K-Means Clustering for N-Dimensional Feature Spaces
 Mohamad Mahmood
Mohamad Mahmood2 min read
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def kmeans(data, k, max_iter=100):
# Randomly initialize centroids
np.random.seed(0) # For reproducibility
centroids = data[np.random.choice(data.shape[0], k, replace=False)]
for _ in range(max_iter):
# Assignment step
distances = np.linalg.norm(data[:, np.newaxis] - centroids, axis=2)
clusters = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)
# Update step
new_centroids = np.array([data[clusters == i].mean(axis=0) for i in range(k)])
# Check for convergence
if np.all(centroids == new_centroids):
break
centroids = new_centroids
return centroids, clusters
def plot_clusters(data, centroids, clusters, title):
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
if data.shape[1] == 1:
plt.scatter(data, np.zeros_like(data), c=clusters, cmap='viridis', s=100)
plt.scatter(centroids, np.zeros_like(centroids), color='red', marker='X', s=200, label='Centroids')
plt.title(title)
plt.xlabel('Feature 1')
plt.yticks([])
elif data.shape[1] == 2:
plt.scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1], c=clusters, cmap='viridis', s=100)
plt.scatter(centroids[:, 0], centroids[:, 1], color='red', marker='X', s=200, label='Centroids')
plt.title(title)
plt.xlabel('Feature 1')
plt.ylabel('Feature 2')
elif data.shape[1] == 3:
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1], data[:, 2], c=clusters, cmap='viridis', s=100)
ax.scatter(centroids[:, 0], centroids[:, 1], centroids[:, 2], color='red', marker='X', s=200, label='Centroids')
ax.set_title(title)
ax.set_xlabel('Feature 1')
ax.set_ylabel('Feature 2')
ax.set_zlabel('Feature 3')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Dataset 1: 1D
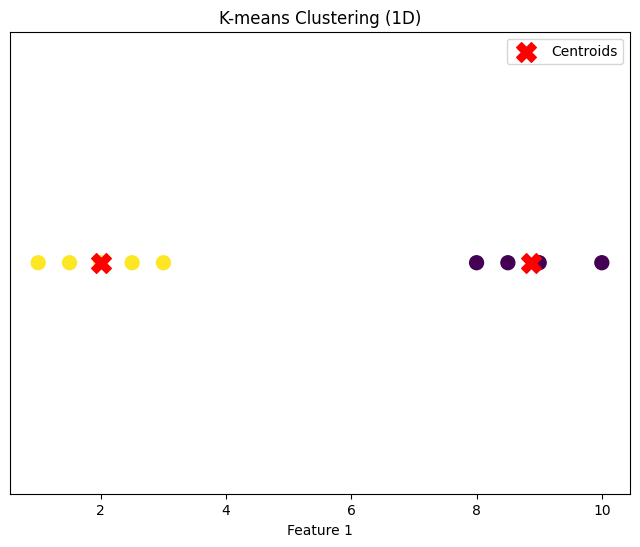
data_1d = np.array([[1], [1.5], [2], [2.5], [3], [8], [8.5], [9], [10]])
k1 = 2
centroids_1d, clusters_1d = kmeans(data_1d, k1)
plot_clusters(data_1d, centroids_1d, clusters_1d, "K-means Clustering (1D)")
# Dataset 2: 2D
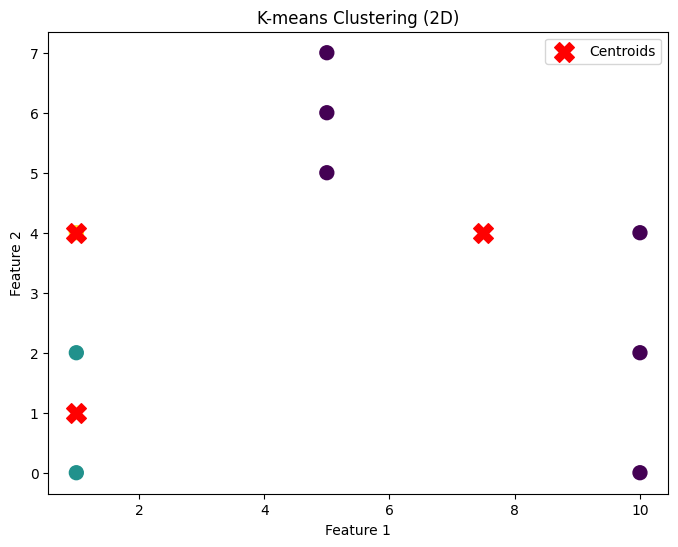
data_2d = np.array([[1, 2], [1, 4], [1, 0],
[10, 2], [10, 4], [10, 0],
[5, 5], [5, 6], [5, 7]])
k2 = 3
centroids_2d, clusters_2d = kmeans(data_2d, k2)
plot_clusters(data_2d, centroids_2d, clusters_2d, "K-means Clustering (2D)")
# Dataset 3: 3D
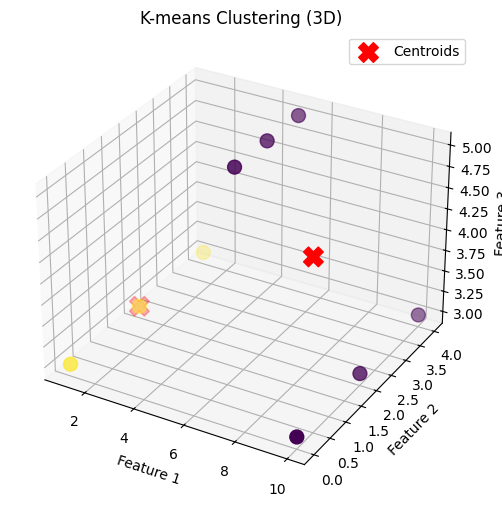
data_3d = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [1, 4, 3], [1, 0, 3],
[10, 2, 3], [10, 4, 3], [10, 0, 3],
[5, 2, 5], [5, 3, 5], [5, 4, 5]])
k3 = 2
centroids_3d, clusters_3d = kmeans(data_3d, k3)
plot_clusters(data_3d, centroids_3d, clusters_3d, "K-means Clustering (3D)")
Output:
1 Dimension
2 Dimension
3 Dimension
0
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mohamad Mahmood directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Mohamad Mahmood
Mohamad Mahmood
Mohamad's interest is in Programming (Mobile, Web, Database and Machine Learning). He studies at the Center For Artificial Intelligence Technology (CAIT), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM).