DevOps Love Story: CI/CD Pipeline for Valentine's Day
 Balraj Singh
Balraj Singh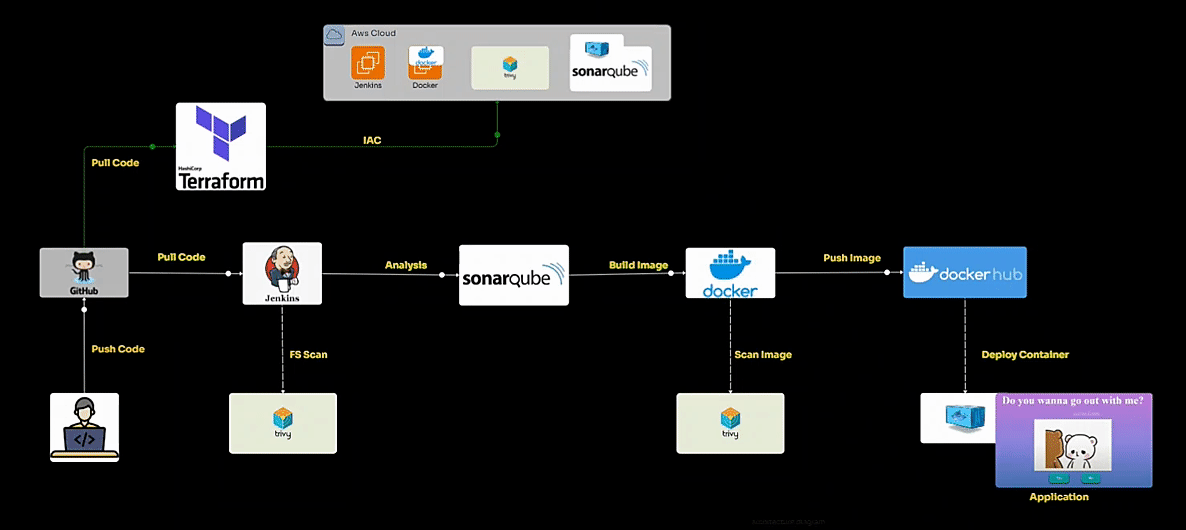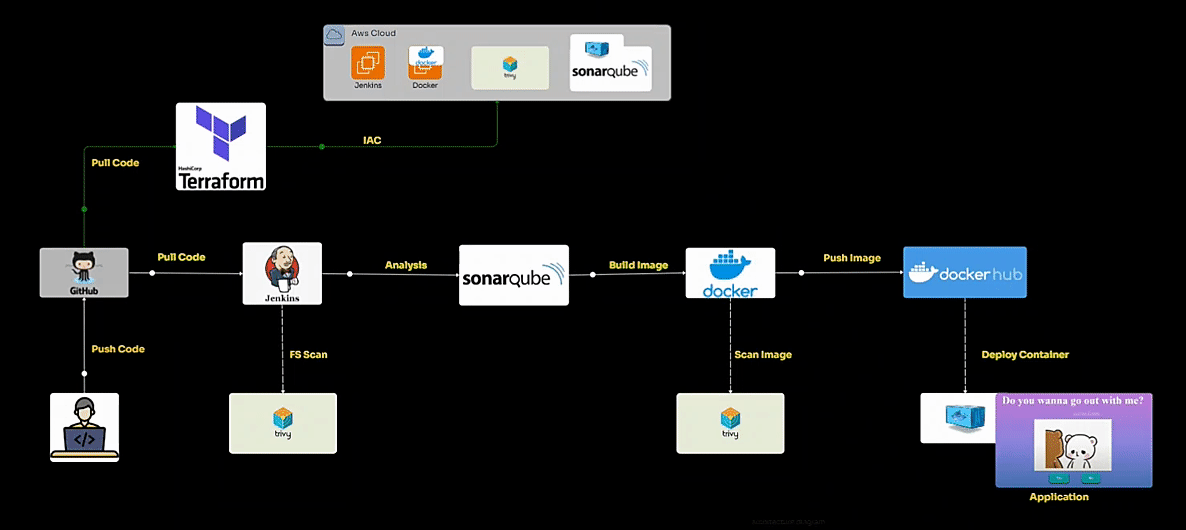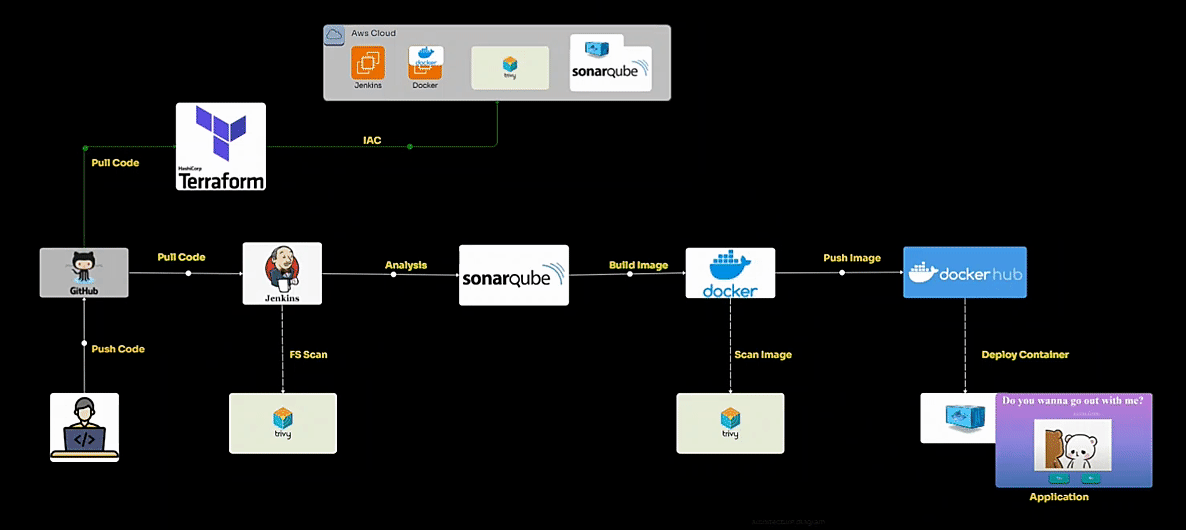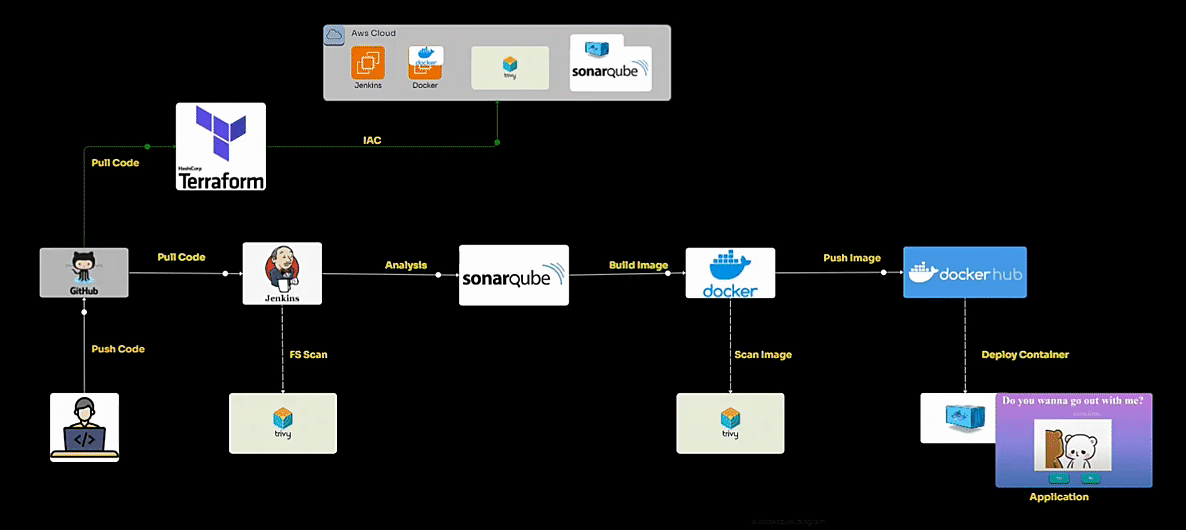
This Valentine’s Day DevOps CI/CD project provides a fun DevOps-themed guide using Jenkins, SonarQube, Docker, and Trivy. It focuses on a playful web app with a Valentine's theme. The project shows how to set up a complete pipeline, from configuring Jenkins and Docker to performing code quality checks with SonarQube and running security scans with Trivy.
