Optimizing AWS Resources with Auto Scaling Groups and RDS Replicas
 Rawad Hossain
Rawad HossainTable of contents

In this blog we’ll learn about Auto Scaling Groups (ASG), CloudWatch Alarms, which monitor metrics to trigger scaling actions. Also, we’ll cover Amazon RDS, Read Replicas and Multi-AZ deployments. Click here to read previous blogs.
Auto Scaling Group (ASG)
Let’s understand this by an example, suppose a live sports streaming platform broadcasts FIFA World Cup. During a usual day, user traffic is moderate. However, during match time or in a high voltage match in World Cup, millions of users worldwide simultaneously log in to watch live, this creates a sudden and massive spike in traffic.
To handle this sudden spike in traffic, AWS offers a service called Auto Scaling Group (ASG). It automatically adjusts the number of resources (EC2 instances) needed to manage the traffic demand. ASG ensures the right amount of computing power is available at any time, scaling up instances during high demand and scaling down during low demand. ASGs automatically register new instances with a load balancer and recreate an EC2 instance if a previous one is terminated. By dynamically adjusting the number of instances, ASGs optimize resource usage and reduce costs.

While launching an ASG, you can specify instance type, AMI, security groups, SSH Key Pair, Load Balancer Information, Min, Max, Initial Capacity, Scaling Policies and other settings for instances within the ASG.
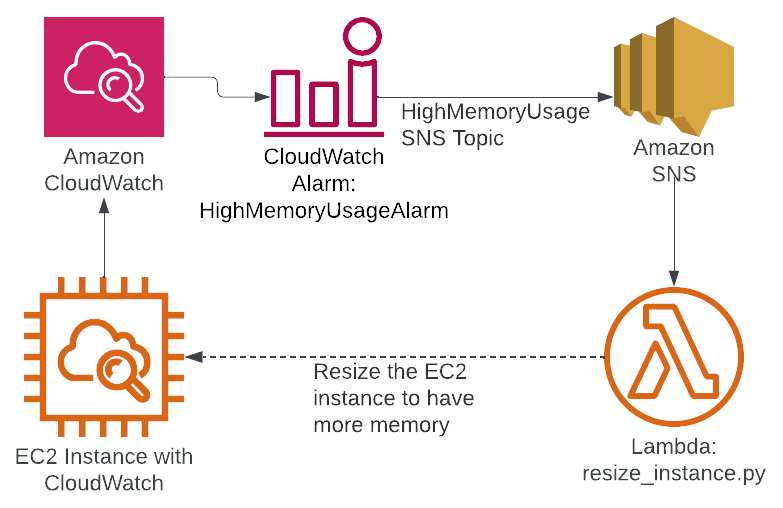
Now, how do we know when to scale up and when to scale down ASG upon traffic demand? For this, there is a trigger that sets alarm on some metrics. This monitoring service is known as CloudWatch Alarms.
CloudWatch Alarms
CloudWatch Alarms monitors and collects like CPU utilization, memory usage, and network traffic for your EC2 instances. As the alarms are triggered based on such specific metrics, you can set thresholds for these metrics. For example, if CPU utilization goes above 80% for a certain period, CloudWatch can trigger an alarm.
