Corporate Project: Seamless Log Rotation Infra streamlining Server Scripts with AWS Lambda and SSM
 Shraddha Suryawanshi
Shraddha Suryawanshi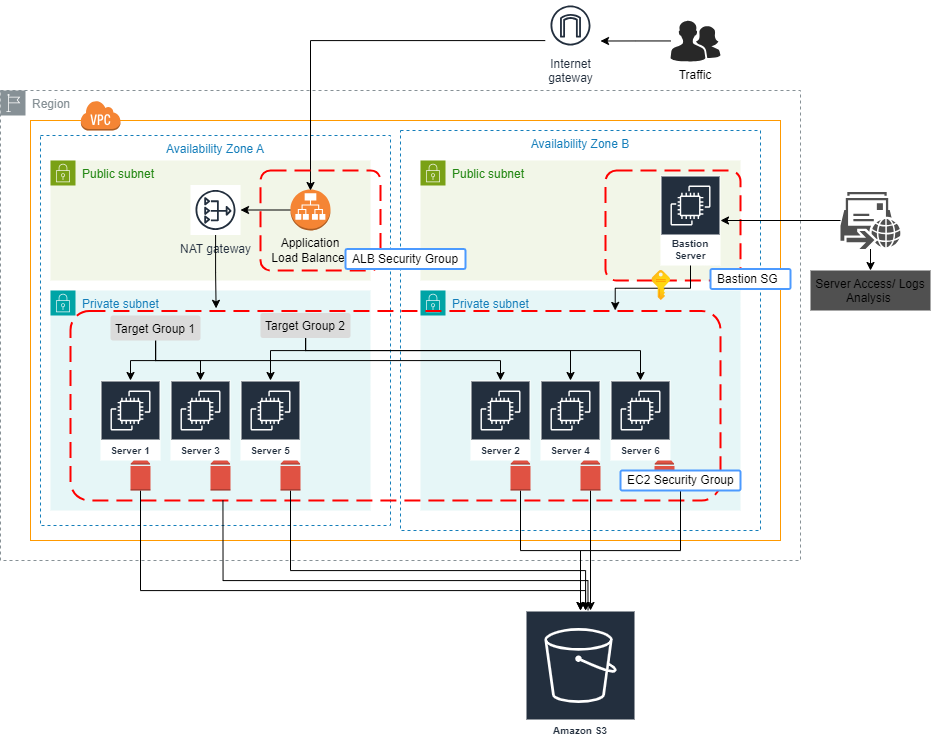
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, effective log management is crucial for maintaining system performance and security. This project explores the implementation of seamless log rotation using AWS Systems Manager (SSM) and Lambda, ensuring that log files are efficiently managed and rotated without manual intervention. By automating this process, we enhance operational efficiency, reduce storage costs, and minimize the risk of log data loss. This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to setting up and managing log rotation, empowering teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Challenges for Log Rotation
Data Overload and Performance Degradation:
As applications generate large volumes of log data, the accumulation of outdated logs can lead to storage exhaustion and performance degradation.
Security Risks and Compliance Challenges:
Logs are critical for auditing, compliance, and incident response. However, retaining logs indefinitely can pose security risks and compliance challenges. Outdated or overly large log files can become targets for unauthorized access or manipulation, potentially jeopardizing sensitive data and violating regulatory requirements.
Manual Management Overhead: Relying on manual log management practices is both time-consuming and error-prone. Teams may struggle to consistently rotate and archive logs, leading to inconsistent log retention policies and potential data loss.
Advantages
Zero Downtime: Achieves log rotation without interrupting traffic or affecting the application's availability.
Automated Failover: Uses load balancer routing to automatically switch between target groups during log rotation.
Efficient Log Archiving: Archives logs to S3 in a compressed format, enabling secure and organized log storage.
Scalable Infrastructure: Can be easily adapted to multiple servers and environments by reusing modular Terraform configurations.
Cost-effective: Uses existing AWS components (ALB, Lambda) with minimal additional cost for log management.
Automate Log Offloading: Send logs to a secure S3 bucket, optimizing local storage and facilitating long-term retention.
Dynamic Scaling: Implement auto-scaling to adjust the number of instances in target groups based on traffic or CPU usage, which would optimize resource usage.