Prerequisites
Before diving into this project, here are some skills and tools you should be familiar with:
[x] Clone repository for terraform code
Note: Replace resource names and variables as per your requirement in terraform code- from the Virtual machine main.tf (i.e keyname-
MYLABKEY*)
- from the Virtual machine main.tf (i.e keyname-
[x] App Repo
[x] Git and GitHub: You'll need to know the basics of Git for version control and GitHub for managing your repository.
[x] Jenkins Installed: You need a running Jenkins instance for continuous integration and deployment.
[x] Docker: Familiarity with Docker is essential for building and managing container images.
[x] SonarQube: For code quality checks, deployed on Docker.
[x] Trivy: For filesystem and Docker image scanning, showcasing security scanning features.
Setting Up the Environment
I have created a Terraform code to set up the entire environment, including the installation of required applications, and tools.
⇒ EC2 machines will be created and named as
"Jenkins⇒ Docker Install
⇒ Trivy Install
⇒ SonarQube install as in a container
EC2 Instances creation
First, we'll create the necessary virtual machines using terraform.
Below is a terraform configuration:
Once you clone repo then go to folder "18.Real-Time-DevOps-Project/Terraform_Code/Code_IAC_Terraform_box" and run the terraform command.
cd Terraform_Code/Code_IAC_Terraform_box
$ ls -l
da---l 07/10/24 4:01 PM scripts
-a---l 29/09/24 10:44 AM 507 .gitignore
-a---l 09/10/24 10:57 AM 8351 main.tf
-a---l 16/07/21 4:53 PM 1696 MYLABKEY.pem
Note ⇒ Make sure to run main.tf from inside the folders.
13.Real-Time-DevOps-Project/Terraform_Code/Code_IAC_Terraform_box/
da---l 07/10/24 4:01 PM scripts
-a---l 29/09/24 10:44 AM 507 .gitignore
-a---l 09/10/24 10:57 AM 8351 main.tf
-a---l 16/07/21 4:53 PM 1696 MYLABKEY.pem
You need to run main.tf file using the following terraform command.
Now, run the following command.
terraform init
terraform fmt
terraform validate
terraform plan
terraform apply
# Optional <terraform apply --auto-approve>
Once you run the terraform command, then we will verify the following things to make sure everything is set up via a terraform.
Inspect the Cloud-Init logs:
Once connected to the EC2 instance then you can check the status of the user_data script by inspecting the log files.
# Primary log file for cloud-init
sudo tail -f /var/log/cloud-init-output.log
or
sudo cat /var/log/cloud-init-output.log | more
If the user_data script runs successfully, you will see output logs and any errors encountered during execution.
If there’s an error, this log will provide clues about what failed.
Outcome of "cloud-init-output.log"
Verify the Installation
- [x] Docker version
ubuntu@ip-172-31-95-197:~$ docker --version
Docker version 24.0.7, build 24.0.7-0ubuntu4.1
docker ps -a
ubuntu@ip-172-31-94-25:~$ docker ps
- [x] trivy version
ubuntu@ip-172-31-89-97:~$ trivy version
Version: 0.55.2
- [x] Terraform version
ubuntu@ip-172-31-89-97:~$ terraform version
Terraform v1.9.6
on linux_amd64
- [x] aws cli version
ubuntu@ip-172-31-89-97:~$ aws version
usage: aws [options] <command> <subcommand> [<subcommand> ...] [parameters]
To see help text, you can run:
aws help
aws <command> help
aws <command> <subcommand> help
Setup the Jenkins
Go to Jenkins EC2 and run the following command Access Jenkins via http://<your-server-ip>:8080. Retrieve the initial admin password using:
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Install the plugin in Jenkins
Manage Jenkins > Plugins view> Under the Available tab, plugins available for download from the configured Update Center can be searched and considered:
Blue Ocean
Pipeline: Stage View
Docker
Docker Pipeline
Docker-build-step
SonarQube Scanner
Configure SonarQube
<public IP address: 9000>
default login: admin/admin
You have to change the password as per the below screenshot
Configure the tools
Configure the sonarqube scanner in Jenkins.
