How to Deploy a Basic App on Tomcat Using Nexus and Master-Slave Architecture
 Uma Mahesh Tammineni
Uma Mahesh TammineniTable of contents
- Prerequisites
- A Step-by-Step Guide
- Step 1: Launching the EC2 Instance for Jenkins
- Step 2: Installing the Jenkins in the EC2 Instance (Master)
- Step 3: Configure a Slave Server
- Step 4: Configure a Slave Server in Jenkins Portal
- Step 5: Adding & Configuring the Job in Jenkins Portal
- Step 6: Configuring the Job in Jenkins Portal (BUILD Phase)
- Step 7: Configuring the NEXUS in Jenkins Portal (NEXUS Phase)
- TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS:
In this guide, ill walk through the steps to deploy a simple application on tomcat server using nexus through Master & Slave Concept
Prerequisites
An AWS Account to create an EC2 Instances for Jenkins, TOMCAT & Nexus
- For Creation of AWS Account - Link
A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Launching the EC2 Instance for Jenkins
Create EC2 Instance (Jenkins/ Master Server)
- Follow the instructions for creating an EC2 instance as outlined in the AWS EC2 Instance creation. When launching, ensure to create a new security group for Jenkins.
Configure Security Group
Edit Network Security: Name your security group (e.g.,
JENKINS-SG).Add Security group rule
Type - Custom TCP
Port range - 8080
Source Type: Anywhere (to allow remote access to Jenkins through port 8080)
Step 2: Installing the Jenkins in the EC2 Instance (Master)
Log in as Default User
- Refer to this detailed tutorial for steps on connecting to your EC2 instance. Remember, the default login user is
ec2-user.
- Refer to this detailed tutorial for steps on connecting to your EC2 instance. Remember, the default login user is
Switch to Root User
- Run the command
sudo -ito switch to the root user.
- Run the command
Once we are in root user, create a file using the command
touch file_name.sh.Once it is created run the commandvim file_name.#STEP-1: INSTALLING GIT JAVA-1.8.0 MAVEN yum install git java-1.8.0-openjdk maven -y #STEP-2: GETTING THE REPO (jenkins.io --> download -- > redhat) sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo sudo rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key #STEP-3: DOWNLOAD JAVA11 AND JENKINS amazon-linux-extras install java-openjdk11 -y yum install jenkins -y update-alternatives --config java #STEP-4: RESTARTING JENKINS (when we download service it will on stopped state) systemctl start jenkins.service systemctl status jenkins.serviceRun the above script by using the command
sh file_name.sh. Once the jenkins is started you can access it by navigating to:http://<public-ip-address>:8080- Here,
8080is the default port for Jenkins, and<public-ip-address>is the public IP of your Jenkins EC2 instance (eg.,54.82.52.147:8080)
- Here,
When the site loads, it will prompt for a password and display the path where the password can be found. To retrieve and access the password, use the following command
cat var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPasswordAfterward, the setup will guide you to install plugins— select the suggested plugins option for a streamlined installation. You’ll then be prompted to create an admin user by providing a username, full name, email address, and password.
Now the Jenkins is running
Step 3: Configure a Slave Server
The Slave Server is utilized to retrieve the code, compile and test it, and deploy the developers' code to the Tomcat server.
As outlined in Step 1, set up an EC2 instance, keeping in mind that Tomcat and Jenkins operate on the same port number.
Switch to Root User and Install TOMCAT SERVER
Run the command
sudo -ito switch to the root userOnce we are in root user, create a file using the command
touch file_name.sh.Once it is created run the commandvim file_nameamazon-linux-extras install java-openjdk11 -y wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.96/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.96.tar.gz tar -zxvf apache-tomcat-9.0.96.tar.gz sed -i '56 a\<role rolename="manager-gui"/>' apache-tomcat-9.0.96/conf/tomcat-users.xml sed -i '57 a\<role rolename="manager-script"/>' apache-tomcat-9.0.96/conf/tomcat-users.xml sed -i '58 a\<user username="tomcat" password="admin@123" roles="manager-gui, manager-script"/>' apache-tomcat-9.0.96/conf/tomcat-users.xml sed -i '59 a\</tomcat-users>' apache-tomcat-9.0.96/conf/tomcat-users.xml sed -i '56d' apache-tomcat-9.0.96/conf/tomcat-users.xml sed -i '21d' apache-tomcat-9.0.96/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml sed -i '22d' apache-tomcat-9.0.96/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml sh apache-tomcat-9.0.96/bin/startup.sh
Run the above script by using the command
sh file_name.sh. Once the TOMCAT is started you can access it by navigating to:http://<public-ip-address>:8080- Here,
8080is the default port for TOMCAT, and<public-ip-address>is the public IP of your Slave Server EC2 instance (eg.,54.82.24.183:8080)
- Here,
Once the TOMCAT Server is running, Navigate to above link and click Manage App to manage any of the deployed application.
