Using AWS Application Load Balancer as an Ingress Controller for EKS Clusters: A Comprehensive Guide
 Prathamesh Bhongale
Prathamesh BhongaleIntroduction
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) provides various options for routing external traffic to your applications. The AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) Ingress Controller offers a powerful, cost-effective way to manage incoming traffic for your Kubernetes applications. In this guide, we'll explore how to set up and optimize ALB as an ingress controller for your EKS cluster.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, ensure you have:
A functioning EKS cluster
kubectl configured to interact with your cluster
AWS CLI installed and configured
Necessary IAM permissions
Helm package manager (optional)
Why Choose ALB as an Ingress Controller?
The AWS ALB Ingress Controller offers several advantages:
Native AWS Integration: Seamless integration with AWS services and features
Cost-Effective: Pay only for the ALB resources you use
Advanced Routing: Support for path-based routing, host-based routing, and TLS termination
AWS WAF Integration: Built-in web application firewall capabilities
Automatic Scaling: Handles traffic spikes without manual intervention
Architecture Diagram
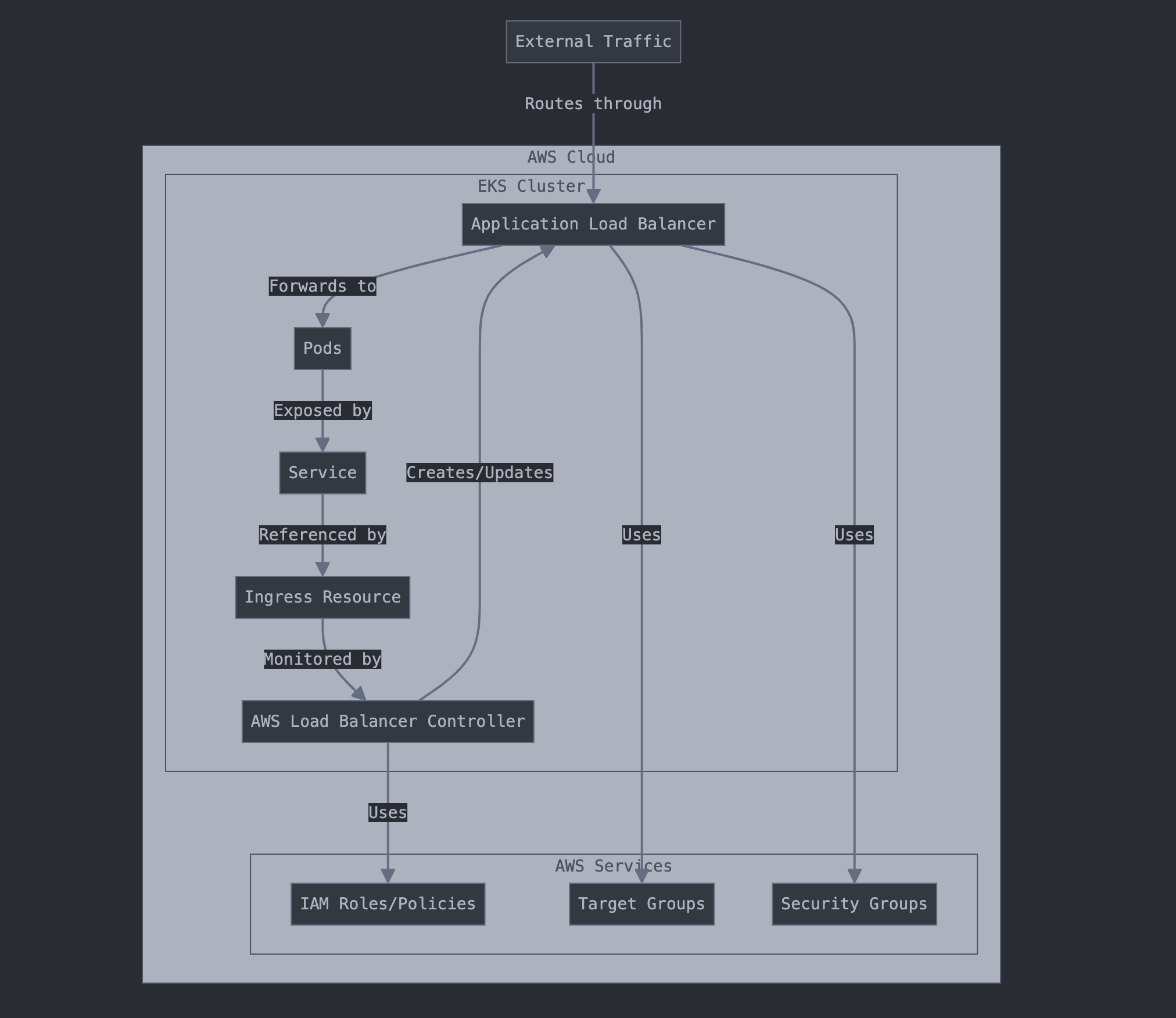
Implementation Steps
1. Create Required IAM Policies
First, create an IAM policy that grants necessary permissions:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"elasticloadbalancing:*",
"ec2:CreateTags",
"ec2:DescribeAccountAttributes",
"ec2:DescribeAddresses",
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:DescribeSubnets",
"ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups",
"ec2:DescribeVpcs",
"iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole",
"cognito-idp:DescribeUserPoolClient"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
2. Create IAM Role for Service Account
eksctl create iamserviceaccount \
--cluster=your-cluster-name \
--namespace=kube-system \
--name=aws-load-balancer-controller \
--attach-policy-arn=arn:aws:iam::YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID:policy/AWSLoadBalancerControllerIAMPolicy \
--override-existing-serviceaccounts \
--approve
3. Install ALB Ingress Controller
Using Helm:
helm repo add eks https://aws.github.io/eks-charts
helm repo update
helm install aws-load-balancer-controller eks/aws-load-balancer-controller \
--namespace kube-system \
--set clusterName=your-cluster-name \
--set serviceAccount.create=false \
--set serviceAccount.name=aws-load-balancer-controller
4. Configure Sample Ingress Resource
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: sample-ingress
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: ip
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: sample-service
port:
number: 80
