Day 1 : Introduction to Generative AI
 Manav Paul
Manav PaulTable of contents
- 1. Introduction to Generative AI
- 1.1 Why Generative AI is Important and Why It is Required?
- 1.2 How Does Generative AI Work?
- 1.3 Real-World Examples of Its Application in Various Industries
- 1.4 Where Does Generative AI Exist?
- 1.5 Discriminative Model vs Generative Model
- 1.6 Unsupervised vs Supervised Learning
- 2. Large Language Models (LLMs)

👋🏻 Hey there! I'm Manav Paul, a 24-year-young spiritual developer with a newfound fascination for generative AI. This blog is my digital diary, where I'll be documenting my exploration of this exciting field. As a curious learner, I'm diving headfirst into understanding the basics, experimenting with different tools, and sharing my insights along the way.
Here are the projects I recently worked on in generative AI:
AI Article Summarizer: Tired of reading lengthy articles? My AI summarizer can do just that.
AI Twin 24/7: Imagine having a digital clone that works 24/7, even while you sleep. I've built one!
Want to learn how? Dive into my beginner friendly 30-day blog series.
🤿 Let’s Dive in!
1. Introduction to Generative AI
1.1 Why Generative AI is Important and Why It is Required?
Generative AI has emerged as a revolutionary force, capable of creating new content, solving complex problems, and driving innovation across various industries. Its importance lies in its ability to:
Automate tasks: From generating creative content to automating routine processes, generative AI can significantly reduce human effort and increase efficiency.
Enhance creativity: By providing new and unique ideas, generative AI can inspire creativity and innovation, leading to groundbreaking discoveries.
Personalize experiences: Generative AI can tailor products and services to individual preferences, creating more personalized and engaging experiences for customers.
Solve complex problems: By analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying patterns, generative AI can help solve complex problems that were previously unsolvable.
1.2 How Does Generative AI Work?