We need to install the git and maven in the same Slave Server
To get the code git and maven is required to compile,test & package the code maven has a dependency on java-1.8.0.
Run the command to install git, java & mavenyum install git java-1.8.0-openjdk maven -y
Step 4: Configure a Slave Server in Jenkins Portal
Access the Jenkins Dashboard: Start by navigating to the Jenkins portal. Click on Dashboard, then go to Manage Jenkins and select Nodes.
Add a New Node: In the Nodes section, look for the Add New Node option in the top right corner. Click on it to initiate the process of adding your new node.
Verify Java Version on the Slave Server: It’s essential to ensure that Java 11 is installed and running on the slave server to configure the node in Jenkins. To check the current Java version, execute the following command in the server’s terminal.
java -versionUpdate Java if Necessary: If the output indicates that a different version of Java is installed, you will need to update it. Since we have already set up Java 11 as part of the Tomcat installation in Step 3, you can run the appropriate command to update the Java version.
update-alternatives --config javaOnce you click Add Node in Jenkins portal you need to add the details.
Name - We need to provide the name for the Node (eg: DEV)
Description - Provide the Description for the Node
Number of executors - we can provide any number between 2- 5. Some times if we keep a big number the EC2 instance cannot handle the load. As our EC2 Instance is low configured.
Remote root directory - We need to specify the Jenkins path in DEV Server as the Jenkins is not installed in DEV server (eg: /home/ec2-user/jenkins)
Label - We can provide any name. Make sure remember it.
Usage - Select Only build jobs with label expressions matching this node from the drop-down.
Launch Method - Select Launch agents via SSH
Host - It's essential to use the private IP address of the Slave EC2 instance for configuration.
Although the public IP address can also be provided, it comes with a risk: stopping the Slave EC2 instance may result in a change of the public IP.
This would require us to reconfigure the node each time. To prevent this inconvenience, we recommend sticking with the private IP address.Credentials - Credentials are required to be added to deploy the application smoothly.
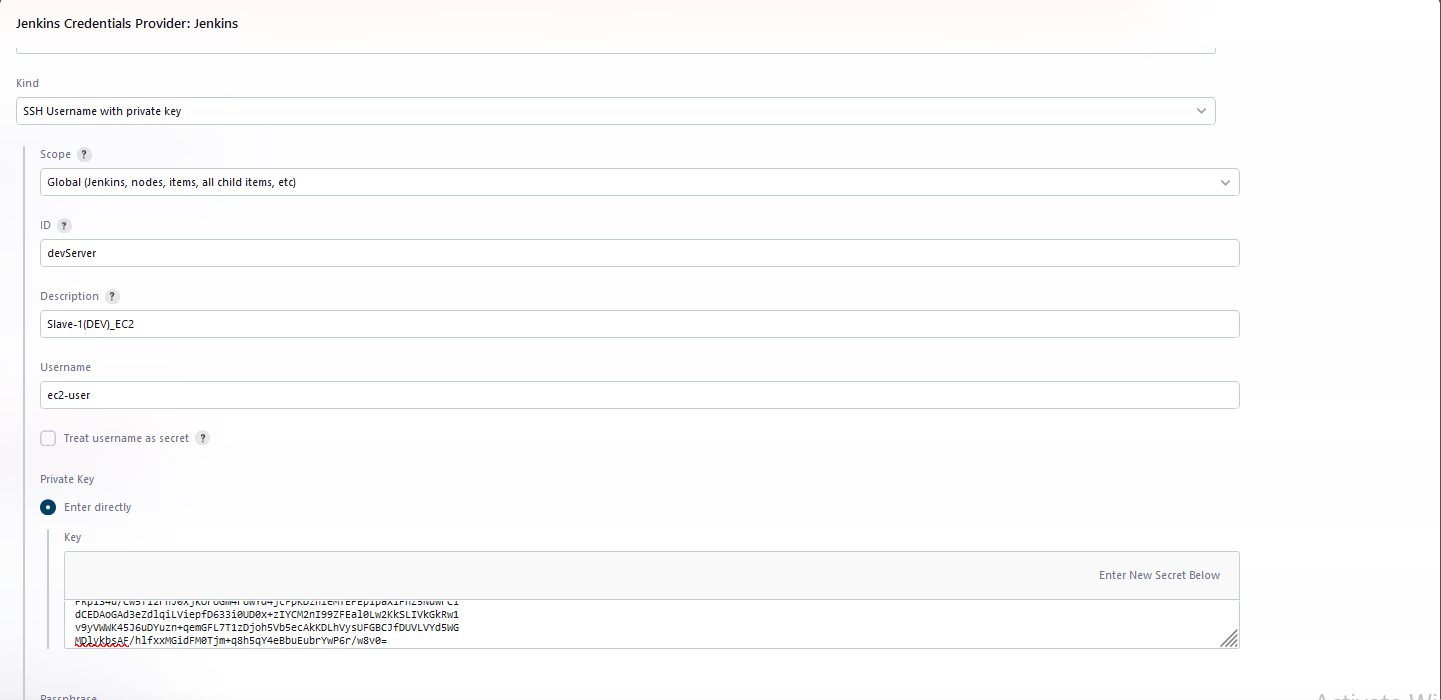
Kind - Select SSH Username with Private Key
ID - Add a appropriate ID
Description - Add a appropriate Description
Username - It should be the default username of the Slave EC2 Instance, In my case it’s
ec2-user.Private Key - Open the
.pemfile used to while creating Slave EC2 Instance and paste the contents of it in Key fieldClick on Add & Select the credentials created.
