Basics of Port Addressing
 ShirishaKuruva
ShirishaKuruvaPort = Communication end point
In computer networking, a port address is a 16 bit numeric identifier used to specify a unique communication end point within a device.
Ports are essential for data traffic.
They enable multiple applications or services on a single device to use the network simultaneously without interference.
Port numbers fall into three main ranges: Well-Known Ports (0–1023) for core services like HTTP (80) and HTTPS (443), Registered Ports (1024–49151) for user-installed applications like MySQL (3306), and Dynamic/Private Ports (49152–65535) for temporary connections.
In the TCP/IP model, a port number combines with an IP address to form a socket, which directs traffic to the correct process or service.
In a node, many processes will be running.The data sent/received must reach the right process.
Fixed port numbers and dynamic port address(0 - 65535).
Example: Fixed port number -25,99 etc.
OS assigned dynamic port numbers :62414.
→Reaching our city = Reaching our network(IP address).
→Reaching our Apartment = Reaching the host(MAC address).
→Reaching the right person = Reaching the right process(Port number).
- Overall, port addresses are essential for managing data flow, allowing for efficient and organized communication between applications and services across a network.
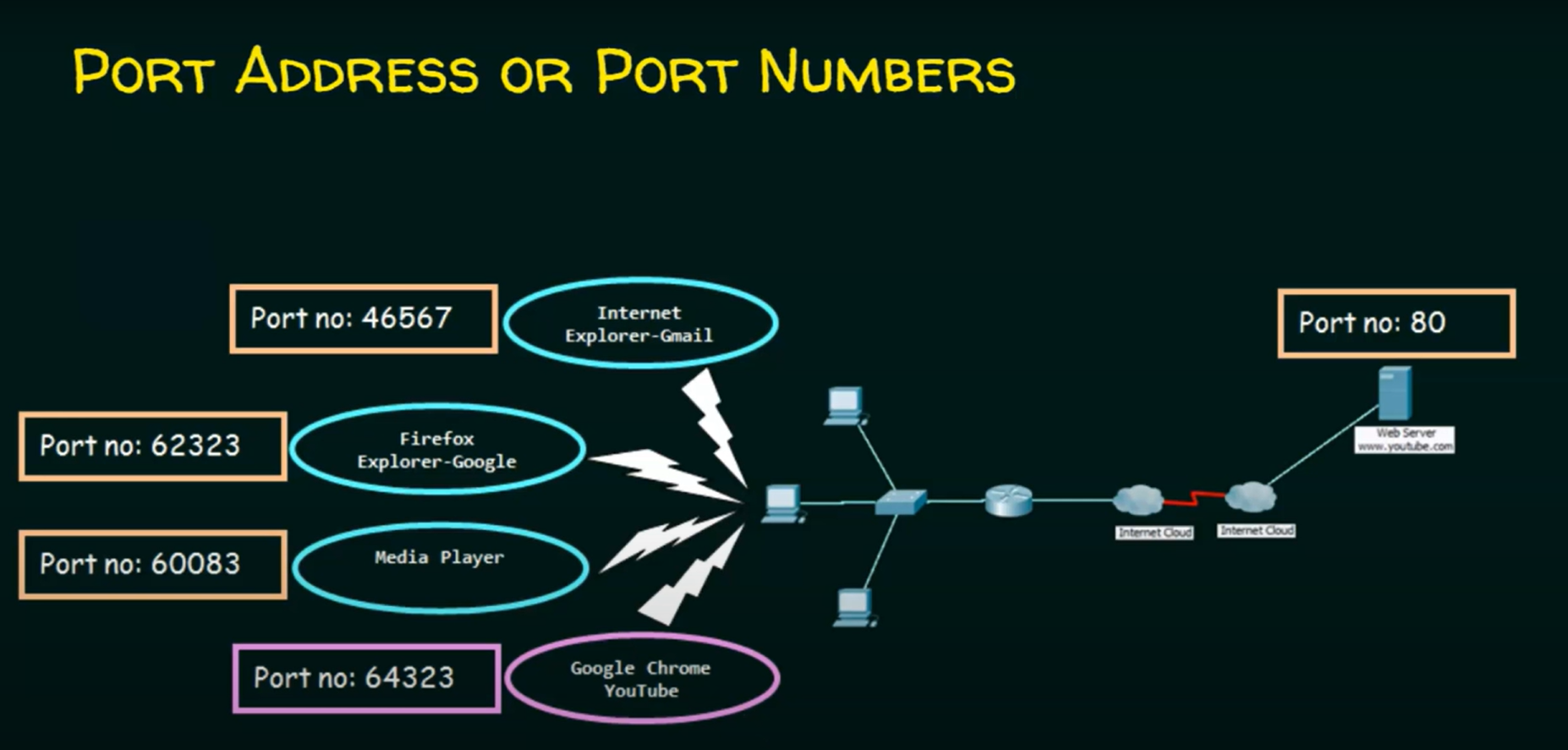
Each application or service (e.g., Internet Explorer, Firefox, Media Player) is assigned a unique port number for data exchange, allowing multiple applications to run simultaneously without conflicts.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from ShirishaKuruva directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
