2024 Guide to Cloud Computing: Benefits and Deployment Models Explained
 Mahmudul Hasan Nisat
Mahmudul Hasan Nisat
Ever wondered how Netflix streams millions of videos simultaneously or how Instagram handles billions of photos without breaking a sweat? The answer lies in cloud computing, specifically Amazon Web Service (AWS). There are many cloud providers besides AWS, such as Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud. Let’s start with the fundamentals that will shape your understanding of the cloud.
Think of cloud computing as renting a fully furnished apartment instead of building a house from scratch. You get all the amenities you need, pay only for what you use, and can upgrade or downgrade based on your needs. That’s exactly how the AWS cloud works for businesses.
In this first blog of our AWS series, we’ll explore:
The fundamental concept of cloud computing and its evolution
Six key advantages that make businesses choose cloud computing
Different deployment models (public, private, and hybrid cloud)
How AWS implements these concepts in real-world scenarios
Whether you’re a complete beginner or have some tech background, this guide will build a strong foundation in cloud computing concepts—crucial for any AWS certification journey.
What is Cloud Computing?
We already have a basic understanding of cloud, but here’s the complete definition: Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of computing resources over the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. Instead of buying, owning, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you can access technology services like computing power, storage, and databases on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider like AWS.
Traditional IT vs Cloud Computing:
Traditional IT: Buy your own servers → Wait for delivery → Install → Configure → Maintain
Cloud Computing: Login to AWS → Start using resources instantly → Pay for what you use
Think of it like electricity: you don't generate your own power; you just plug in and pay for what you consume. AWS works the same way for computing resources.
Six Core Advantages of Cloud Computing
1. Trade Fixed Expense for Variable Expense
Instead of investing heavily in data centers and servers before knowing how you'll use them, you pay only for what you consume. It's like paying for your electricity—you only pay for the lights you use, not the entire power plant.
2. Benefit from Massive Economies of Scale
By using cloud computing, you can achieve a lower variable cost than you could get on your own. Because usage from hundreds of thousands of customers is aggregated in the cloud, AWS can achieve higher economies of scale, translating into lower pay-as-you-go prices.
3. Stop Guessing Capacity
Eliminate guessing about your infrastructure capacity needs. When you make a capacity decision prior to deploying an application, you often end up with expensive idle resources or dealing with limited capacity. With cloud computing, these problems go away.
4. Increase Speed and Agility
In the cloud, new IT resources are just a click away, which means you reduce the time to make those resources available to your developers from weeks to just minutes. This dramatically increases your organization's agility.
5. Stop Spending Money Running/Maintaining Data Centers
Cloud computing lets you focus on your projects rather than on operating infrastructure. Just like you don't need to know how electricity is made to use it, you can focus on what you want to build.
6. Go Global in Minutes
Easily deploy your application in multiple regions around the world with just a few clicks. This means you can provide lower latency and a better experience for your customers at minimal cost.
Cloud Deployment Models
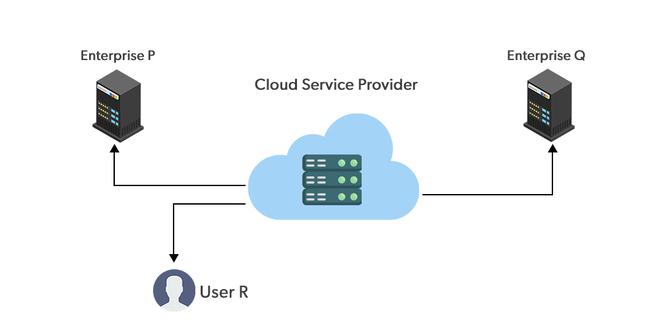
Public Cloud
What is it?: Cloud resources owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider delivered over the internet.
AWS Example: Using Amazon EC2 instances or S3 storage
Best for: Startups, websites, development/test environments
Benefits: No upfront costs, high scalability, pay-per-use
Private Cloud
What is it?: Cloud computing resources used exclusively by a single business or organization.
AWS Example: AWS Outposts
Best for: Financial institutions, hospitals, government agencies
Benefits: Enhanced control, security, and privacy
Hybrid Cloud
What is it?: Combination of public cloud and private cloud/on-premises infrastructure.
