Decoding MVC Architecture : Blueprint for Streamlined Software Development
 Pranav Kumbhar
Pranav Kumbhar
MVC stands for Model-View-Controller and is a software architecture pattern commonly used to develop software applications. Although originally designed for desktop computing, MVC has been widely adopted as a design for World Wide Web applications in major programming languages.
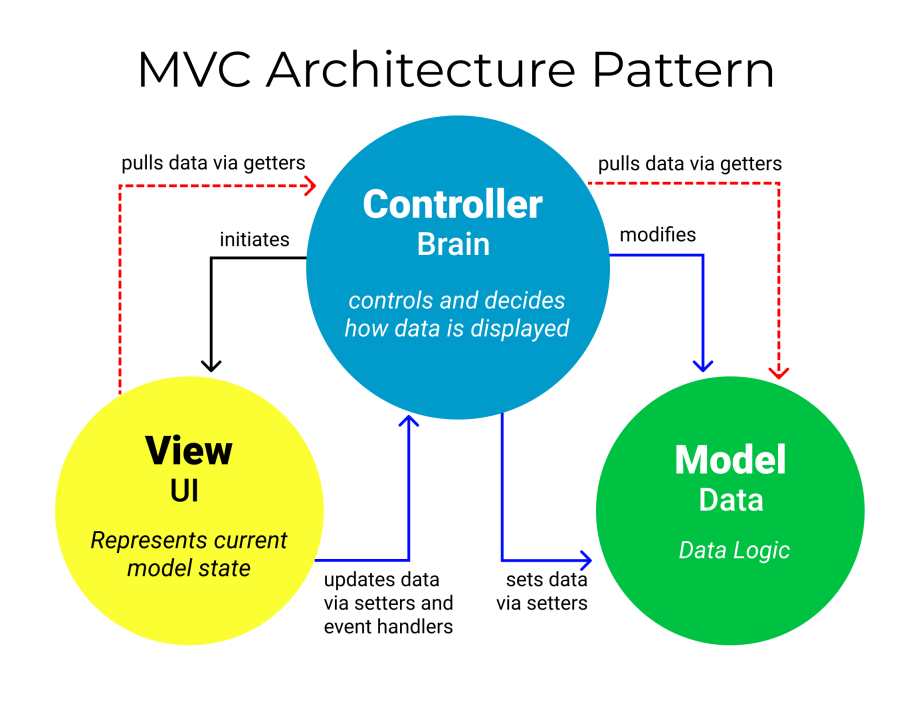
Components of MVC :
- Model : -
Represents the data and the business logic of the application.
It directly manages the data, logic, and rules of the application.
The model is responsible for interacting with the database, performing calculations, and ensuring data consistency.
Example: In an e-commerce application, the model could be responsible for retrieving product data from a database.
- View : -
This is the user interface or the presentation layer.
It displays the data from the model to the user and sends the user’s input to the controller.
The view only handles the presentation and is not concerned with the underlying business logic or data.
Example: In a weather app, the view is responsible for showing the current weather, temperature, and forecast.
- Controller : -
Acts as an intermediary between the Model and the View.
It processes user input from the View, updates the Model, and then updates the View with new data.
Example: If a user clicks on a "Submit" button, the controller handles the input, updates the model (perhaps saving data to a database), and then updates the view to show the result.
How MVC Works ???
User Interaction: The user interacts with the interface (View).
Controller Response: The Controller interprets the input, updates the Model.
Model Update: The Model performs business logic and updates the data.
View Update: The View is updated with the data from the Model and rendered to the user.
Benefits of MVC : -
separation of Concerns: Each component is independent, making it easier to manage and scale the application.
Reusability: The same Model can be used with different Views, and multiple Views can present the same Model.
Maintainability: Code is more modular, making it easier to update and maintain.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Pranav Kumbhar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