Use Cases
High-Availability Web Applications with Heavy Logging Scenario: Large e-commerce platforms, news sites, or social media applications often generate a high volume of log entries due to user interactions, error tracking, and transaction monitoring. In these applications, log rotation is crucial for performance, as it prevents storage overflow and ensures timely access to logs for troubleshooting.
Fintech and Banking Applications with Compliance Requirements Scenario: Fintech companies need to log every transaction, login, and access attempt for regulatory compliance, such as PCI-DSS or SOX, often resulting in vast amounts of logs. In this case, logs need to be rotated and retained without impacting system performance or violating compliance requirements.
SaaS Platforms with Multi-Instance Logging Needs Scenario: SaaS platforms with microservices architecture have multiple services running across instances, each producing individual logs that need rotation. Log management is crucial for performance monitoring and quick troubleshooting, especially when logs grow rapidly with each client’s activity.
Media and Streaming Platforms Scenario: Streaming services (e.g., video or music) often log user sessions, media playback metrics, and error states, producing substantial logs that need to be archived and rotated regularly. These logs are crucial for analyzing user engagement, optimizing content recommendations, and maintaining uptime.
Healthcare Applications with Patient Data Tracking Scenario: Healthcare applications often track sensitive patient data, including login information, activity tracking, and treatment updates, generating considerable logs for monitoring and auditing. These logs are necessary for compliance with HIPAA and similar healthcare regulations, requiring secure storage and efficient management.
Project Structure
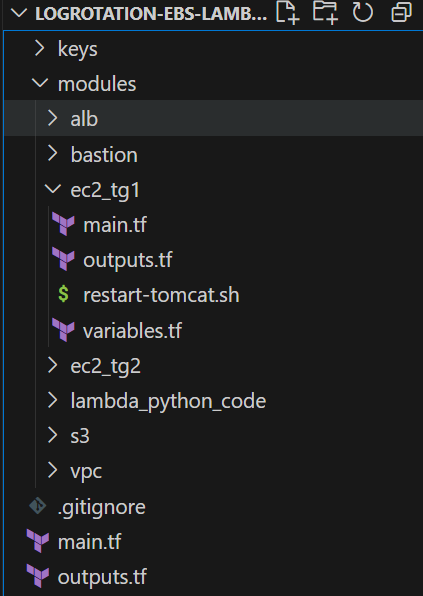
Check out the project at, Project Git Repository Link.
The project structure consists of a root main.tf file that orchestrates various modules, including a VPC module for networking, an ALB module for load balancing, EC2 modules for target groups (TG1 and TG2) to host application instances, a Lambda module for server management, a Bastion module for secure access, and an S3 module for storage. This modular architecture promotes reusability and maintainability, allowing for efficient resource management across different environments.
VPC Module Overview
This module sets up a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with public and private subnets, an internet gateway, NAT gateway, route tables, and security groups for an application environment.
VPC Creation:
The module creates a VPC with a CIDR block of 10.0.0.0/16, tagged as "tf-log-rotation", which allows for a significant number of subnets and resources within the defined range.
Availability Zones Data Source:
Utilizes the aws_availability_zones data source to dynamically retrieve available availability zones, ensuring the configuration is adaptable to the current AWS region.
Public Subnets:
Defines two public subnets, each with a CIDR block derived from the VPC CIDR, and assigns public IP addresses upon instance launch. The subnets are tagged for easy identification.
Private Subnets:
Similar to the public subnets, this module creates two private subnets with separate CIDR blocks to isolate resources without public internet access.
Internet Gateway:
An Internet Gateway is created and attached to the VPC, allowing instances in public subnets to communicate with the internet.
NAT Gateway:
A NAT Gateway is provisioned to enable outbound internet access for resources in private subnets while preventing inbound traffic from the internet.
Elastic IP for NAT:
An Elastic IP address is allocated for the NAT Gateway, ensuring a static IP is used for outbound connections from private subnets.
Public Route Table:
A route table for the public subnets is created with a route that directs all outbound traffic (0.0.0.0/0) through the Internet Gateway.
Public Route Table Association:
Associates the public route table with both public subnets, ensuring they inherit the defined routing rules.
Private Route Table:
Defines a route table for private subnets that routes outbound traffic through the NAT Gateway, allowing internet access while maintaining privacy.
Private Route Table Association:
Associates the private route table with both private subnets, establishing proper routing for outbound traffic.
Security Group for ALB:
Creates a security group (alb_sg) for the Application Load Balancer (ALB) that allows incoming traffic on ports 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), and 8080, with egress rules permitting all outbound traffic.
