Overview of EBS Volumes, Snapshots, and AMIs
 Rawad Hossain
Rawad Hossain
In this blog, we will learn about EBS, its volume types, snapshots, backup, and AMIs. To better understand this, it's helpful to have some knowledge about EC2.
AWS EBS (Elastic Block Store)
On your local machine (laptop), you have physical storage drives (HDD or SSD). Whenever you need to store something, you use your machine's storage.
Similarly, EC2 instances also have storage. They use a network drive that can be attached to the instances while they run. This storage service provided by AWS is known as EBS, and it works specifically with Amazon EC2 instances.
Why is EBS needed?
EC2 instances do not provide persistent storage on their own, which means if an instance is terminated, its data can be lost.
However, by attaching an EBS Volume to an EC2 instance, the data remains even after termination.
When selecting an EBS volume, you can create volumes of various sizes and types based on your workload's needs. These can be backed up and used with other instances through Snapshots (more on this later).
Although EBS storage is a paid service, the free tier offers 30 GB of General Purpose (SSD) or Magnetic storage per month. Learn more about pricing here.
In EC2 Servers there are two kinds of storage types
EBS Volumes
Instance Store
EBS Volumes
As we mentioned earlier, an EBS volume is an external network drive attached to your EC2 instance. When your instance is terminated, it does not affect your EBS volume, which can later be attached to another EC2 instance.
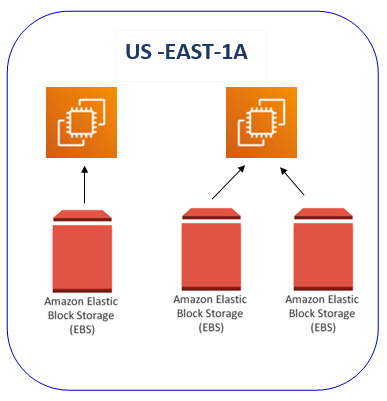
Here are some key points about EBS Volumes:
EBS volumes are locked to its Availability Zone (AZ). To move it, you need to snapshot it first.
An EBS volume is not created inside the EC2 instance. It exists outside the instance but within the same availability zone.
These have a set capacity that you can increase as needed, and you will be billed based on the capacity you choose.
EBS volume can only be attached to an EC2 instance located in the same Availability Zone where the EBS volume was created. For example, if an EBS volume is created in ap-south-1b, it can only be attached to an EC2 instance in ap-south-1b.
Instance Store
Instance Store is a local storage physically attached where the EC2 instance is running. It is a temporary storage where data on an instance store is lost when the instance stops or terminates.
Instance Store is suitable for buffer, cache, scratch data, or temporary content. Since it is physically attached, it offers very high performance and is fast for your EC2 instance.
An Instance Store is created inside the EC2 machine, meaning it is part of the machine. In contrast, an EBS volume is separate from the EC2 machine and exists on a different machine. When we connect the EBS volume to the EC2 instance, it connects virtually, not physically, and the data travels from the EBS to the EC2 instance over a network.
As the Instance Store is inside the EC2 machine, it has lower latency and better I/O performance compared to EBS. However, its data is lost when the instance is terminated. EBS is more reliable because its data persists even after the instance is terminated.
EBS Volume Types
Various kinds of EBS volume are there available in AWS depending upon pricing and workload use cases
General Purpose SSD (gp2, gp3) is used for cost-effective, low-latency storage. gp3 is the newer generation compared to gp2.
Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1 and io2) designed for critical applications that require high, consistent IOPS with low latency. Supports Multi attach.
Throughput Optimized HDD
Cold HDD
You can read more about it in detail in the AWS documentation here.
EBS Snapshots
Whenever you want to move the storage drive (EBS volume) of your EC2 instance to another instance within the same Availability Zone, you can actually detach it from the first instance and reattach it directly to the other instance. However, if you want to use it in a different region, you’ll need a backup or a copy of the storage data. For this, you would have to create an EBS Snapshot. An EBS Snapshot is a backup of the EBS volume at a specific point in time and can be used to create new EBS volumes in the same or different regions.
