🌟 My Deployment Journey with Country Bank! 🌟
 RAKESH DUTTA
RAKESH DUTTA
Introduction
I’m excited to share my recent experience deploying the Country Bank application using a streamlined Jenkins Pipeline. This journey has enhanced my understanding of CI/CD practices and demonstrated the power of automation in ensuring security and efficiency in software deployment. Join me as I delve into the details of this process and share insights that might help you in your own deployment adventures! 🚀
Overview of the Deployment Process
The deployment process was meticulously designed to incorporate various essential steps, ensuring that the application is built securely and is production-ready. Here’s a breakdown of the key highlights:
🛠️ Jenkinsfile Highlights
A well-structured Jenkinsfile was the backbone of this deployment process. Below are the key components that made our pipeline efficient and secure:
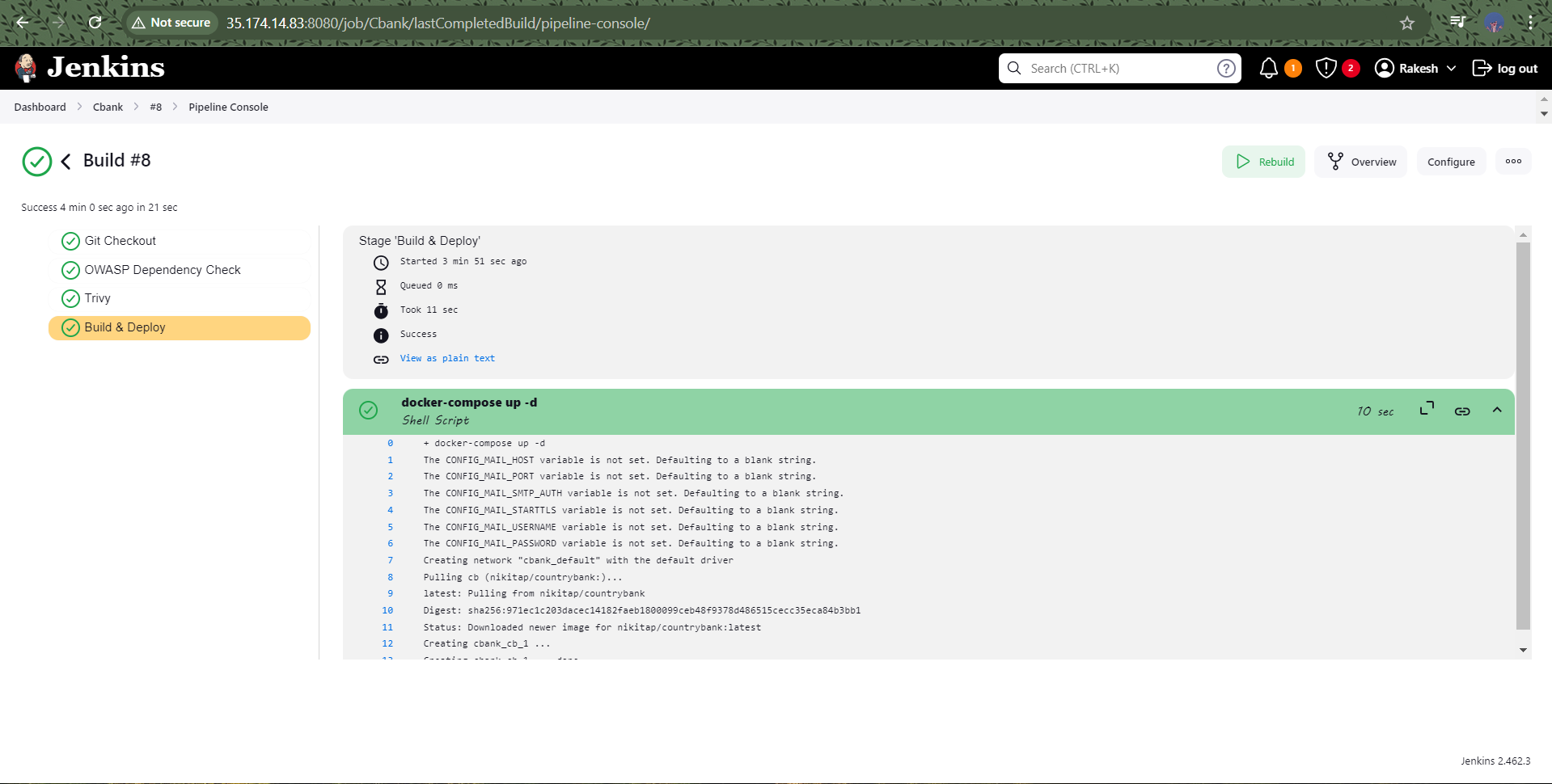
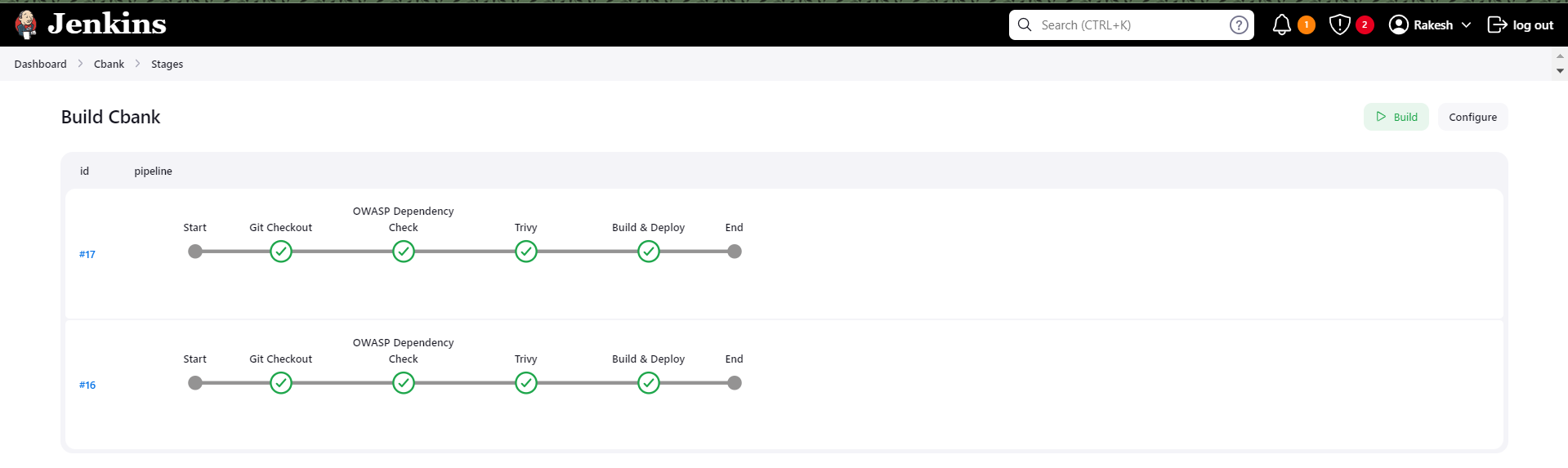
1. Git Checkout
The first step in our pipeline involves pulling the latest code from the Country Bank repository. This ensures that the deployment reflects the most recent changes made by the development team, keeping the application up-to-date and in sync with ongoing work.