Generative AI models are trained on massive datasets to learn patterns and relationships within the data. They then use this knowledge to generate new, original content that is similar to the training data. This process involves:
Data ingestion: Collecting and preparing large datasets relevant to the task.
Model training: Using algorithms like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) to train the model on the data.
Content generation: Using the trained model to generate new content based on specific prompts or constraints.
1.3 Real-World Examples of Its Application in Various Industries
Generative AI is being used in a wide range of industries, including:
Healthcare: Drug discovery, medical image analysis, and personalized treatment plans.
Entertainment: Game development, music composition, and movie production.
Marketing: Personalized advertising, content creation, and customer service.
Finance: Fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading.
Design: Product design, architecture, and fashion.
Companies using Generative AI models:
OpenAI: GPT-3, DALL-E 2
Google: LaMDA, Imagen
Meta: Galactica, Make-A-Scene
Stability AI: Stable Diffusion
Midjourney: Midjourney AI
1.4 Where Does Generative AI Exist?
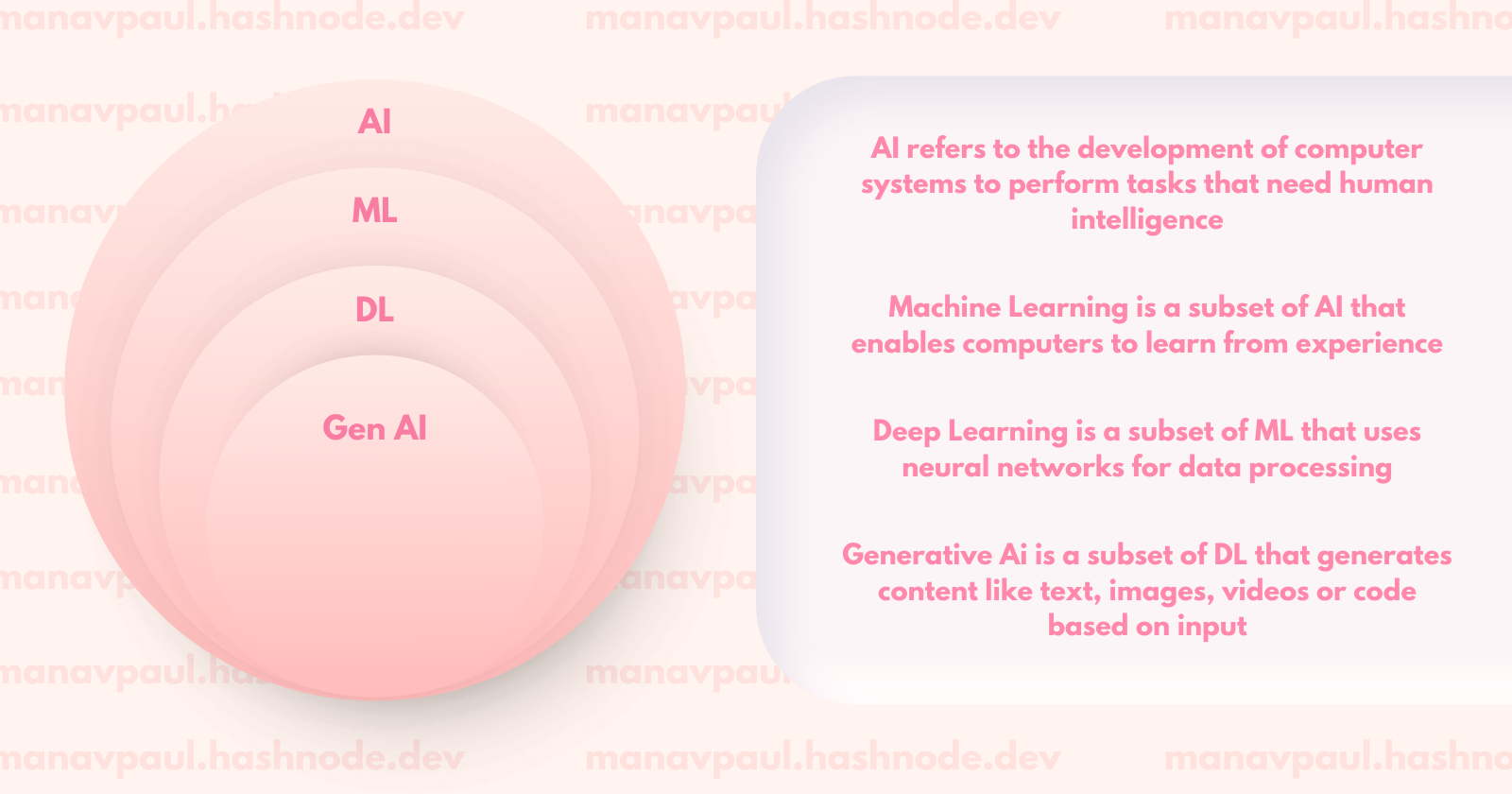
AI: Artificial Intelligence is the broad field of creating intelligent agents.
ML: Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on algorithms that can learn from data.
DL: Deep Learning is a subset of ML that uses artificial neural networks to learn complex patterns.
Generative AI: A subset of DL that focuses on generating new content.
1.5 Discriminative Model vs Generative Model
Discriminative Model: Learns to classify data into predefined categories.
- Example: A model that classifies images as cats or dogs.
Generative Model: Learns to generate new data that is similar to the training data.
- Example: A model that generates new images of cats or dogs.
1.6 Unsupervised vs Supervised Learning
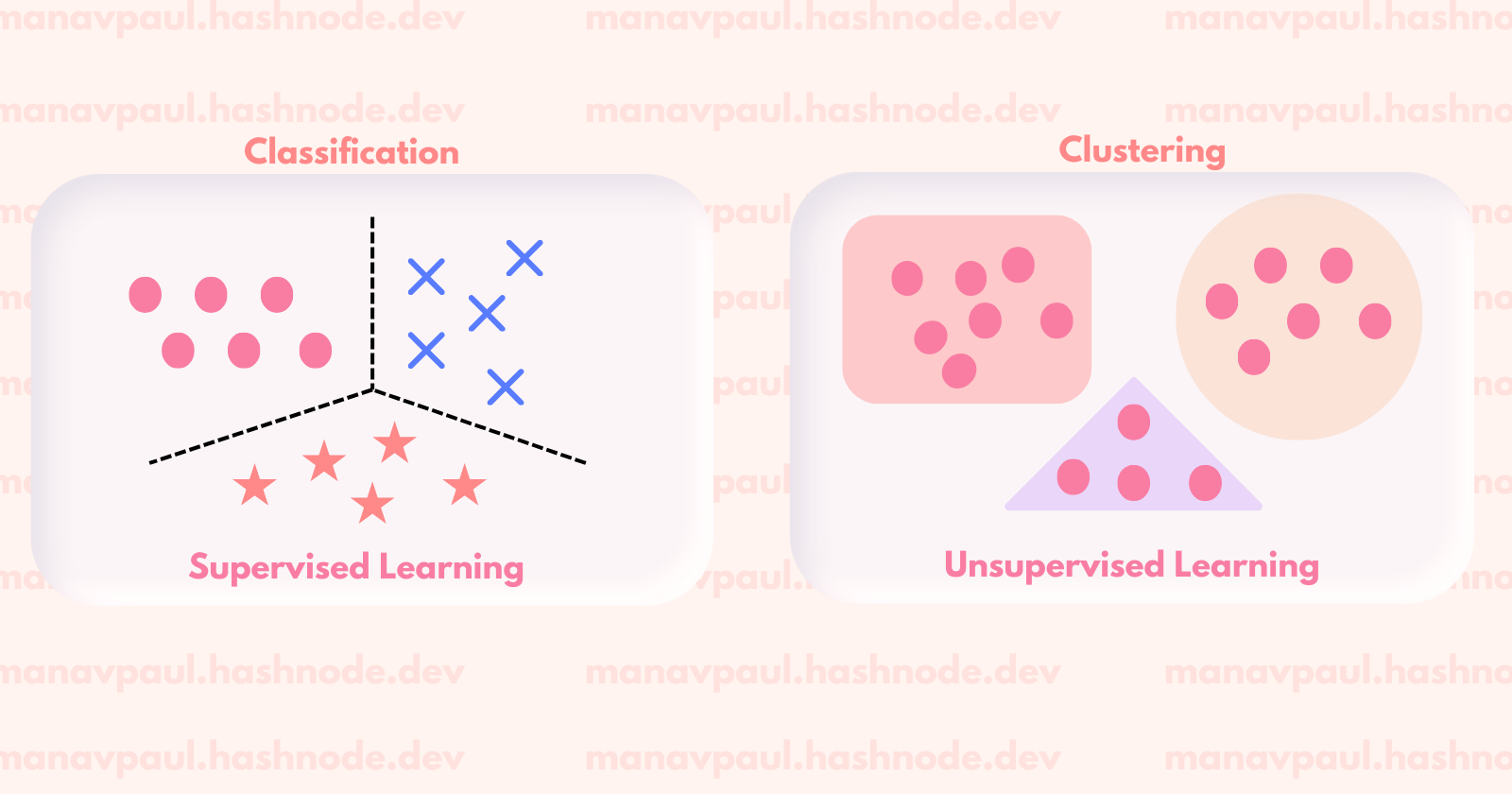
Unsupervised Learning: Algorithms learn patterns in data without labeled examples.