Host key Verification Strategy - Select Non Verifying Strategy.
Availability - Keep this agent online as much as possible.
Step 5: Adding & Configuring the Job in Jenkins Portal
In the Jenkins Dashboard > Click on New Item on the top left.
Enter the Job Name
Item Type - Pipeline
In General Section, Add the Description
In Pipeline Section, Select Hello World from the left to get the basic Pipeline Syntax
We need to change few of the things in the syntax to below syntax to integrate the Master-Slave conceptpipeline { agent { label 'DEV' } stages { stage('Code') { steps { } } } }DEV is the Label name mentioned during the Node Setup in Jenkins Portal in
Step 4.To retrieve code from Bitbucket or GitHub, you need to install the necessary plugins in the Jenkins portal via the Manage Jenkins tab.
Bitbucket Code - Plugin Name: Bitbucket
GitHub Code—this will already be downloaded as specified in Point 6 of Step 2.
After installing the plugins, navigate to the Configure tab of your job. Under the Pipeline section, click on Pipeline Syntax and select Git.
Add your Repository URL from GitHub or Bitbucket
Select the Branch you want code from.
If it's a private repository, you'll need to add the credentials. This step can be skipped for a public repository.
For Private repository - Under the Credentials, Click Add>Jenkins
Kind - Username and password
Username - it should be your Bitbucket or GitHub Username
Password - To generate a app password go to your Bitbucket settings
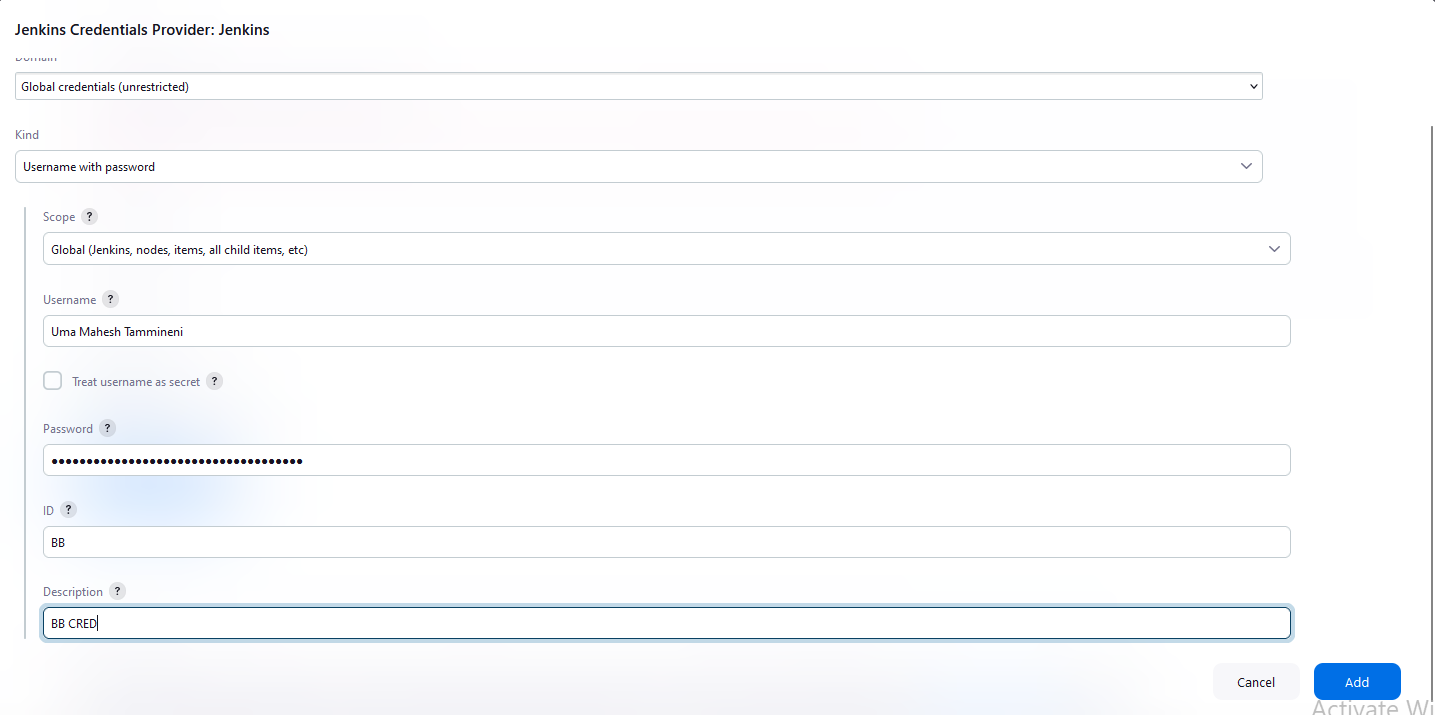
