🚀 Day 26 Jenkins Declarative Pipeline
 Dhruv Moradiya
Dhruv Moradiya
This approach to defining your pipeline is crucial for automating processes and improving the efficiency of your development workflow. Let’s break down some key concepts and why you should consider using a pipeline in Jenkins.
📖 What is a Pipeline?
A pipeline is a collection of steps or jobs interlinked in a sequence, allowing you to automate your build, test, and deployment processes efficiently. It serves as a roadmap for your CI/CD workflow, helping to ensure that every part of the process is executed in the correct order.
🆚 Declarative vs. Scripted Pipeline
In Jenkins, there are two primary types of pipeline syntax: Declarative and Scripted.
Declarative:
A more recent and advanced implementation of a pipeline as code.
It offers a simplified and more structured syntax, making it easier to read and maintain.
Best suited for most use cases where you need a straightforward configuration.
Scripted:
The first and most traditional implementation of a pipeline as code in Jenkins.
Built with Groovy as a general-purpose DSL (Domain Specific Language).
Offers more flexibility but can be more complex and harder to read.
💡 Why You Should Have a Pipeline
Having a Jenkins Pipeline brings numerous advantages:
Version Control: The definition of a Jenkins Pipeline is written into a text file called a Jenkinsfile. This file can be committed to a project’s source control repository.
Pipeline-as-Code: By treating the Continuous Delivery (CD) pipeline as part of the application, it can be versioned and reviewed just like any other code. This promotes better collaboration among team members.
Automation: Creating a Jenkinsfile automates the process, which reduces the risk of human error and speeds up the CI/CD workflow.
Immediate Benefits of a Jenkins Pipeline:
Automatically creates a pipeline build process for all branches and pull requests, ensuring every piece of code is validated.
Enables code review and iteration on the pipeline alongside the remaining source code, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
📝 Pipeline Syntax Example
Here’s a basic structure of a Declarative Pipeline:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
// Add build steps here
echo 'Building...'
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
// Add test steps here
echo 'Testing...'
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
// Add deploy steps here
echo 'Deploying...'
}
}
}
}
In this example:
The
agent anyline specifies that Jenkins can run the pipeline on any available agent.Each
stagerepresents a phase in your pipeline: Build, Test, and Deploy. Within each stage, you define the steps required to execute that phase.
🔧 Task-01: Create a New Jenkins Job
Objective:
Create a new job in Jenkins using the Declarative Pipeline syntax to automate your CI/CD processes.
Steps to Complete the Task:
Open Jenkins:
Navigate to your Jenkins server URL in your web browser. Log in with your credentials.http://localhost:8080Create a New Job:
Click on "New Item" on the left-hand side of the dashboard.
Enter a name for your job in the "Enter an item name" field.
Select "Pipeline" as the type of job instead of Freestyle Project.
Click "OK" to proceed to the configuration page.
Configure the Pipeline:
In the General section, you can add a description for your job if desired.
Scroll down to the Pipeline section.