AWS Example: Using AWS Direct Connect to combine on-premises data center with AWS
Best for: Banks, large enterprises, government organizations
Benefits: Flexibility, data sovereignty, existing infrastructure utilization
Real-World Examples
Case Study 1: Netflix
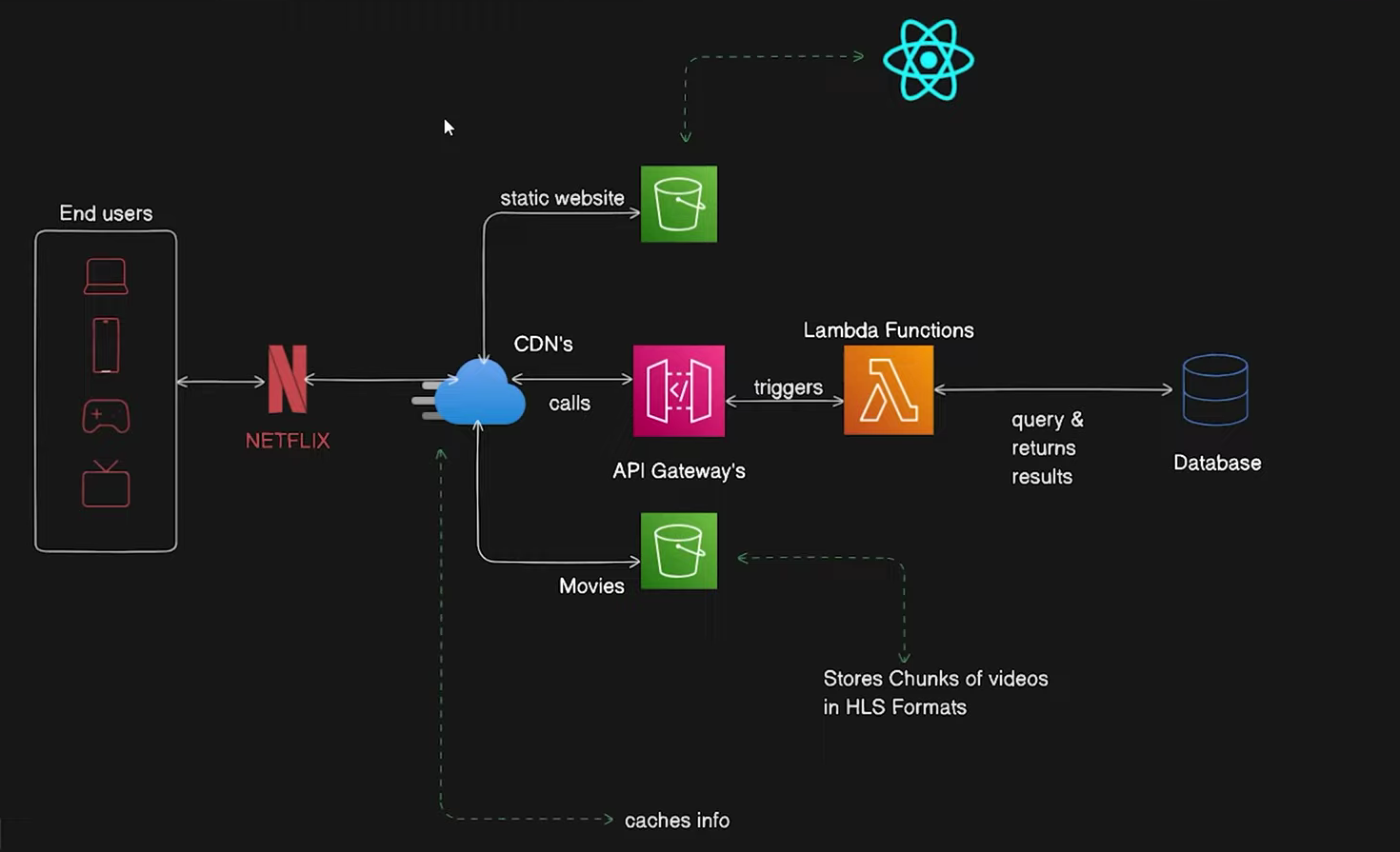
Netflix uses AWS public cloud for:
Streaming videos to millions of users
Content recommendation systems
Database management
Analysis of viewing patterns
Case Study 2: Capital One

Uses hybrid cloud approach for:
Customer-facing applications in public cloud
Sensitive financial data in private cloud
Seamless integration between both environments
Cloud Practitioner Exam Tips
Remember these key points for your exam:
Know the six advantages of cloud computing
Understand the differences between deployment models
Be able to provide examples of each deployment model
Understand basic AWS services that represent each model
Practice Questions:
Which cloud computing benefit allows you to deploy globally in minutes?
- Answer: Global Reach/Go Global in Minutes
What type of cloud deployment model would a bank typically use for processing sensitive financial data?
- Answer: Private Cloud or Hybrid Cloud
Which AWS service is an example of Private Cloud deployment?
- Answer: AWS Outposts
What's Next?
In our next blog post, we'll dive deeper into AWS Global Infrastructure, exploring Regions, Availability Zones, and Edge Locations. Stay tuned!
Additional Resources
This blog is part of my AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner certification journey. Follow along as we explore all the fundamental concepts of AWS cloud computing!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mahmudul Hasan Nisat directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Mahmudul Hasan Nisat
Mahmudul Hasan Nisat
I am deeply committed to continuous learning and keeping up with the latest developments in DevOps, ML, and cloud technologies. Beyond my technical skills, I actively engage in open-source contributions and participate in the broader tech community. I am also passionate about mentoring and helping others harness technology to drive positive impact.