Advanced Configuration Options
SSL/TLS Termination
To enable SSL/TLS:
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: arn:aws:acm:region:account-id:certificate/certificate-id
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-policy: ELBSecurityPolicy-TLS-1-2-2017-01
Cross-Zone Load Balancing
Enable cross-zone load balancing:
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-attributes: routing.http2.enabled=true,load_balancing.cross_zone.enabled=true
Custom Health Checks
Configure custom health checks:
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /health
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-interval-seconds: '15'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-timeout-seconds: '5'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/success-codes: '200-299'
Best Practices and Optimization Tips
Resource Management
Configure appropriate instance target groups
Set proper health check parameters
Enable cross-zone load balancing for better availability
Security Considerations
Use security groups effectively
Implement WAF rules when needed
Enable access logs for auditing
Cost Optimization
Use IP targeting mode when possible
Configure proper idle timeout settings
Monitor and adjust capacity as needed
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Enable ALB access logs
Set up CloudWatch metrics
Configure proper alerting
Common Issues and Solutions
Subnet Configuration
Ensure subnets are tagged correctly
Verify subnet routing configuration
Check security group rules
Service Account Issues
Verify IAM role associations
Check OIDC provider configuration
Validate policy attachments
Health Check Failures
Verify health check paths
Check timeout settings
Monitor target group health
Conclusion
AWS Application Load Balancer as an ingress controller provides a robust, scalable solution for managing incoming traffic to your EKS cluster. Following this guide and implementing the best practices, you can create a reliable and efficient ingress setup for your Kubernetes applications.
Remember to regularly monitor your setup and adjust configurations based on your specific use case and requirements. The ALB Ingress Controller continues to evolve with new features and improvements, so stay updated with the latest releases and documentation.
Additional Resources
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Prathamesh Bhongale directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Prathamesh Bhongale
Prathamesh Bhongale
DevOps Engineer | AWS Solutions Architect Associate | Terraform Certified Passionate about automating cloud infrastructure, scaling applications, and optimizing CI/CD pipelines. Experienced in AWS, Azure, Kubernetes, Docker, Jenkins, and microservices architecture. Sharing knowledge and tips on DevOps, cloud technologies, and best practices.