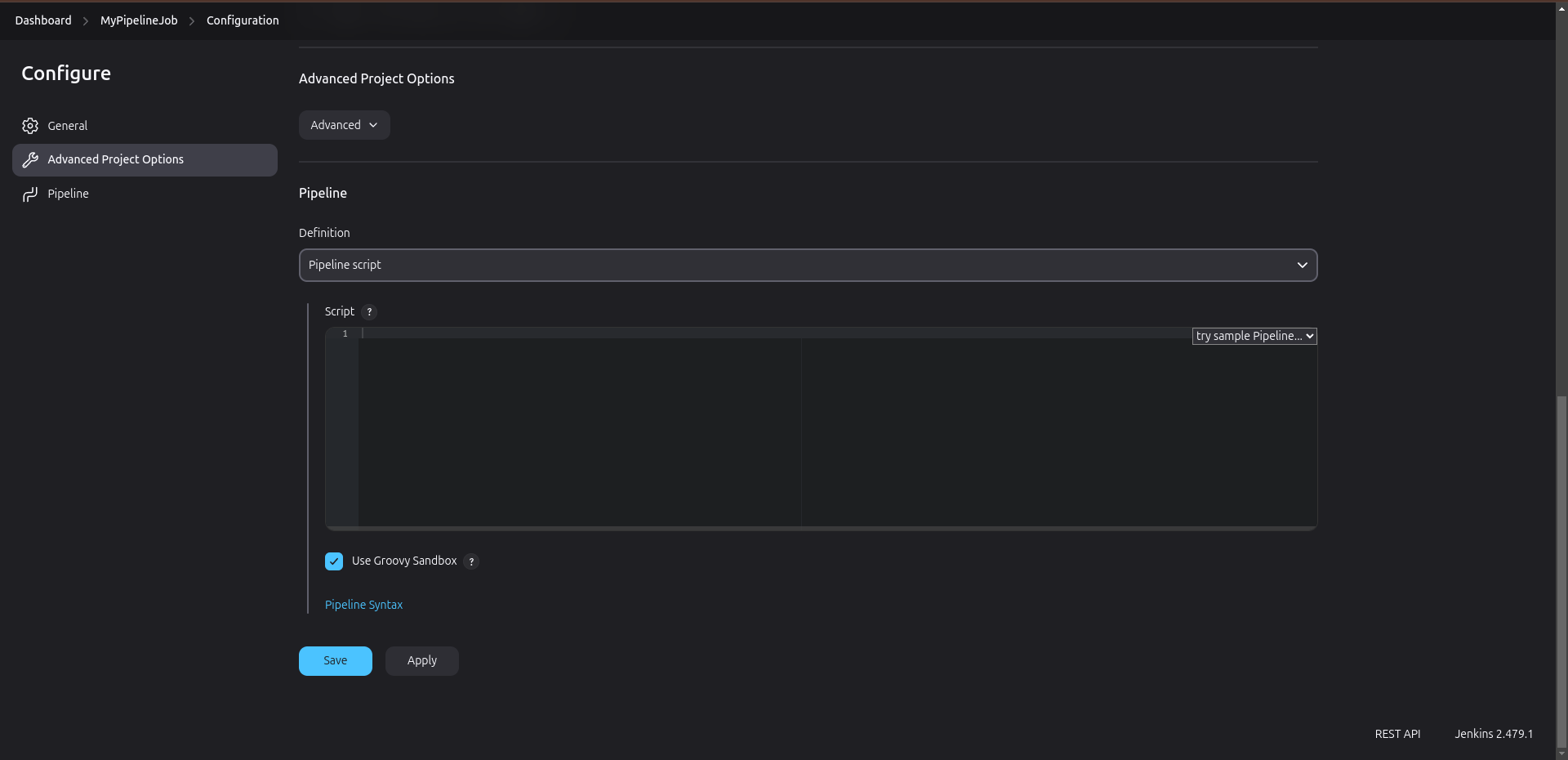
Define the Pipeline:
In the Pipeline section, you will specify your pipeline script using the Declarative syntax. Use the following example as a template:pipeline { agent any stages { stage('Build') { steps { echo 'Building...' // Add your build commands here (e.g., sh 'make') } } stage('Test') { steps { echo 'Testing...' // Add your test commands here (e.g., sh 'npm test') } } stage('Deploy') { steps { echo 'Deploying...' // Add your deployment commands here (e.g., sh 'deploy.sh') } } } }In this script:
- Replace the
echostatements with actual commands relevant to your project (e.g., build commands, test commands, and deployment scripts).
- Replace the
Save the Configuration:
After entering your pipeline script, scroll to the bottom of the page and click "Save" to save your job configuration.Run the Pipeline:
To run the pipeline, go back to the job page and click on "Build Now" in the left-hand menu.
You can monitor the progress of your pipeline by clicking on the build number under Build History. This will show you the console output and any logs generated during the execution.