Click Add and select the credentials you created, ensuring the check-boxes are selected.
Click Generate Pipeline Script and copy the output generated.
Paste the generated output within the steps of the Code stage.
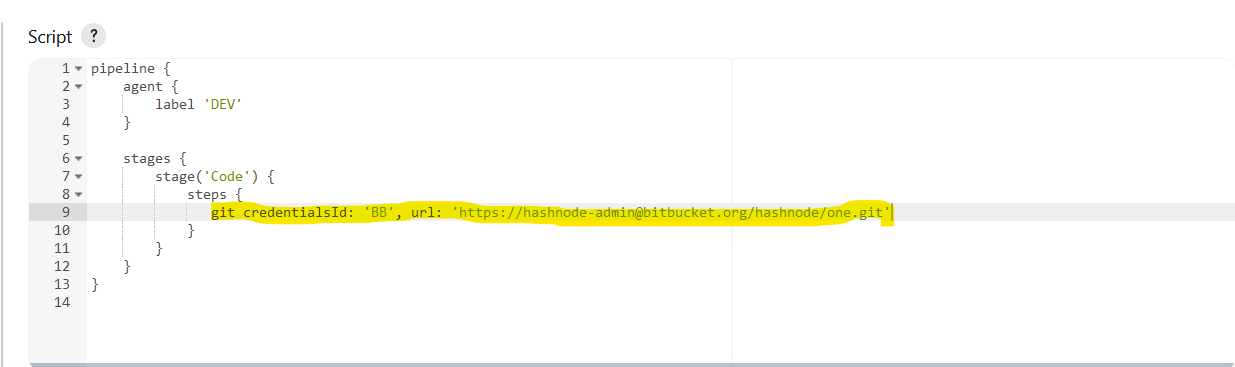
The script above pulls code from the Bitbucket repository into the Jenkins pipeline job. This configuration may vary depending on the repository.
Step 6: Configuring the Job in Jenkins Portal (BUILD Phase)
- Next, we need to add another stage to the pipeline to compile, test, and package the code..
We'll use the Maven tool to build the code, with the mvn clean package command for compiling, testing, and packaging. This command will be configured within the pipeline.
Step 7: Configuring the Job in Jenkins Portal (DEPLOY Phase)
Now the Code will be build in DEV Server, To Deploy the Code to TOMCAT server
we need to configure the TOMCAT SERVER in pipeline as we have already installed the TOMCAT in the Slave server in Step 3.
Now create a new stage with name 'Deploy'. we need Deploy to Container plugin to deploy in server.
Once the plugin is installed, click on the Pipeline Syntax
Select deploy: Deploy war/ear to a container
WAR/EAR files - it should be
target/*.war. As the package will be coming to DEV Server of Remote root directory with the name target which we configured on 5th point of Step 4.i have mentioned /*.war - Which represents starting name can be any but the ending of the name must be .war
Context path - It represents the name of the application in TOMCAT Server.