Security Group for EC2 Instances:
Configures a separate security group (ec2_sg) for EC2 instances, allowing traffic on ports 22 (SSH), 80, 443, and 8080, while restricting access from unwanted sources for security.
Null Resource for ENI Cleanup:
A null_resource is included to detach and delete unused network interfaces (ENIs) associated with Lambda functions, helping maintain a clean environment and prevent resource leaks.
Dependency Management:
Uses the depends_on argument to ensure that security group creation waits for the completion of the ENI cleanup process, enhancing resource dependency management.
S3 Module Overview
S3 Bucket Creation:
Creates an S3 bucket named with a unique suffix for app deployment, allowing forced destruction for testing purposes, and tags it for identification.
Random Suffix Generation:
Generates a 6-character random string (lowercase, no special characters) to ensure unique bucket names.
S3 Object Upload:
Uploads an SSH key file (
tf-10-24-test-key-pair.pem) to the created S3 bucket with private access control, ensuring the file is secure.
EC2_TG1 Module Overview
IAM Role Creation:
Creates an IAM role (
ec2-access-s3-and-ssm) that allows EC2 instances to assume this role via an assume role policy.IAM Policy Definition:
Defines a policy (
ec2-s3-ssm-policy) that grants permissions for EC2 instances to access S3 and SSM services, allowing various actions on these resources.Policy Attachment:
Attaches the previously defined policy to the IAM role, linking the permissions to the role for use by EC2 instances.
IAM Instance Profile:
Creates an IAM instance profile (
ec2-instance-profile) that associates the IAM role with EC2 instances, allowing them to inherit the role's permissions.EC2 Instance Creation:
Launches three EC2 instances using a specified AMI and instance type, assigns an IAM instance profile for permissions, and includes user data for initial configuration.
User Data Script:
The user data script installs the SSM agent, updates the system, creates an HTML file for Tomcat, and sets up a cron job to generate logs every minute while also handling Tomcat service management.
Restart-tomcat.sh defines a function to check if commands like
unzipandzipexist before installing them to ensure the necessary tools are available. Checks for the AWS CLI installation. Stops the Tomcat service before creating a timestamped zip of thecatalina.outlog file for archiving. Uploads the zipped log file to a specified S3 bucket for storage and backup. Finally, restarts the Tomcat service to resume operations after log management.Target Group Attachment:
Attaches the created EC2 instances to a target group (
tg1_attachment), enabling load balancing for traffic directed to those instances
EC2_TG2 Module Overview
This module has the same configuration as EC2_TG1
Bastion Module Overview
A bastion host is a special-purpose instance designed to act as a secure gateway for accessing instances in a private network. Bastion hosts provide a controlled access point to instances in private subnets, typically via SSH, reducing exposure to potential threats from the internet.
IAM Role Creation (
instance_connect_role):Defines an IAM role that allows EC2 instances to assume the role for specific AWS actions related to instance connectivity.
IAM Policy Definition (
instance_connect_policy):Creates a policy granting permissions to perform EC2 actions, including sending SSH public keys and accessing S3 resources.
Policy Attachment:
Attaches the defined IAM policy to the IAM role, enabling EC2 instances to inherit the specified permissions.
Security Group Creation (
bastion_sg):Defines a security group allowing inbound SSH traffic on port 22 from all IP addresses (
0.0.0.0/0), which is suitable for a bastion host.Bastion Host Instance Creation:
Launches an EC2 instance (
bastion) using a specified AMI and instance type, within a public subnet and associated with the created security group.Provisioner for SSH Key Setup:
Utilizes a
remote-execprovisioner to set up SSH keys on the bastion host, allowing secure SSH access to the instance.Connection Configuration:
Configures the connection type to use SSH with the
ec2-useras the user, specifying the private key for authentication.User Data Script:
Executes a shell script during the instance launch to update the system, install Telnet, install Apache HTTP Server, and install the AWS CLI.
ALB Module Overview
Application Load Balancer (ALB):
Defines an ALB (
app_alb) with a specified name, type (application), and associated security group and subnets.The ALB is set as external (
internal = false), allowing traffic from the internet to reach it.The
enable_deletion_protectionattribute is set to false, allowing the ALB to be deleted without additional safeguards.Target Group 1 (
tg1):Configures a target group that routes traffic to instances on port 80 using HTTP, with health checks set to monitor the target's availability.