Dashboard> Manage Jenkins> Tools
Search for Sonarqube Scanner installations
- create a below pipeline, build it and verify the outcomes.
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('code') {
steps {
echo 'This is cloning the code'
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/mrbalraj007/Valentine-Day-DevOps-Project.git'
echo "This is cloning the code"
}
}
}
}
Integrate SonarQube in Jenkins.
Go to Sonarqube and generate the token
Administration> Security> users>
now, open Jenkins UI and create a credential for Sonarqube
Dashboard> Manage Jenkins> Credentials> System> Global credentials (unrestricted)
Configure the sonarqube server in Jenkins.
On Jenkins UI:
Dashboard> Manage Jenkins> System > Search for
SonarQube installations
Name: sonar server URL: <HTTP: Sonarqube IP address:9000> Server authentication Token: select the sonarqube token from the list.
- build a pipeline with sonarqube parameter
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
SCANNER_Home= tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages {
stage('Git Checkout') {
steps {
echo 'This is cloning the code'
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/mrbalraj007/Valentine-Day-DevOps-Project.git'
}
}
stage('Trivy FileSystem Scan') {
steps {
echo 'This is for scan file system the code'
sh "trivy fs --format table -o trivy-fs-report.html ."
}
}
stage('Sonarqube Analysis') {
steps {
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar'){
echo 'Analysis the code'
sh "$SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectKey=Valentine -Dsonar.projectName=Valentine"
}
}
}
}
}
- add docker build and tag to the image
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
SCANNER_Home= tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages {
stage('Git Checkout') {
steps {
echo 'This is cloning the code'
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/mrbalraj007/Valentine-Day-DevOps-Project.git'
}
}
stage('Trivy FileSystem Scan') {
steps {
echo 'This is for scan file system the code'
sh "trivy fs --format table -o trivy-fs-report.html ."
}
}
stage('Sonarqube Analysis') {
steps {
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar'){
echo 'Analysis the code'
sh "$SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectKey=Valentine -Dsonar.projectName=Valentine"
}
}
}
stage('Build and Tag Docker Image') {
steps {
echo 'This step for building a docker image and tag it'
sh "docker build -t balrajsi/valentine:v1 ."
}
}
}
}
Build Failed
Troubleshooting
I was getting the below error message:
[Pipeline] { (Build and Tag Docker Image)
[Pipeline] echo
This step for building a docker image and tag it
[Pipeline] sh
+ docker build -t balrajsi/valentine:v1 .
DEPRECATED: The legacy builder is deprecated and will be removed in a future release.
Install the buildx component to build images with BuildKit:
https://docs.docker.com/go/buildx/
permission denied while trying to connect to the Docker daemon socket at unix:///var/run/docker.sock: Post "http://%2Fvar%2Frun%2Fdocker.sock/v1.24/build?buildargs=%7B%7D&cachefrom=%5B%5D&cgroupparent=&cpuperiod=0&cpuquota=0&cpusetcpus=&cpusetmems=&cpushares=0&dockerfile=dockerfile&labels=%7B%7D&memory=0&memswap=0&networkmode=default&rm=1&shmsize=0&t=balrajsi%2Fvalentine%3Av1&target=&ulimits=null&version=1": dial unix /var/run/docker.sock: connect: permission denied
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // stage
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // withEnv
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // node
[Pipeline] End of Pipeline
ERROR: script returned exit code 1
Finished: FAILURE
Solution:
Add Jenkins to the Docker Group:
Run the following command to add the Jenkins user to the docker group:
bash sudo usermod -aG docker jenkins
After adding Jenkins to the Docker group, restart the Jenkins service to apply the changes: sudo systemctl restart jenkins
Verify Docker Permissions:
Confirm that the docker group has appropriate permissions for /var/run/docker.sock: bash sudo chmod 666 /var/run/docker.sock
This command makes the Docker socket accessible to all users, which is useful for testing but should be secured in production.
- Add docker credential.
Below is the updated pipeline
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
SCANNER_Home= tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages {
stage('Git Checkout') {
steps {
echo 'This is cloning the code'
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/mrbalraj007/Valentine-Day-DevOps-Project.git'
}
}
stage('Trivy FileSystem Scan') {
steps {
echo 'This is for scan file system the code'
sh "trivy fs --format table -o trivy-fs-report.html ."
