Day 6 File Permissions and Access Control Lists
 Fauzeya
Fauzeya
Understanding File Permissions
Writing an article about file permission
Access control list
Additional task
Understanding sticky bit, SUID, SGID
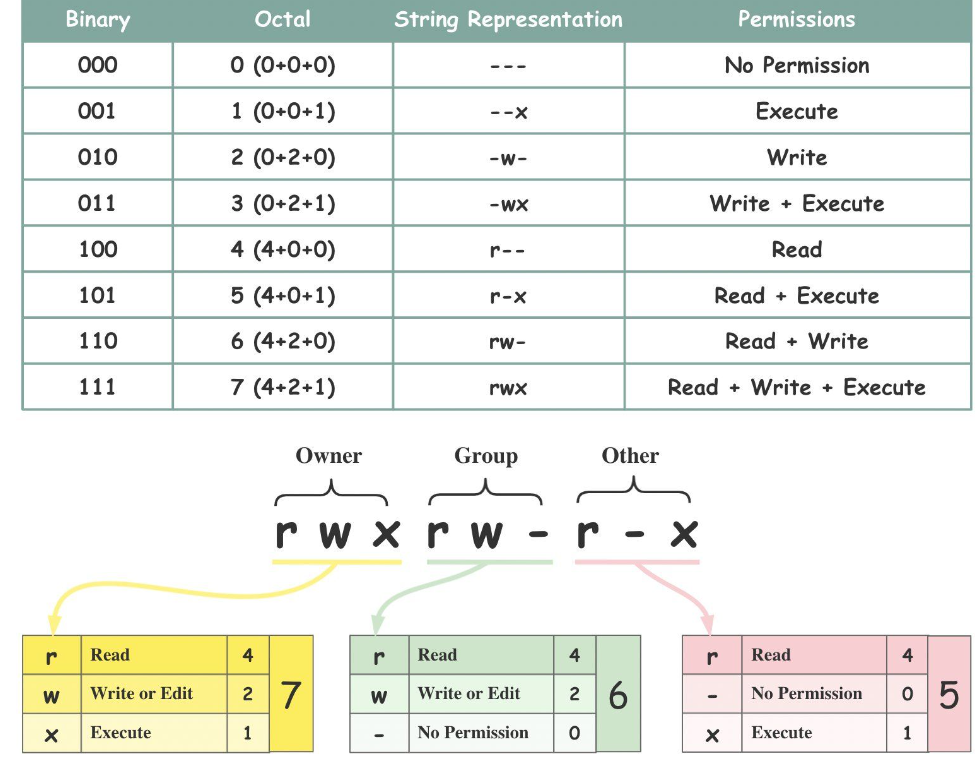
1. Understanding File Permissions
Create a Simple File and Check Permissions
# Create a simple file
touch myfile.txt
# List files with detailed permissions
ls -ltr
Change Ownership and Group
Change ownership with
chown:chown username:groupname myfile.txtChange group with
chgrp:chgrp groupname myfile.txt
Change User Permissions
Change permissions with
chmod:chmod 755 myfile.txt # Example: full access to owner, read/execute for group and othersNote the changes after running
ls -ltragain:ls -ltr myfile.txt
2. Writing an Article about File Permissions
Sample Article Title: Understanding File Permissions in Linux
Content: In Linux, file permissions determine who can access or modify files and directories. Each file has three categories of users:
Owner: The individual who created the file, possesses the highest level of permissions.
Group: Users who belong to a specific group assigned to the file, with shared permissions.
Others: All other users on the system who do not fall into the previous two categories.
Each of these categories can have three types of permissions:
Read (r): Allows viewing the contents of a file.
Write (w): Allows modifying or deleting the file.
Execute (x): Allows running the file as a program.
Permissions can be modified using the following commands:
chown: Change ownership of a file.chgrp: Change the group ownership of a file.chmod: Change the permissions assigned to the owner, group, and others.
Understanding and managing file permissions is essential for maintaining system security and proper access control.
