🌐 Day-11:Automated Website Deployment with AWS: EC2, Target Groups, and Application Load Balancer 🌐
 Santhosh Haridass
Santhosh Haridass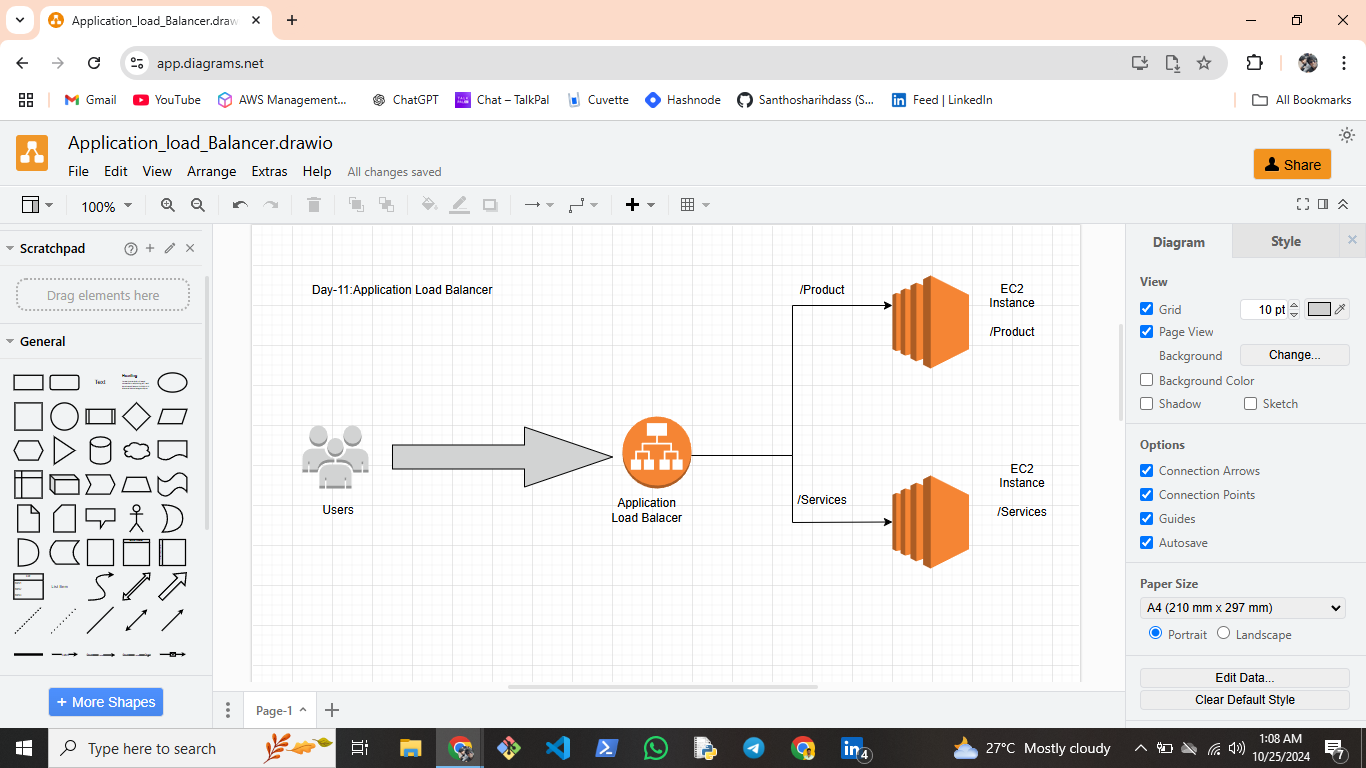
Step - by- Steps:
Project Overview
I recently completed a hands-on project where I automated the deployment of a web application using AWS services and Bash scripting. This project taught me how to leverage AWS infrastructure for high availability, scalability, and streamlined automation.
🚀 EC2 Instance Launch
To begin, I created a Bash script that launches two EC2 instances configured to host a web server. Automating this process reduced manual provisioning, making the setup faster and less error-prone.
🎯 Target Group Configuration
Once the EC2 instances were live, I set up two Target Groups to distribute incoming traffic across both instances. This redundancy improves the availability of the application and ensures an even distribution of traffic.
🔄 Application Load Balancer (ALB) Setup
Next, I configured an Application Load Balancer (ALB) and connected it to the Target Groups. Using DNS, I routed traffic through the ALB and set up path-based routing to direct users to different sections of the application based on URL paths.
✅ Testing & Validation
After configuring the infrastructure, I ran tests to confirm that traffic routed correctly according to URL paths and that it was evenly balanced across both instances, providing a seamless experience.
💡 Why Choose an Application Load Balancer?
Efficient Traffic Management: The ALB ensures no single instance gets overwhelmed, delivering a better user experience and reducing downtime risks.
Path-Based Routing: Using path-based routing, I directed traffic to specific parts of the website based on URL paths, making it perfect for handling multiple services or microservices.
Enhanced Security: Operating at Layer 7, the ALB inspects HTTP/S headers, adding a layer of security against common web attacks.
⚙ Key ALB Use Cases
Microservices Architectures: ALB is well-suited for distributing requests among microservices.
Multi-Region Deployments: ALB enables efficient routing across regions for high availability.
Path-Based Routing for Web Applications: Ideal for applications that need to direct users to specific endpoints (e.g.,
/apifor backend API services).
🏆 Advantages of Application Load Balancer
Automatic Scaling: ALB scales with traffic, saving costs by scaling down when traffic is low.
Health Checks: ALB performs health checks and routes traffic away from unhealthy instances, enhancing reliability.
SSL Termination: ALB manages SSL certificates, reducing load on backend servers.
This project has deepened my understanding of AWS automation, load balancing, and cloud architecture, allowing me to manage web applications with high availability, scalability, and security.
💬 Have you tried deploying a web application with AWS ALB? Share your experiences or challenges in the comments below!
Tags:
#AWS #DevOps #CloudComputing #LoadBalancer #EC2 #Automation #InfrastructureAsCode #WebDevelopment #PathRouting #CloudEngineer #Microservices #Hashnode
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Santhosh Haridass directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Santhosh Haridass
Santhosh Haridass
🚀 𝐀𝐛𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐌𝐞 "Hi, I'm Santhosh Haridass, a DevOps student passionate about cloud computing and automation. I'm currently learning AWS, Linux, Docker, and CI/CD pipelines, with a focus on automating workflows and building scalable solutions. My goal is to become a skilled DevOps/Cloud engineer, and I'm excited to share my learning journey and projects with the community."