}
}
stage('Sonarqube Analysis') {
steps {
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar'){
echo 'Analysis the code'
sh "$SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectKey=Valentine -Dsonar.projectName=Valentine"
}
}
}
stage('Build and Tag Docker Image') {
steps {
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker-cred') {
echo 'This step for building a docker image and tag it'
sh "docker build -t balrajsi/valentine:v1 ."
}
}
}
}
stage('Trivy Image Scan') {
steps {
echo 'This step for scanning docker image'
sh "trivy image --format json -o trivy-image-report.json balrajsi/valentine:v1"
}
}
}
}
Again build failed
Issue:less space was reported on the drive.Troubleshooting/Solution:
Extend the drive
Select the EC2 instance and modify the volume to 20 GB
Yes, after modifying the volume size in AWS, you'll need to extend the partition within the Ubuntu OS so that the filesystem recognizes the new space.
Here are the steps to extend the root volume:
Check the new disk size to confirm that the OS recognizes the additional storage:
lsblk
You should see /dev/nvme0n1 with the new 20 GB size.
Extend the partition: Use growpart to extend the partition to the full size of the disk. First, install cloud-guest-utils if it's not already installed:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install cloud-guest-utils -y
Then extend the partition:
sudo growpart /dev/nvme0n1 1
Resize the filesystem: After extending the partition, resize the filesystem to use the additional space:
sudo resize2fs /dev/root
Verify the updated size: Check that the filesystem now reflects the increased space:
df -h
This should show /dev/root with approximately 20 GB of total space available.
Before: Disk Utilization
ubuntu@Jenkins-svr:~$ df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/root 6.8G 5.4G 1.4G 81% /
tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 768M 1008K 767M 1% /run
tmpfs 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
efivarfs 128K 3.6K 120K 3% /sys/firmware/efi/efivars
/dev/nvme0n1p16 881M 76M 744M 10% /boot
/dev/nvme0n1p15 105M 6.1M 99M 6% /boot/efi
tmpfs 384M 12K 384M 1% /run/user/1000
After Extend the drive : Disk Utilization
ubuntu@Jenkins-svr:~$ df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/root 19G 5.4G 13G 30% /
tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 768M 1012K 767M 1% /run
tmpfs 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
efivarfs 128K 3.6K 120K 3% /sys/firmware/efi/efivars
/dev/nvme0n1p16 881M 76M 744M 10% /boot
/dev/nvme0n1p15 105M 6.1M 99M 6% /boot/efi
tmpfs 384M 12K 384M 1% /run/user/1000
Build the pipeline again if it goes well.
- Append the pipeline to push the docker image
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
SCANNER_Home= tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages {
stage('Git Checkout') {
steps {
echo 'This is cloning the code'
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/mrbalraj007/Valentine-Day-DevOps-Project.git'
}
}
stage('Trivy FileSystem Scan') {
steps {
echo 'This is for scan file system the code'
sh "trivy fs --format table -o trivy-fs-report.html ."
}
}
stage('Sonarqube Analysis') {
steps {
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar'){
echo 'Analysis the code'
sh "$SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectKey=Valentine -Dsonar.projectName=Valentine"
}
}
}
stage('Build and Tag Docker Image') {
steps {
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker-cred') {
echo 'This step for building a docker image and tag it'
sh "docker build -t balrajsi/valentine:v1 ."
}
}
}
}
stage('Trivy Image Scan') {
steps {
echo 'This step for scanning docker image'
sh "trivy image --format json -o trivy-image-report.json balrajsi/valentine:v1"
}
}
stage('Push Docker Image') {
steps {
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker-cred') {
echo 'This step for pushing image to docker hub'
sh "docker push balrajsi/valentine:v1"
}
}
}
}
}
}
Outcomes
View from Docker Hub
Append the pipeline to Deploy an image to a container
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
SCANNER_Home= tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages {
stage('Git Checkout') {
steps {
echo 'This is cloning the code'
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/mrbalraj007/Valentine-Day-DevOps-Project.git'
}
}
stage('Trivy FileSystem Scan') {
steps {
echo 'This is for scan file system the code'
sh "trivy fs --format table -o trivy-fs-report.html ."