Health Check Settings:
Specifies health check settings such as the protocol, path, interval, timeout, and thresholds for determining target health.
Listener Resource:
Creates a listener for the ALB on port 80 using HTTP protocol, defining the default action to forward traffic to
tg1.The default action for the listener routes incoming traffic to the first target group (
tg1).Listener Rule for Target Group 1:
Defines a listener rule that matches incoming requests based on query parameters, forwarding them to
tg1when conditions are met (priority 1).Listener Rule for Target Group 2:
Configures a second listener rule with a lower priority (250), forwarding traffic to
tg2under specific conditions defined by the query parameters.
Lambda_Python_Code Module Overview
Data Archive:
data "archive_file": This resource zips the Python script for shifting traffic to target group 2 and stores it at the specified output path.S3 Object Upload:
resource "aws_s3_object": This uploads the zipped Python script for Part 1 to the S3 bucket, making it available for the Lambda function.IAM Role and Policy:
resource "aws_iam_role"andresource "aws_iam_role_policy": These resources define an IAM role and policy allowing the Lambda function to perform necessary actions (like invoking other functions and accessing EC2 resources).Lambda Function:
resource "aws_lambda_function": This defines the Lambda function that executes the traffic shift to target group 2, specifying the handler, runtime, role, and environment variables needed for execution.CloudWatch Event Rule:
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_rule": This sets up a schedule (using a cron expression) for when the Lambda function should be triggered.Event Target:
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_target": This specifies that the scheduled CloudWatch event should invoke the Lambda function for Part 1.Lambda Permissions:
resource "aws_lambda_permission": This grants CloudWatch permission to invoke the Lambda function for Part 1 when the scheduled event triggers.
Lambda Functions Overview:
tf-part-1-traffic-shift-to-tg2
This Lambda function gradually shifts traffic from one target group (TG1) to another (TG2) in an Application Load Balancer (ALB) by adjusting the weights of the target groups based on their health status, ensuring a smooth transition without disrupting service. If successful, it triggers a subsequent Lambda function for further processing.
Imports: The function uses the
boto3library to interact with AWS services and standard libraries for JSON handling, time management, and logging.Environment Variables: It retrieves ARNs for two target groups (TG1 and TG2) and an ALB listener from environment variables.
Logging Setup: Configures logging to capture and output information for debugging and monitoring.
Health Check: Defines a function to check the health status of targets in a specified target group, returning healthy instances.
Traffic Shift Logic: Implements a function to gradually shift traffic from TG1 to TG2 over a specified number of steps and intervals, modifying listener weights accordingly.
Lambda Handler: The main function checks if TG2 has healthy instances; if not, it aborts. If healthy, it initiates the traffic shift and invokes a subsequent Lambda function for further processing.
Return Values: Returns HTTP status codes and messages indicating the success or failure of the operations.
tf-part-2-tg1-log-rotation
This Lambda function manages the log rotation process by restarting the Tomcat service on instances in Target Group 1 (TG1) after verifying their health and ensuring that they are running correctly. If successful, it triggers the next Lambda function for further traffic routing.
Imports and Constants:
Imports necessary libraries (
boto3,json,time,os).Defines constants for target group ARN and instance IDs, converting instance IDs from a comma-separated string into a list.
SSM Command Execution:
run_ssm_command: Sends a command to execute on specified EC2 instances using the SSM (Systems Manager).run_restart_script: Callsrun_ssm_commandto run the specified Tomcat restart script.Health Check Functions:
check_health: Checks the health status of the target group and identifies healthy and unavailable instances.wait_for_healthy_instances: Waits for a specified number of healthy instances to be available in the target group.Tomcat Status Check:
check_tomcat_status: Verifies whether Tomcat is running on the specified instances.poll_command_status: Monitors the status of SSM commands sent to instances and retrieves their outputs.Lambda Handler:
Verifies the health of instances in TG1. If healthy, it executes the
restart-tomcat.shscript on those instances.Continuously checks the Tomcat service status and restarts it if it is not running.
After ensuring that all instances are healthy, it invokes the next Lambda function for traffic routing back to TG1.
Error Handling:
Catches exceptions and logs errors if any part of the process fails, returning a 500 status code.
tf-part-3-traffic-route-back-to-tg1
This Lambda function handles the gradual traffic shift from Target Group 2 (TG2) to Target Group 1 (TG1) in an Application Load Balancer (ALB) after ensuring that the instances in TG1 are healthy. Upon completion of the traffic shift, it triggers the next Lambda function for subsequent log rotation tasks.