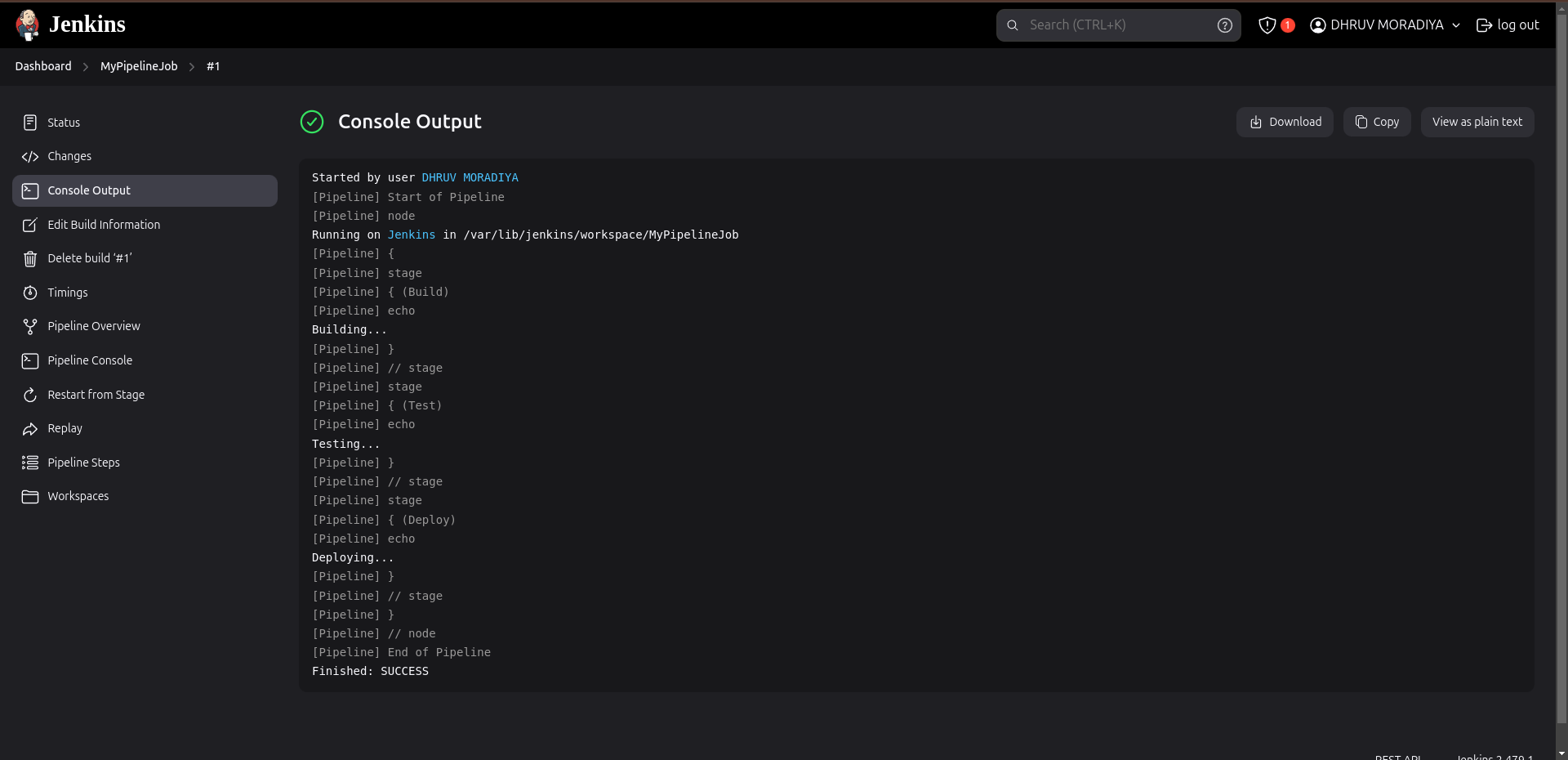
Monitor and Review:
After the pipeline completes, review the output in the console to ensure each stage executed successfully.
If there are any errors, the console output will help you diagnose issues in your pipeline configuration or your project scripts.
📚 Follow the Official Jenkins Hello World Example
For additional guidance and best practices, follow the Official Jenkins Hello World example to complete your setup and explore more about Jenkins pipelines.
By mastering the Jenkins Declarative Pipeline, you pave the way for a more organized and efficient CI/CD process, making your development workflow smoother and more reliable. This hands-on experience will be invaluable as you continue to refine your skills in DevOps. Happy coding! 🎉
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Dhruv Moradiya directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
