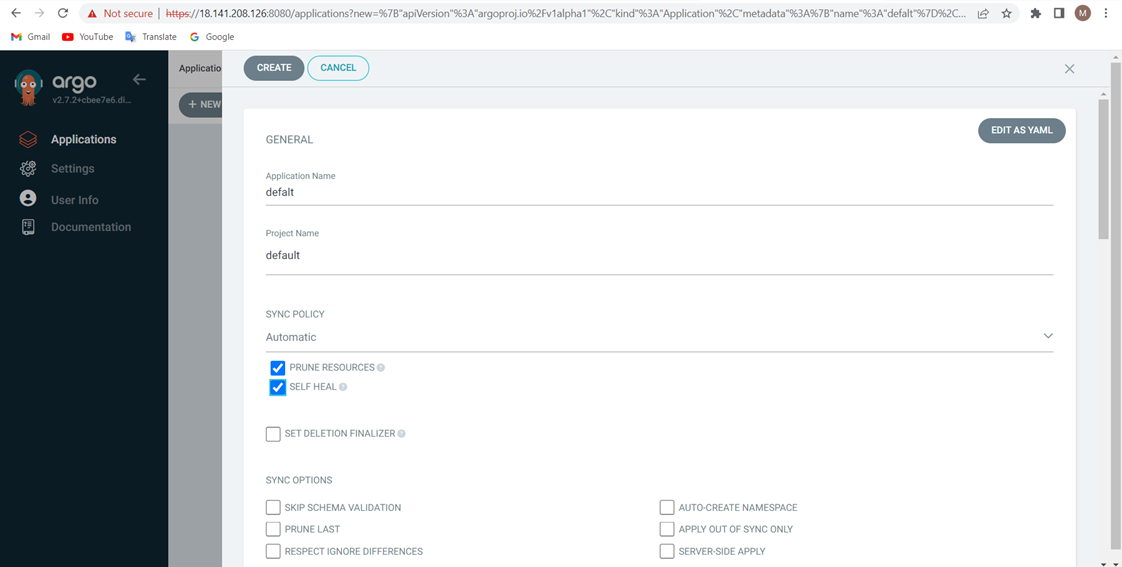
Set up Github Repository manifest and Kubernetes cluster.
After Create. You can check if pods are running for sprint-boot-app
kubectl get pods
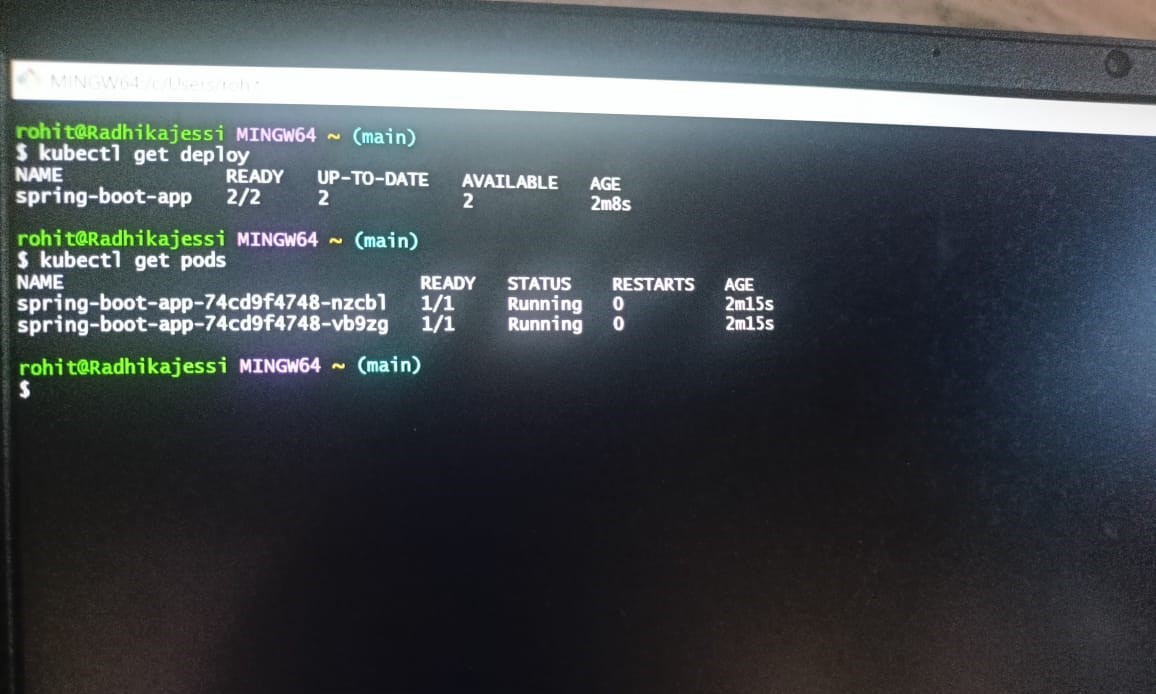
You have now successfully deployed an application using Argo CD.