Containers - Select Tomcat 9.x Remote
Add the credentials to the jenkins
Kind - Username and password
Username -
tomcatPassword -
admin@123
If anyone want to change the username and password, One can edit the Line
sed -i '58 a\<user username="tomcat" password="admin@123" roles="manager-gui, manager-script"/>' apache-tomcat-9.0.96/conf/tomcat-users.xmlmentioned in the 2nd point of Step 3.Add the appropriate ID and Description to the credential
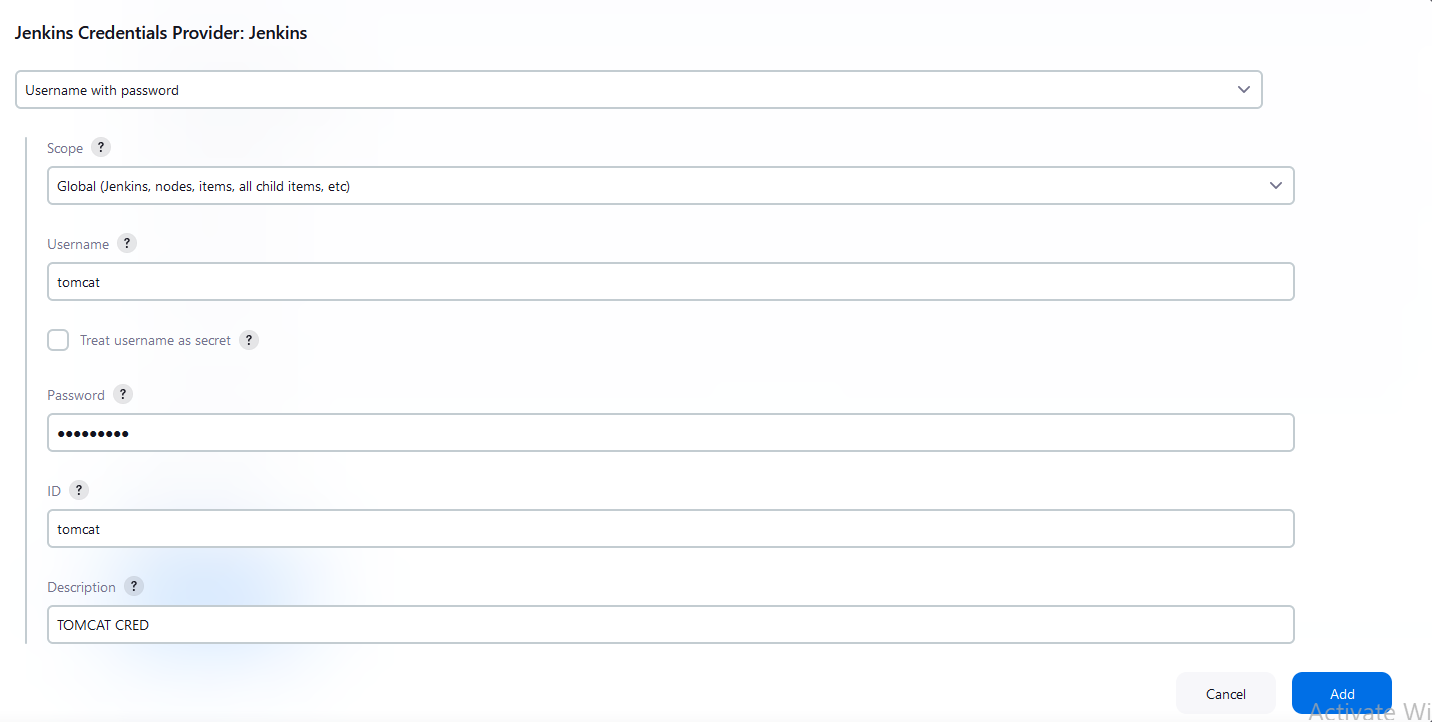
Select the TOMCAT Credentials
The TOMCAT URL - It should be the http:://<ipaddress>:8080 (eg: http://44.211.216.198.8080)
The <ipaddress> - the Public IPADDRSS of the instance where the TOMCAT is installed, In our case it’s Slave server.