Imports and Constants:
Imports required libraries (
boto3,json,time,os).Defines constants for the ARNs of the target groups and the ALB listener, and retrieves the instance IDs for TG1.
Health Check Functions:
check_health: Checks the health status of instances in a target group and returns healthy and unavailable instances.wait_for_healthy_instances: Waits for a specified number of healthy instances in a target group, printing the current status at each interval.Traffic Shift Function:
traffic_shift_to_tg1: Gradually shifts traffic from TG2 to TG1 over a defined number of steps and intervals. It modifies the ALB listener's target group weights in each step to adjust the traffic flow.Lambda Handler:
Checks if all instances in TG1 are healthy using
wait_for_healthy_instances. If any instance is unhealthy, it aborts the traffic shift.Calls
traffic_shift_to_tg1to perform the gradual shift of traffic from TG2 to TG1.After successfully shifting traffic, it invokes the next Lambda function (
tf-part-4-tg2-log-rotation-stop-servers).Error Handling:
Catches any exceptions during execution and returns a 500 status code with an error message.
tf-part-4-tg2-log-rotation-stop-servers
This Lambda function executes a script to restart Tomcat on Target Group 2 (TG2) instances and, upon successful execution, stops those instances. It ensures that the Tomcat service is restarted properly before proceeding with the instance shutdown.
Imports and Constants:
Imports necessary libraries (
boto3,json,time,os).Defines the command to restart Tomcat and retrieves the instance IDs for TG2 from environment variables.
Run Script Function:
run_restart_script: Uses AWS Systems Manager (SSM) to send a command to execute therestart-tomcat.shscript on the specified TG2 instances.Polling Function:
poll_command_status: Continuously checks the status of the command execution on the specified instances. It waits until all instances have either succeeded or failed in executing the command, logging the output for each instance.Lambda Handler:
Calls
run_restart_scriptto execute the restart script on TG2 servers and logs the statuses.If all servers execute the script successfully, it stops the TG2 instances using the
stop_instancesmethod from the EC2 client and logs the action.Error Handling:
Catches any exceptions during execution, logs the error message, and returns a 500 status code with the error details.
tf-part-0-start-tg2-check-tomcat
This Lambda function ensures that instances in Target Group 2 (TG2) are running and that the Tomcat service is active on those instances. Here's a detailed breakdown of the code:
Imports and Constants:
Imports necessary libraries (
boto3,json,time,os).Retrieves the instance IDs and the ARN for TG2 from environment variables.
Defines commands for checking and starting the Tomcat service.
Health Check Function:
check_health: Uses the ELB client to describe the target health of the specified target group. It returns a list of healthy instances.Start Instances Function:
start_instances: Starts the specified EC2 instances and waits until they are running.Run SSM Command Function:
run_ssm_command: Sends a command to execute on the specified instances using AWS Systems Manager (SSM).Poll Command Status Function:
poll_command_status: Polls the command status to check whether it was successful on all specified instances. It waits for a maximum of 30 retries and logs the output for each instance.Lambda Handler:
Part 1:
Checks the status of each TG2 instance. If any instances are not running, it starts them and waits for 30 seconds for them to become active.
Part 2:
Runs a command to check the status of the Tomcat service on each instance. If Tomcat is not running, it sends a command to start the service.
Part 3:
Continuously checks the health status of the TG2 instances until all of them are healthy.
Return Statement:
Returns a 200 status code and a success message indicating that TG2 instances are started and Tomcat is running.
Key Takeaways
This Lambda function automates the management of EC2 instances running Tomcat in Target Group 2, ensuring their availability and service health. By leveraging AWS Systems Manager and Elastic Load Balancing, it simplifies operational tasks, reduces downtime, and enhances application resilience. Implementing such automation can significantly improve efficiency and reliability in cloud infrastructure management, allowing teams to focus on higher-value activities while ensuring seamless service delivery.
Conclusion
This solution effectively automates log rotation in AWS using a combination of Lambda, CloudWatch, and ALB. By dynamically routing traffic and archiving logs, it addresses key operational challenges in log management without requiring manual intervention. This setup ensures continuous application uptime, cost savings, and robust log retention, making it ideal for production-like environments needing seamless log handling.
end
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Shraddha Suryawanshi directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