}
}
stage('Sonarqube Analysis') {
steps {
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar'){
echo 'Analysis the code'
sh "$SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectKey=Valentine -Dsonar.projectName=Valentine"
}
}
}
stage('Build and Tag Docker Image') {
steps {
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker-cred') {
echo 'This step for building a docker image and tag it'
sh "docker build -t balrajsi/valentine:v1 ."
}
}
}
}
stage('Trivy Image Scan') {
steps {
echo 'This step for scanning docker image'
sh "trivy image --format json -o trivy-image-report.json balrajsi/valentine:v1"
}
}
stage('Push Docker Image') {
steps {
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker-cred') {
echo 'This step for pushing image to docker hub'
sh "docker push balrajsi/valentine:v1"
}
}
}
}
stage ('Deploy to Container') {
steps {
sh 'docker run -d -p 8081:80 balrajsi/valentine:v1'
}
}
}
}
Pipeline status
Try to access the application
http://publicIPAddressofServer:8081
http://35.174.11.211:8081/
- Application is accessible on the below URL
http://publicIPAddressofServer:8081/yes.html
http://35.174.11.211:8081/yes.html
If you try to build it again, it will fail because it already exists. So, we are introducing Docker Compose, and the updated pipeline is provided below.
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
SCANNER_Home= tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages {
stage('Git Checkout') {
steps {
echo 'This is cloning the code'
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/mrbalraj007/Valentine-Day-DevOps-Project.git'
}
}
stage('Trivy FileSystem Scan') {
steps {
echo 'This is for scan file system the code'
sh "trivy fs --format table -o trivy-fs-report.html ."
}
}
stage('Sonarqube Analysis') {
steps {
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar'){
echo 'Analysis the code'
sh "$SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectKey=Valentine -Dsonar.projectName=Valentine"
}
}
}
stage('Build and Tag Docker Image') {
steps {
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker-cred') {
echo 'This step for building a docker image and tag it'
sh "docker build -t balrajsi/valentine:v1 ."
}
}
}
}
stage('Trivy Image Scan') {
steps {
echo 'This step for scanning docker image'
sh "trivy image --format json -o trivy-image-report.json balrajsi/valentine:v1"
}
}
stage('Push Docker Image') {
steps {
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker-cred') {
echo 'This step for pushing image to docker hub'
sh "docker push balrajsi/valentine:v1"
}
}
}
}
stage ('Deploy to Container') {
steps {
# // sh 'docker run -d -p 8081:80 balrajsi/valentine:v1' # Remove the `hash` if you ware using the same pipeline.
sh 'docker compose up -d'
}
}
}
}
Image view from Docker Hub:
View from SonarQube:
Congratulations! :-) You have deployed the application successfully.
Resources used in AWS:
EC2 instances
Environment Cleanup:
As we are using Terraform, we will use the following command to delete
To delete the
Virtual machine. Go to folder "18.Real-Time-DevOps-Project/Terraform_Code/Code_IAC_Terraform_box" and run the Terraform command.
cd Terraform_Code/
$ ls -l
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
da---l 26/09/24 9:48 AM Code_IAC_Terraform_box
Sudo Terraform destroy --auto-approve
Conclusion
In the Valentine's Day DevOps CICD project, we used various DevOps tools and practices to build a strong pipeline that ensures code quality, security, and smooth deployment. By using Jenkins as our main CI/CD tool, we managed several stages: retrieving source code, performing quality checks with SonarQube, conducting security scans with Trivy, building and scanning Docker images, and deploying to a target environment. The project effectively integrated these tools and showcased best practices in automation and container management.
This project provides a practical way to deepen your understanding of CI/CD pipelines, including key components like automated testing, image scanning, and secure Docker deployment. Additionally, the Valentine's Day theme makes the DevOps experience more engaging and enjoyable, creating a memorable learning journey. Whether for personal skill development or as a demonstration of DevOps expertise, this project serves as a valuable template for building reliable and secure CI/CD pipelines.
References For a deeper understanding and detailed steps on similar setups, feel free to check the following technical blogs:
Ref Link
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Balraj Singh directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