8080 : its the default port for TOMCAT
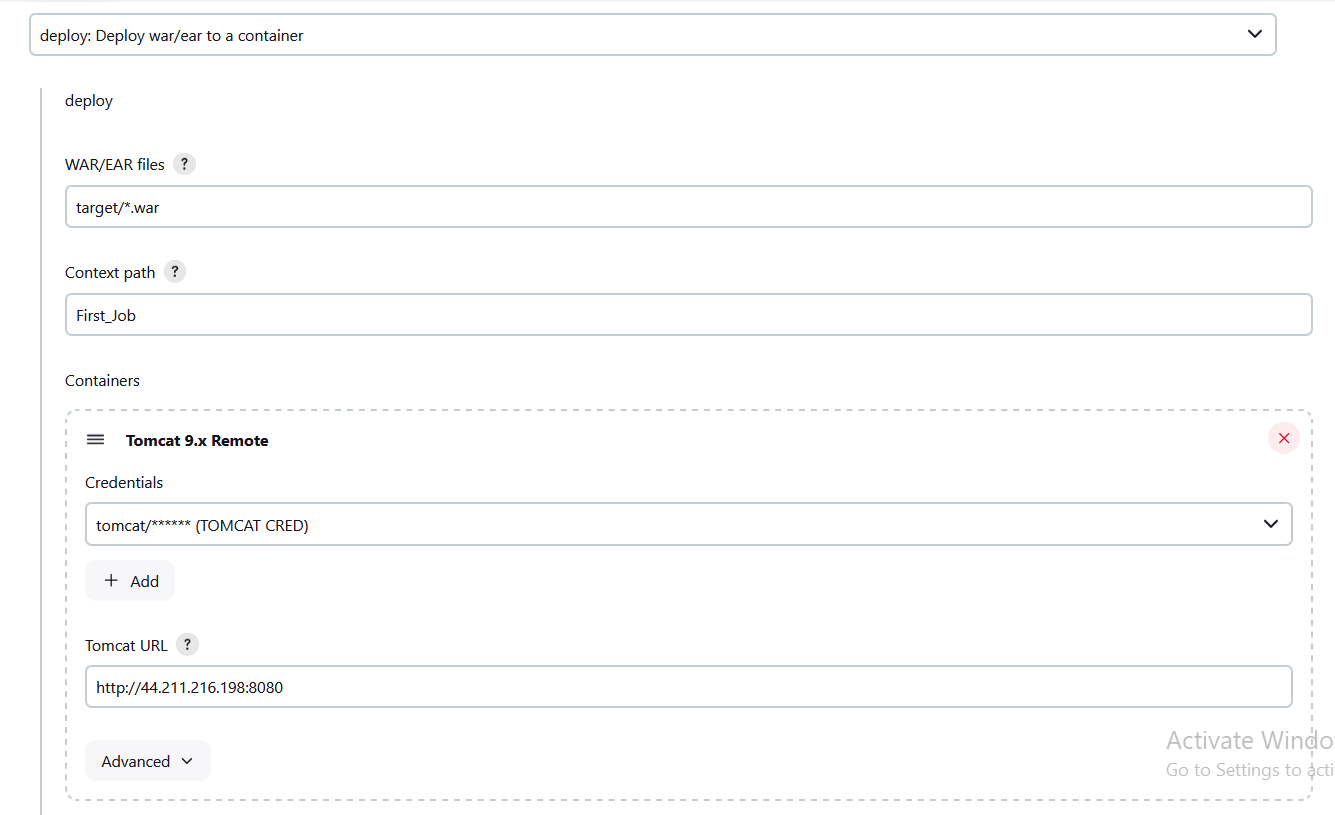
Click on Generate Pipeline Scripts and copy the output and paste it in steps section of Deploy Stage.
pipeline { agent { label 'DEV' } stages { stage('Code') { steps { git credentialsId: 'BB', url: 'https://hashnode-admin@bitbucket.org/hashnode/one.git' } } stage('Build') { steps { sh 'mvn clean package' } } stage('Deploy') { steps { deploy adapters: [tomcat9(credentialsId: 'tomcat', path: '', url: 'http://44.211.216.198:8080')], contextPath: 'First_Job', war: 'target/*.war' } } } }
Step 7: Configuring the NEXUS in Jenkins Portal (NEXUS Phase)
As the Artifacts will be stored in NEXUS after the package is done i will be adding that step inside the build stage itself.
Create EC2 Instance (NEXUS Server)
Follow the instructions for creating an EC2 instance as outlined in the AWS EC2 Instance creation. When launching, ensure to create a new security group for NEXUS.
Configure Security Group
Edit Network Security: Name your security group (e.g.,
NEXUS-SG).Add Security group rule
Type - Custom TCP
Port range - 8081
Source Type: Anywhere (to allow remote access to NEXUS through port 8081)
Add Storage of 20GB EBS Volume.