K-means: You have a clear idea of the number of clusters or your data is relatively well-separated.
Pros: Simple, efficient, scales well.
Cons: Requires specifying K, sensitive to outliers and initialization.
Best for: Well-separated, spherical cluster.
DBSCAN: Your data has irregular shapes or contains noise or you don't know the number of clusters beforehand.
Pros: Does not require specifying K, handles irregular shapes, robust to noise.
Cons: Can be computationally expensive, sensitive to parameter selection.
Best for: Clusters with arbitrary shapes or noise.
Supervised Learning: Algorithms learn to predict outcomes based on labeled examples.
Classification: Predicting categorical outcomes (e.g., spam or not spam).
Regression: Predicting numerical outcomes (e.g., house prices).
2. Large Language Models (LLMs)
2.1 What are LLMs?
LLMs are foundational ML models that use deep learning algorithms to process and understand natural language. They are trained on massive datasets to learn patterns and entity relationships in language. LLMs can perform various tasks, including:
Text-to-text generation: Creating new text based on a prompt or context.
Text-to-image generation: Creating images based on a text description.
Image-to-text generation: Describing an image in words.
Sentiment analysis: Determining the emotional tone of a piece of text.
2.2 What Makes LLMs Powerful?
Multimodal capabilities: LLMs can perform multiple tasks, unlike traditional language models that are specialized for a single task.
Scale: LLMs are trained on massive amounts of data, allowing them to learn complex patterns and relationships.
Examples of LLMs:
Gemini
GPT-4
XLM-R
LLaMA
Claude
Mistral Falcon
In our next post, we'll dive deeper into the world of generative AI and explore the end-to-end pipeline for creating generative models. Stay tuned for more insights and exciting experiments!
▶ Next → Day 2: End-to-End Generative AI Pipeline
⭐Github Repo : Journey Roadmap
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Manav Paul directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Manav Paul
Manav Paul
24, Documenting my journey of DevOps | GenAI | Blockchain | NFTs