3. Access Control Lists (ACL)
Reading about ACL
Get ACL permissions:
getfacl myfile.txtSet ACL permissions:
setfacl -m u:username:rwx myfile.txt # Granting rwx permissions to a specific user
Create a Directory and Set ACL
# Create a directory
mkdir mydirectory
# Set specific ACL permissions
setfacl -m u:username:rwx mydirectory # Set rwx permissions for a specific user
setfacl -m g:groupname:rx mydirectory # Set rx permissions for a group
# Verify permissions
getfacl mydirectory
4. Additional Tasks
Script to Change Permissions of Multiple Files
#!/bin/bash
# Script to change permissions of multiple files in a directory
if [ "$#" -ne 2 ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 <directory_path> <permissions>"
exit 1
fi
DIRECTORY=$1
PERMISSIONS=$2
# Change permissions for all files in the specified directory
chmod -R "$PERMISSIONS" "$DIRECTORY"
echo "Permissions changed to $PERMISSIONS for all files in $DIRECTORY."
Usage:
chmod +x change_permissions.sh
./change_permissions.sh /path/to/directory 755
Script to Set ACL Permissions
#!/bin/bash
# Script to set ACL permissions for a user on a given file
if [ "$#" -ne 3 ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 <file_path> <username> <permissions>"
exit 1
fi
FILE=$1
USER=$2
PERMISSIONS=$3
# Set ACL permissions for the specified user
setfacl -m u:"$USER":"$PERMISSIONS" "$FILE"
echo "ACL permissions set for user $USER on $FILE."
Usage:
chmod +x set_acl.sh
./set_acl.sh myfile.txt username rwx
5. Understanding Sticky Bit, SUID, and SGID
Sticky Bit Example
The sticky bit is typically set on directories to allow only the file's owner to delete or rename the file.
# Set sticky bit on a directory
mkdir sticky_dir
chmod +t sticky_dir
SUID Example
The SUID (Set User ID) allows a user to execute a file with the permissions of the file owner.
# Create a script with SUID
touch myscript.sh
chmod 4755 myscript.sh # Set SUID
SGID Example
The SGID (Set Group ID) allows a user to execute a file with the permissions of the group owner.
# Create a directory and set SGID
mkdir sgid_dir
chmod g+s sgid_dir # Set SGID
6. Backup and Restore Permissions
Backup Current Permissions
#!/bin/bash
# Script to backup permissions of files in a directory
if [ "$#" -ne 2 ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 <directory_path> <backup_file>"
exit 1
fi
DIRECTORY=$1
BACKUP_FILE=$2
# Backup permissions to a file
ls -l "$DIRECTORY" > "$BACKUP_FILE"
echo "Permissions backed up to $BACKUP_FILE."
Restore Permissions
#!/bin/bash
# Script to restore permissions from a backup file
if [ "$#" -ne 2 ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 <directory_path> <backup_file>"
exit 1
fi
DIRECTORY=$1
BACKUP_FILE=$2
# Restore permissions from the backup file
while read -r line; do
# Extract filename and permissions
PERMISSIONS=$(echo "$line" | awk '{print $1}')
FILENAME=$(echo "$line" | awk '{print $9}')
chmod "$PERMISSIONS" "$DIRECTORY/$FILENAME"
done < "$BACKUP_FILE"
echo "Permissions restored from $BACKUP_FILE."
Summary
This comprehensive guide includes practical tasks and scripts to help you understand and manage Linux file permissions and ownership, ACLs, and advanced concepts like sticky bit, SUID, and SGID. Each script is designed to automate common tasks in a DevOps environment, enhancing efficiency and control over file systems.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Fauzeya directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Fauzeya
Fauzeya
Hi there! I'm Fauzeya 👩💻, a passionate DevOps Engineer with a background in Computer Science Engineering🎓. I’m committed to enhancing security🔒, efficiency⚙️, and effectiveness in software development and deployment processes. With extensive knowledge in cloud computing☁️, containerization📦, and automation🤖, I aim to stay updated with the latest tools and methodologies in the DevOps field. Currently, I’m on a journey to deepen my understanding of DevOps I enjoy sharing my learning experiences and insights through my blog, 📝where I cover topics related to DevOps practices, tutorials, and challenges. I believe in continuous growth and learning and am excited to connect with fellow tech enthusiasts and professionals🤝. Let’s embark on this journey together!🚀