Argo CD is a Kubernetes controller, responsible for continuously monitoring all running applications and comparing their live state to the desired state specified in the Git repository.
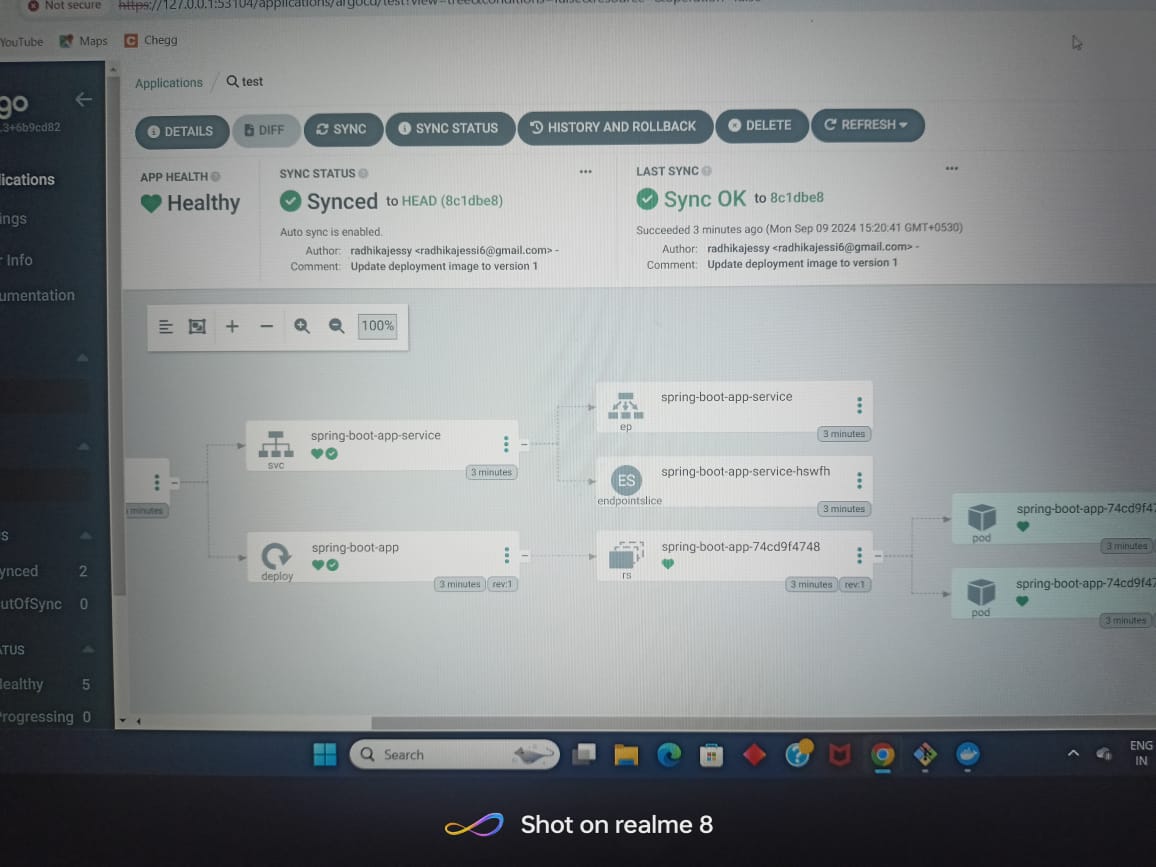
References
https://github.com/radhikajessy/Jenkins-Zero-To-Hero.git
Thank you so much
I hope you found the information valuable and insightful.
Thank you🙏
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Radhika's Blog directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Radhika's Blog
Radhika's Blog
Hello Folks, Enthusiastic and results-driven aspiring DevOps engineer with a solid background in cloud technologies, software development, and automation. AWS Certified Developer with expertise in building and deploying cloud-native applications and CI/CD pipelines. Adept at leveraging tools like Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and Terraform to optimize system performance, streamline deployments, and enhance scalability. Strong understanding of version control systems (Git). Exploring tools like monitoring tools (Prometheus, Grafana) to ensure system reliability and efficiency. Let's Connect and Happy Learning.