groovyCopy codestage('Checkout') {
steps {
git url: 'https://github.com/your-repo/country-bank.git', branch: 'main'
}
}
2. OWASP Dependency Check
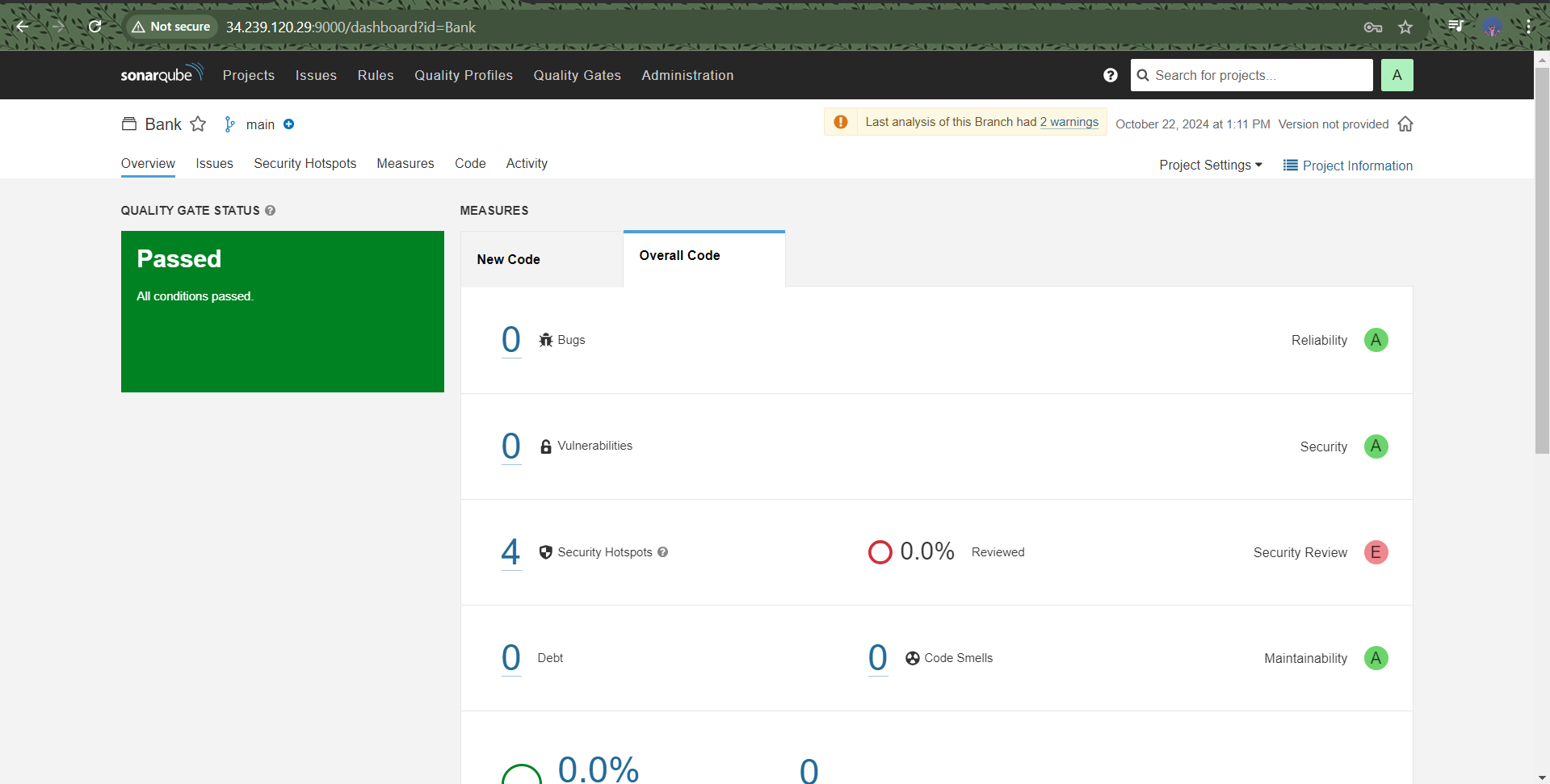
Security is a top priority in modern software development. Integrating OWASP Dependency Check helps identify vulnerabilities in the project’s dependencies. This step is crucial for maintaining the integrity of our application and protecting user data.
groovyCopy codestage('Dependency Check') {
steps {
sh 'dependency-check.sh --project "Country Bank" --scan ./ --failOnCVSS 7'
}
}
This step scans for known vulnerabilities and generates a report that can guide developers in addressing any identified issues.
3. Trivy Scan
To further enhance security, I incorporated Trivy, a popular vulnerability scanner for container images. This ensures that the Docker images used in deployment are free from known vulnerabilities.
groovyCopy codestage('Trivy Scan') {
steps {
sh 'trivy image --exit-code 1 nikitap/countrybank'
}
}
If any vulnerabilities are found, the build will fail, preventing potentially insecure images from being deployed.