Switch to Root User
Run the command
sudo -ito switch to the root userOnce we are in root user, create a file using the command
touch file_name.sh.Once it is created run the commandvim file_name#create amazonlinux ec2 with t2.micro and 30 gb of ebs with port 8081 sudo yum update -y sudo yum install wget -y sudo yum install java-17-amazon-corretto-jmods -y sudo mkdir /app && cd /app sudo wget -O nexus.tar.gz https://download.sonatype.com/nexus/3/latest-unix.tar.gz sudo tar -xvf nexus.tar.gz sudo mv nexus-3* nexus sudo adduser nexus sudo chown -R nexus:nexus /app/nexus sudo chown -R nexus:nexus /app/sonatype-work sudo echo "run_as_user="nexus"" > /app/nexus/bin/nexus.rc sudo tee /etc/systemd/system/nexus.service > /dev/null << EOL [Unit] Description=nexus service After=network.target [Service] Type=forking LimitNOFILE=65536 User=nexus Group=nexus ExecStart=/app/nexus/bin/nexus start ExecStop=/app/nexus/bin/nexus stop User=nexus Restart=on-abort [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOL sudo chkconfig nexus on sudo systemctl start nexus sudo systemctl status nexus
Run the above script by using the command
sh file_name.sh. Once the nexus is started you can access it by navigating to:http://<public-ip-address>:8081- Here,
8081is the default port for Jenkins, and<public-ip-address>is the public IP of your Jenkins EC2 instance (eg.,http://3.90.184.91:8081/)
- Here,
When the site loads, we need to sign-in to nexus portal, it will display the username and path where the password can be found. To retrieve and access the password, use the following command
cat /app/sonatype-work/nexus3/admin.passwordcat - cat command is used to see the content of the file.
Once logged in it will ask to change the password.
disable or enable access.
Now navigate to Security administrators and configuration tab.
Create a Repository, select the recipe as maven2hosted as we are using maven for build the package.

Make sure to select Allow redeploy in Deployment Policy and create.
Lets Configure the Pipeline of the Job in Jenkins portal
Navigate to configure in Jenkins portal, Click on Pipeline Syntax
Select nexusArtifactUploader
Nexus Version - NEXUS3
Protocol - HTTP
NEXUS URL :
<public-ip-address>:8080Here,
8081is the default port for NEXUS<public-ip-address>is the public IP of your NEXUS EC2 instance
(eg:3.90.184.91:8081)
Added the Credentials
Kind - Username and Password
Give any appropriate ID and Description
Provide the username and password for the NEXUS
After adding the Credentials and select it.
GroupId & Version - it will be present in the
pom.xmlfileRepository - Name of the Repository created in NEXUS Portal.

Click the Add Artifacts
ArtifactID - it will be present in the
pom.xmlfileType -It is the type of file generated after maven builds the package.
File - it is the file which will goes into the artifactory after a successful build (eg:
target/myweb-8.6.9.war)
After successfully adding click on Generate Pipeline Script
Add the generated script below
sh 'mvn clean package'in pipeline present in Build stage.pipeline { agent { label 'DEV' } stages { stage('Code') { steps { git credentialsId: 'BB', url: 'https://hashnode-admin@bitbucket.org/hashnode/one.git' } } stage('Build') { steps { sh 'mvn clean package' nexusArtifactUploader artifacts: [[artifactId: 'myweb', classifier: '', file: 'target/myweb-8.6.9.war', type: 'war']], credentialsId: 'nexus_up', groupId: 'in.javahome', nexusUrl: '3.90.184.91:8081', nexusVersion: 'nexus3', protocol: 'http', repository: 'First_Job', version: '8.6.9' } } stage('Deploy') { steps { deploy adapters: [tomcat9(credentialsId: 'tomcat', path: '', url: 'http://44.211.216.198:8080')], contextPath: 'First_Job', war: 'target/*.war' } } } }Save the job and build the Pipeline Job.
After a successful build, the WAR file will be available in the Nexus repository.