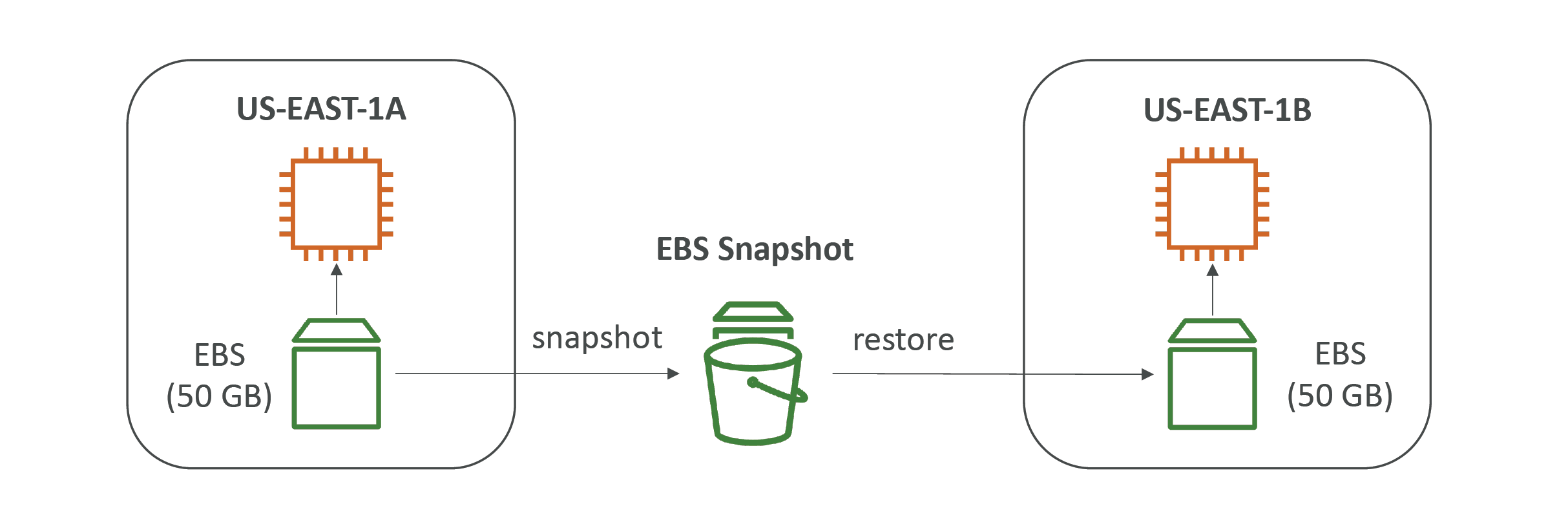
Some key points:
EBS Snapshots are incremental backups stored in S3.
Can copy snapshots across region or AZ
Cost-effective
Snapshots allow for fast restoration of EBS volumes
Creating a snapshot in the console:
AMI (Amazon Machine Image)
Suppose you’re setting up a computer and want to have all the essential software. Instead of installing everything each time, you create a template setup that includes all these essentials. Now, whenever you are setting up a new computer, you can quickly replicate this setup.
Similarly, an AMI provides a template (pre-configured image) that you can use to launch multiple EC2 instances with the same software, operating system (e.g., Linux, Windows), settings, and configurations. This way, each new instance launched from the AMI will replicate that original setup.
AMIs can be customized for different applications, software, and configurations and used across regions. They offer faster boot time as repeated installations are minimized, saving time and resources.
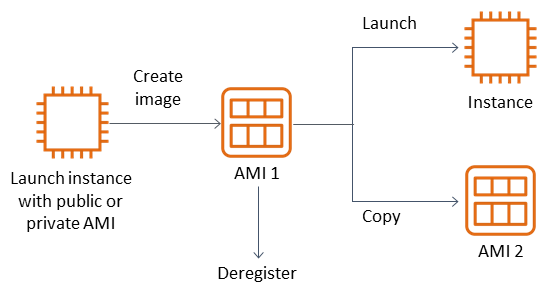
Types of AMIs
Public AMIs: Provided by AWS, free to use
AWS Marketplace AMIs: Pre-configured by others, these AMIs often include licensed software and require payment.
Custom AMIs: Created by users according to their requirements.
Selecting AMIs when launching an instance:
This is the End of this Blog.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rawad Hossain directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
