Day-3Essential commands in Linux 🧑💻🐧
 Fauzeya
FauzeyaTable of contents

History of Linux?
Linux Hierarchy
Basic commands
Linux is a free and open-source operating system that belongs to the Unix family. Linus Torvalds developed it in September 1991.
The initial version, Linux 0.01, was posted on the Minix newsgroup on September 17, 1991. Due to its popularity, Torvalds continued developing the code, which led to the official release of Linux version 0.02 on October 5, 1991.
Today, Linux is one of the most widely used operating systems, with 90% of the fastest supercomputers (including the top 10) running on various Linux variants.
Linux Hierarchy:
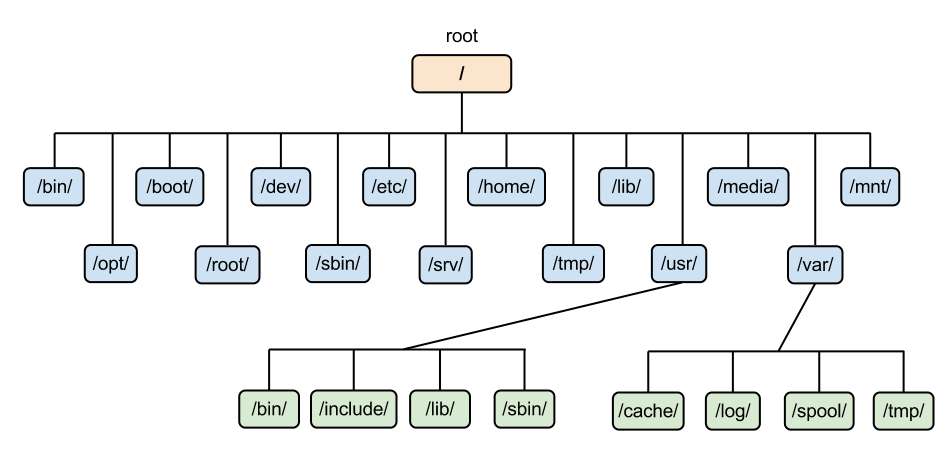
The Linux directory structure is organized into a tree-like hierarchy starting from the root (/). Each directory serves a specific purpose, helping to keep system files and user data organized efficiently.
/ (Root)
- The root directory is the base of the Linux file system. All other directories stem from here.
/bin (Binary)
- Contains essential user binaries (executables) like
ls,cp, andmkdir.
- Contains essential user binaries (executables) like
/sbin (System Binary)
- Holds essential system binaries used for system administration, such as
ifconfig,reboot.
- Holds essential system binaries used for system administration, such as
/etc (Configuration)
- Stores configuration files for the system and services. For example,
/etc/passwdfor user information.
- Stores configuration files for the system and services. For example,
/home (Home Directory)
- Contains personal directories for users, like
/home/username. Each user stores personal files here.
- Contains personal directories for users, like
/var (Variable)
- Holds files that are expected to grow dynamically, such as logs (
/var/log), caches, and temporary files.
- Holds files that are expected to grow dynamically, such as logs (
/tmp (Temporary)
- Stores temporary files created by applications. Files here may be deleted automatically after a reboot.
/usr (User Binaries and Programs)
- Contains user-installed software and utilities. Subdirectories like
/usr/bin,/usr/libhold binaries and libraries for programs.
- Contains user-installed software and utilities. Subdirectories like
/opt (Optional)
- Used to install additional third-party software.
/dev (Device Files)
- Contains special files that represent hardware devices (e.g.,
/dev/sda1for a hard drive).
- Contains special files that represent hardware devices (e.g.,
/mnt and /media (Mount Points)
- Used as mount points for temporary media, like USB drives or CDs.
/lib (Libraries)
- Contains shared libraries required by binaries in
/binand/sbin.
- Contains shared libraries required by binaries in
/proc (Process Information)
- A virtual filesystem that provides system information and running processes, like
/proc/cpuinfo.
- A virtual filesystem that provides system information and running processes, like
/boot (Boot Loader Files)
- Contains boot loader files, like the kernel and
grub.
- Contains boot loader files, like the kernel and
/root (Root User's Home)
- The home directory for the root user is separate from other users’ home directories.
Basic Commands
clear→ it is used for clear screenwhoami→ it shows the current login user namehistory→ it shows a list of previously used commandsdate→ it shows the time and datedf-h→ it shows the disk space usage of a systemfree -h→ it shows the memory usage of a system
ls option_flag arguments --> List the sub-directories and files available in the present directory
ls -l--> List the files and directories in a long list format with extra informationls -a--> List all including hidden files and directoryls *.sh--> List all the files having .sh extension.ls -i--> List the files and directories with index numbers Inodesls -d */--> list only directories.(we can also specify a pattern)
Directory commands
pwd--> print work directory. Gives the present working directory.cd path_to_directory--> Change the directory to the provided pathcd ~or justcd--> change directory to the home directorycd ---> Go to the last working directory.cd ..--> Change the directory to one step back.cd ../..--> Change directory to 2 levels back.mkdir directoryName--> To make a directory in a specific location
Next, I’ll dive deeper into process management and other essential Linux commands to further strengthen my DevOps toolkit!
Stay tuned for more updates!🔍🚀Uncover the Beginnings of Linux
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Fauzeya directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Fauzeya
Fauzeya
Hi there! I'm Fauzeya 👩💻, a passionate DevOps Engineer with a background in Computer Science Engineering🎓. I’m committed to enhancing security🔒, efficiency⚙️, and effectiveness in software development and deployment processes. With extensive knowledge in cloud computing☁️, containerization📦, and automation🤖, I aim to stay updated with the latest tools and methodologies in the DevOps field. Currently, I’m on a journey to deepen my understanding of DevOps I enjoy sharing my learning experiences and insights through my blog, 📝where I cover topics related to DevOps practices, tutorials, and challenges. I believe in continuous growth and learning and am excited to connect with fellow tech enthusiasts and professionals🤝. Let’s embark on this journey together!🚀