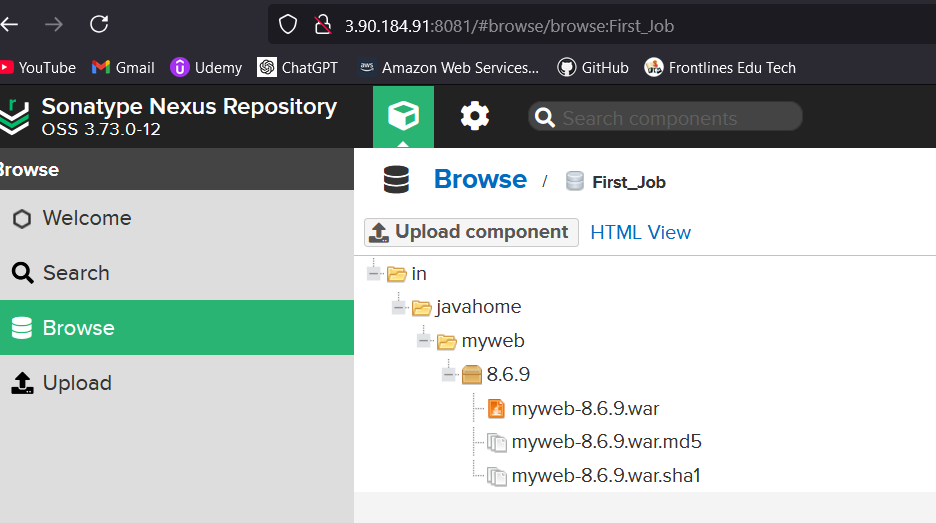
The Application will be deployed to TOMCAT Server
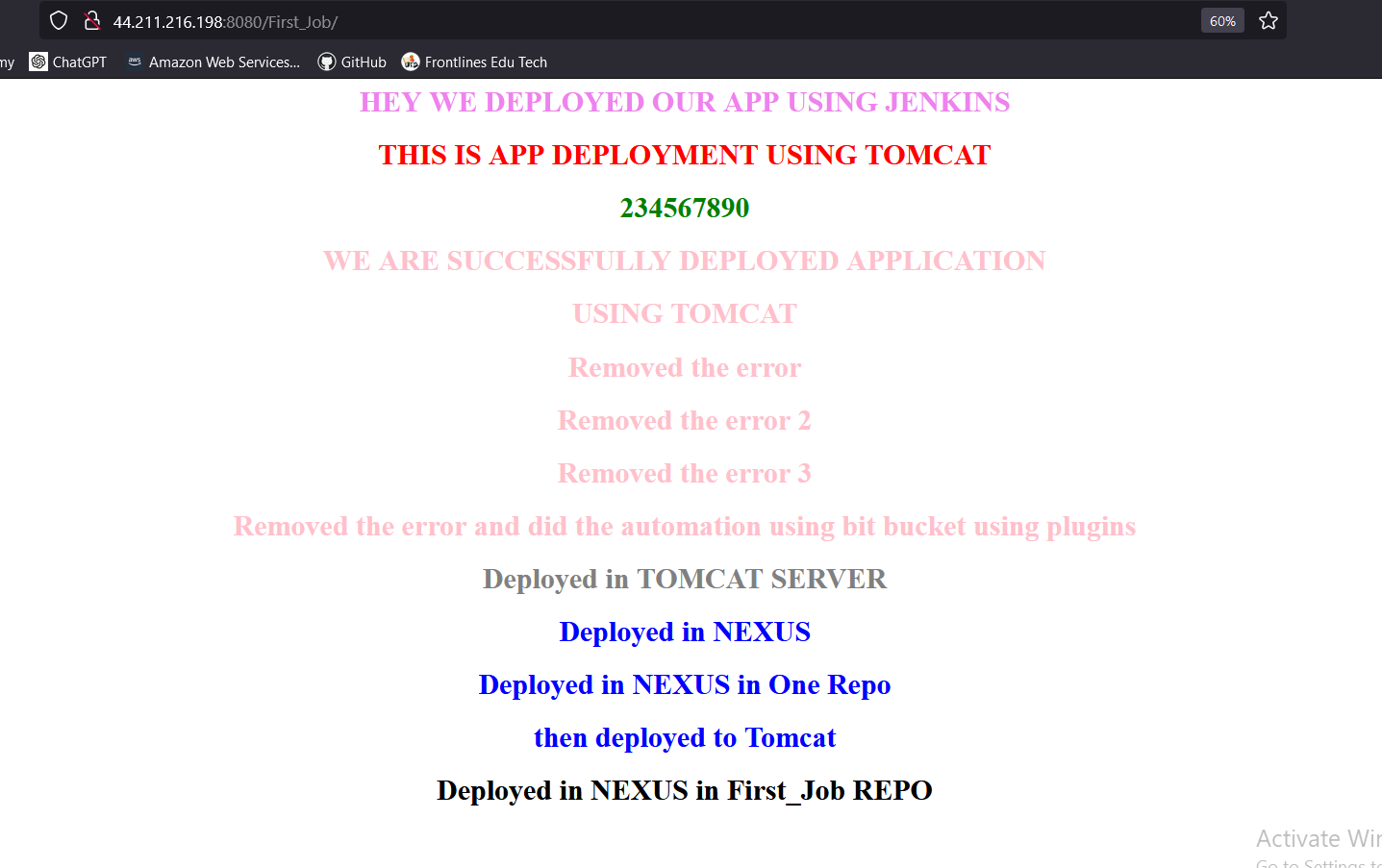
TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS:
- After Opening pipeline syntax, If you can’t find the option you are looking for then we can restart the Jenkins. you can execute
systemctl restart jenkinscommand in Jenkins EC2 Instance
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Uma Mahesh Tammineni directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