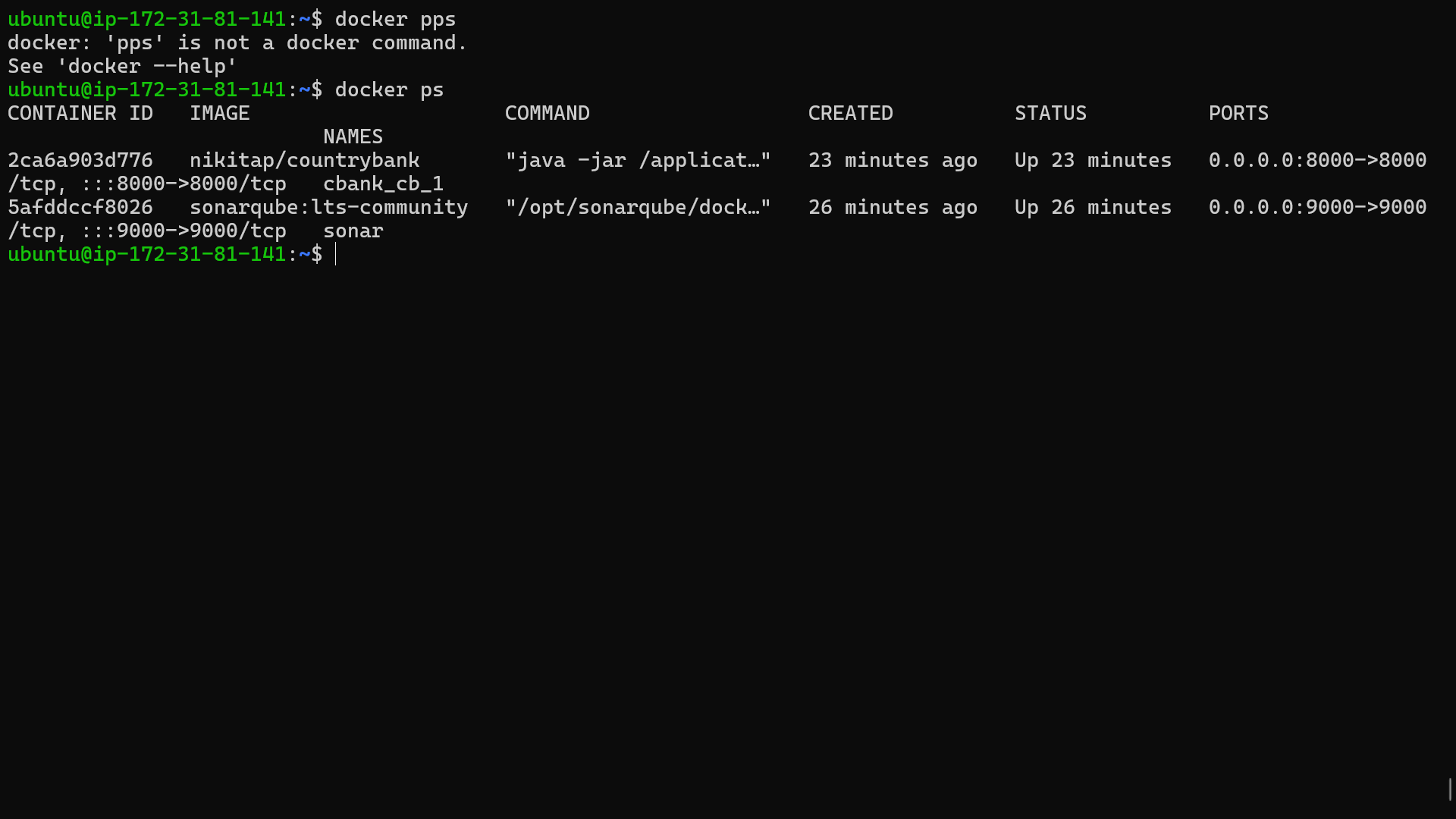
4. Docker Build & Deploy
The final stages of the pipeline involve building the Docker image and deploying it seamlessly. Once built, the image is tagged and pushed to Docker Hub, making it ready for production.
groovyCopy codestage('Build & Deploy') {
steps {
sh 'docker build -t nikitap/countrybank .'
sh 'docker push nikitap/countrybank'
}
}
By using Docker, we ensure that the application runs consistently across various environments, mitigating the "it works on my machine" syndrome that often plagues developers.
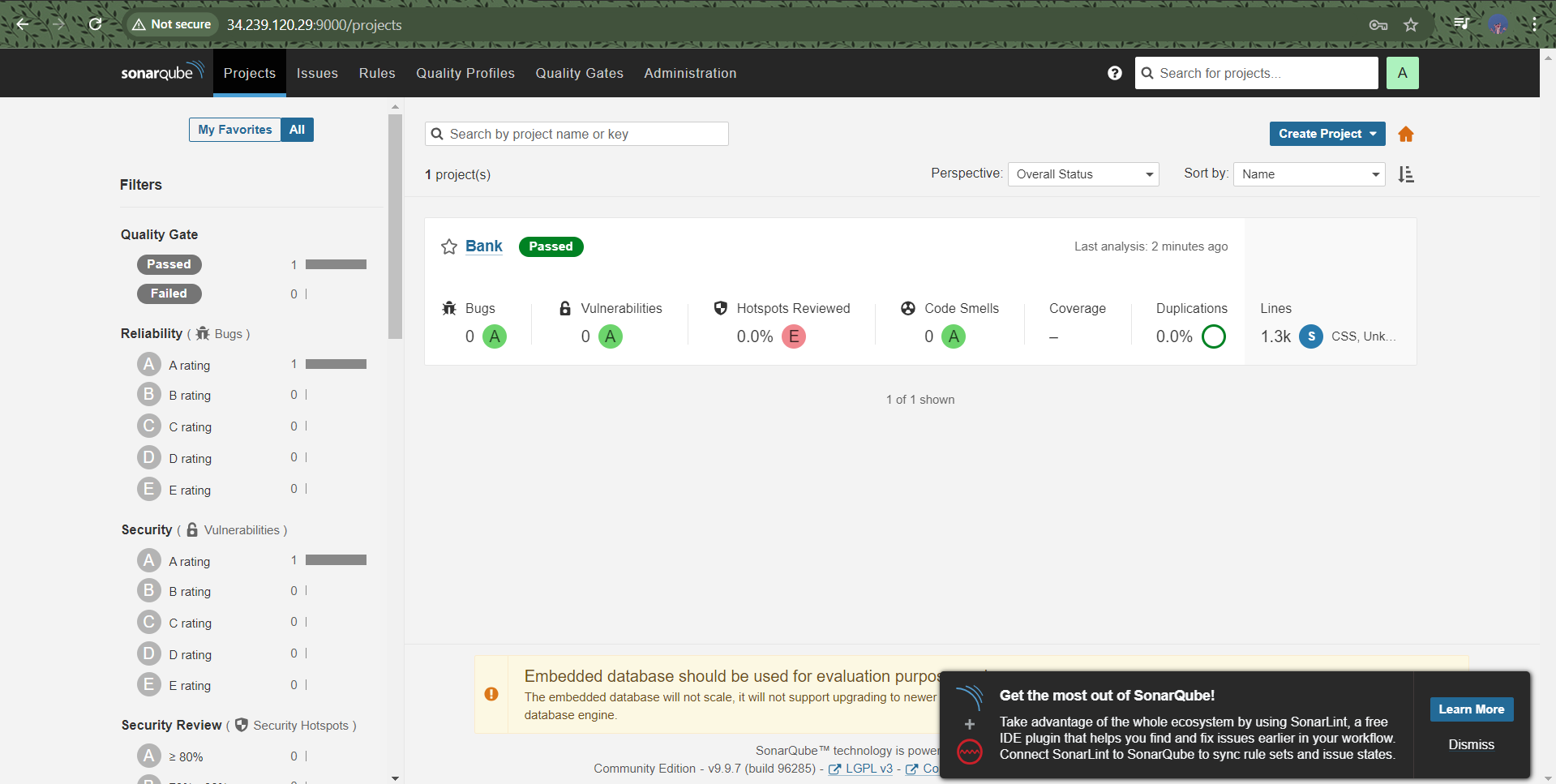
📦 Docker Image
After the build process, the final Docker image is tagged as nikitap/countrybank. This image is optimized, secure, and ready to be deployed in a production environment. Using Docker containers provides several advantages:
Consistency: Docker ensures that the application behaves the same way in development, testing, and production environments.
Isolation: Each container runs in its own environment, minimizing conflicts with other applications or dependencies.
Scalability: Docker makes it easy to scale applications by running multiple containers across different servers.
🔄 Continuous Integration
