Application Layer In OSI Reference Model
 ShirishaKuruva
ShirishaKuruvaApplication layer is the topmost layer in the OSI model.
It provides services to the user.
It serves as the interface between the user and the network.
It facilitates communication, data sharing and resource access over a network.
It is responsible for providing network services directly to end user applications.
Application programs are based on client server model.
Services provided by the Application layer:
→Transferring files.
→Accessing files.
→Managing files.
→Addressing files(From source to destination).
→Mail services.
→Directory service (To access global information).
Application layer functions includes:
*Identification of communication partners.
*Determining resource availability.
*Synchronizing communication.
*Application services.
*Data translation and Presentation.
*Communication Initiation & Termination.
*User authentication.
*Data formatting.
*Error handling and Data recovery.
Application layer protocols
HTTP / HTTPS.
FTP.
SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
DNS(Domain Name System).
Telnet & SSH(Secure Shell).
SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol).
1. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
Purpose: HTTP is used for transferring web pages and resources (such as images, videos, scripts) over the World Wide Web (WWW).
Use Case: Accessing websites via web browsers.
Ports: Default port 80 for HTTP, port 443 for HTTPS (secure version of HTTP).
Example: When you visit a website, your browser sends an HTTP request to the server, and the server responds with an HTTP response containing the requested web page.

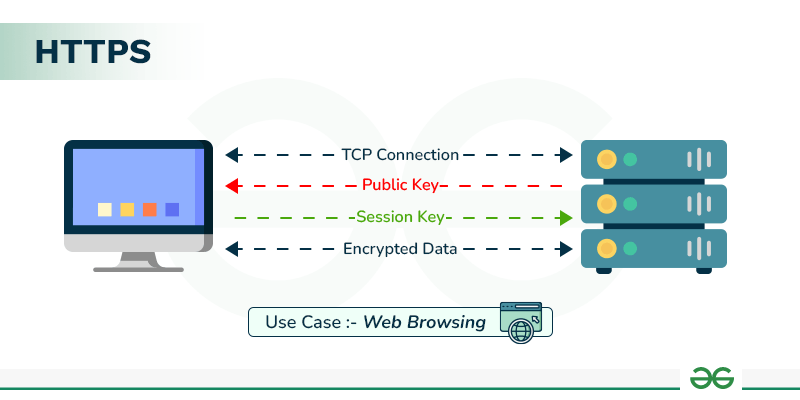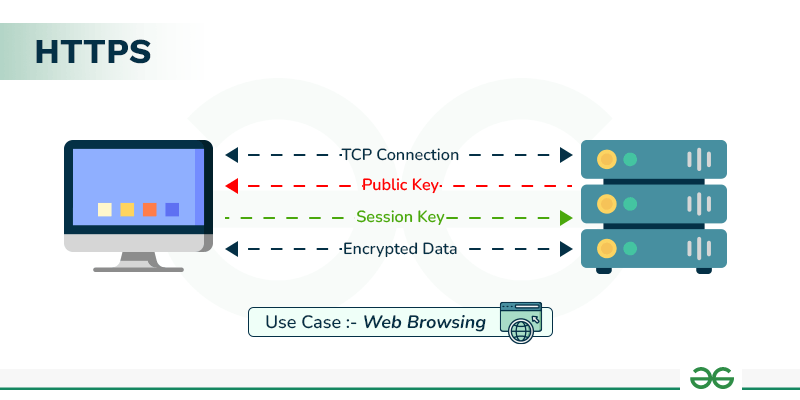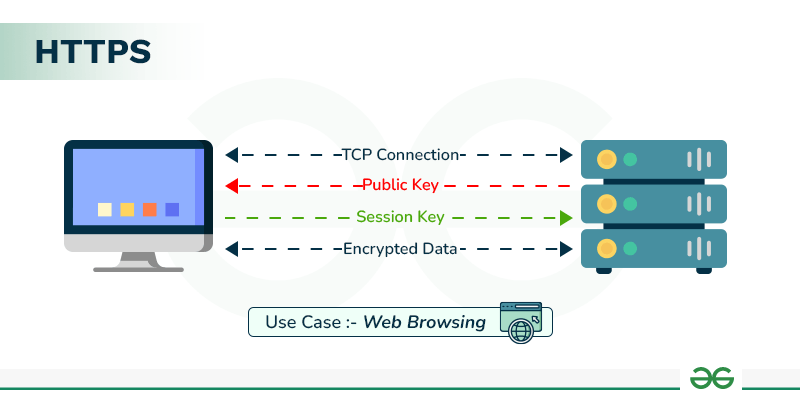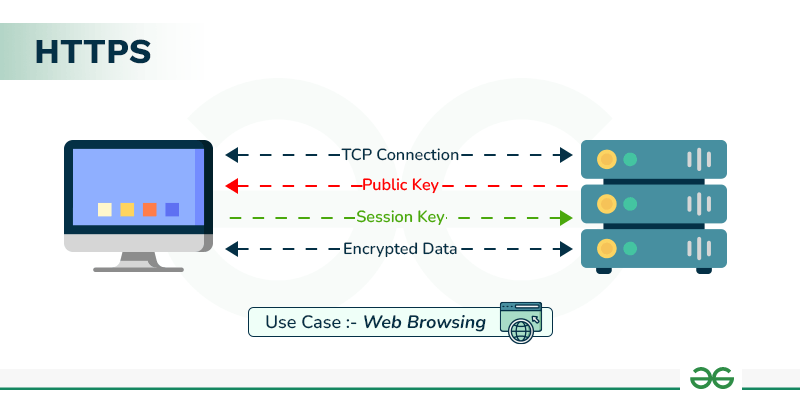
2. HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
Purpose: HTTPS is an extension of HTTP that includes security features like encryption via SSL/TLS.
Use Case: Secure communication over the internet, used by online banking, e-commerce, and any site requiring privacy and data protection.
Ports: Default port 443.
Example: When you access a secure website, such as an online store or your bank's website, the communication between the server and your browser is encrypted with HTTPS.
3. FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
Purpose: FTP is used for transferring files between computers on a network.
Use Case: Uploading/downloading files to/from web servers, managing files on remote systems.
Ports: Default ports are 20 and 21.
Example: You can use an FTP client to upload files to a website's server or download large files from an FTP server.

4. SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
Purpose: SMTP is used for sending and routing emails across networks.
Use Case: Sending emails from a client (e.g., Outlook or Gmail) to an email server or between email servers.
Ports: Default port 25 for unencrypted communication, 587 for encrypted communication (STARTTLS).
Example: When you send an email, SMTP handles the process of sending your email to its destination.

5.DNS (Domain Name System)
Purpose: DNS translates human-readable domain names (e.g., www.example.com) into IP addresses, allowing browsers and other software to connect to the appropriate server.
Use Case: Resolving domain names to IP addresses to access websites or services.
Ports: Default port53.
Example: When you type a URL into your web browser, DNS queries the appropriate server to get the IP address of the website you want to visit.

6.TELNET
Purpose: TELNET is used for accessing remote devices and servers over a network, typically in a command-line interface.
Use Case: Remote access and management of network devices or servers.
Ports: Default port 23.
Example: TELNET can be used to log into remote servers to configure network equipment or troubleshoot systems. However, it is insecure, so SSH is often preferred.

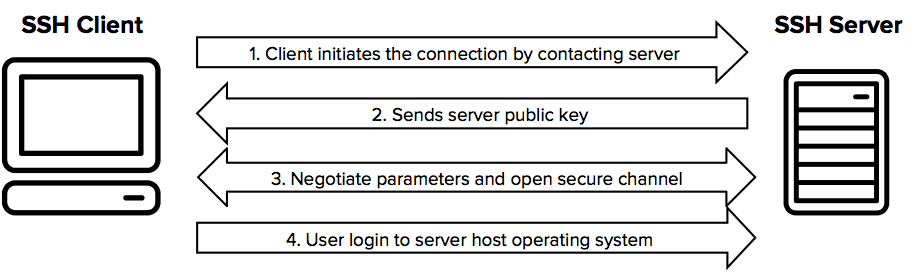
7.SSH (Secure Shell)
Purpose: SSH is a cryptographic network protocol used for secure communication between devices, allowing secure remote login and other network services.
Use Case: Secure remote access to servers and devices, typically used for system administration.
Ports: Default port 22.
Example: System administrators use SSH to remotely access and manage servers over a secure channel.
8.SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
Purpose: SNMP is used for managing and monitoring network devices, such as routers, switches, and servers.
Use Case: Collecting performance data, checking device status, and configuring devices remotely.
Ports: Default port 161 for sending requests and port 162 for receiving notifications (traps).
Example: Network administrators use SNMP to monitor the performance and status of routers and switches.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from ShirishaKuruva directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