This Jenkins pipeline setup not only automates the build process but also significantly enhances code quality and security. By incorporating tools like OWASP Dependency Check and Trivy, I ensured that any vulnerabilities are identified and addressed before deployment. This proactive approach to security helps maintain a robust application that users can trust.
Best Practices Learned
Throughout this deployment journey, I encountered several best practices that can benefit anyone looking to implement a similar CI/CD pipeline:
Automate Security Scans: Incorporating security tools early in the development process helps identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before they reach production.
Maintain Clear Documentation: Keeping documentation up to date ensures that all team members understand the deployment process and the tools being used.
Implement Monitoring and Alerts: After deployment, implementing monitoring tools to track application performance and security helps catch issues before they affect users.
Regularly Update Dependencies: Continuously reviewing and updating project dependencies helps prevent security vulnerabilities that may arise from outdated libraries.
Encourage Collaboration: CI/CD practices should promote collaboration between developers, testers, and operations teams. Regular communication ensures that everyone is aligned and working towards the same goals.

Conclusion
Deploying the Country Bank application has been a rewarding experience that highlighted the importance of CI/CD practices in modern software development. The use of a Jenkins pipeline to automate the build and deployment process has improved both efficiency and security. By integrating security scans and employing Docker for containerization, I’ve ensured that the application is not only functional but also secure and robust.
I hope this journey inspires you to explore the benefits of automation and robust security practices in your own deployments. If you have any questions or would like to share your own experiences with CI/CD, feel free to comment below! Let’s continue to learn and grow together in this exciting field. 🌟
Resources
Jenkins Official Documentation
OWASP Dependency Check
Trivy Vulnerability Scanner
Docker Documentation
Thank yu !!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from RAKESH DUTTA directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