CloudWatch continuously monitors instance metrics within an ASG, and when a metric crosses its threshold, a scale-up action is triggered if traffic demand increases, adding instances to handle the load. Else, a scale-down action occurs if traffic decreases, reducing instances to save costs. This rigorous checking and scaling happen automatically based on demand.
Amazon RDS
RDS stands for Relational Database Service. It is a managed database service which allows to create databases in the cloud. This is significantly important to handle tasks like backup, recovery, patching, and scaling.
With RDS, you can scale storage and compute resources according to your needs, and this happens dynamically though you have to set a maximum storage limit for the database storage. It is useful for developers who want to focus on building applications instead of managing database infrastructure.
In Amazon RDS, there is a feature called RDS Read Replicas, which is a copy of your main database designed for read-only data. It helps manage extra traffic without overloading the main database.
RDS Read Replicas
Let's understand, suppose you want to visit a busy website with many visitors reading information at the same time. To prevent slowing down, you can create a read-only version of your database. This copy is called a Read Replica.
For each RDS database instance, you can create up to 15 read replicas. And it can be created within the same Availability Zone (AZ), across different AZ or even Cross Region.
RDS Read Replicas use asynchronous replication to distribute read traffic. That is, if any changes made to the main database, then asynchronously the changes are applied to the replicas as well. In terms of cost, Read Replicas within the same region are free. However, replicas across different regions are more expensive but effective for disaster recovery.
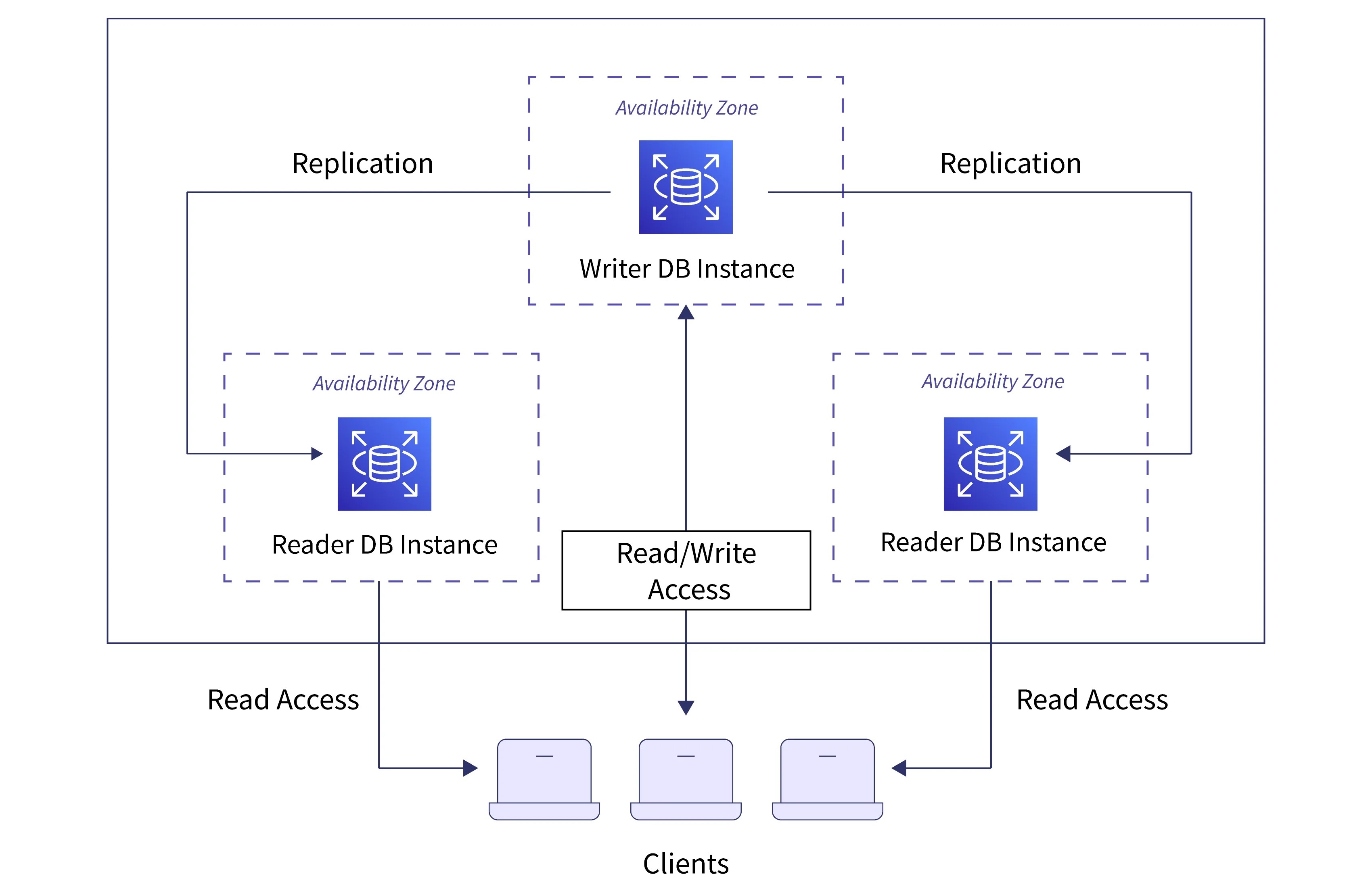
In order to convert RDS database from single AZ to a Multiple AZ, it can be done by clicking “Modify“ option in the console. For this, a snapshot of the main (primary) database can be made and then restored by the instance (standby databases) created in other AZ. Hence, RDS establishes synchronous replication between the primary and standby databases. By this database load is managed and high availability is ensured.

This is the end of this blog.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rawad Hossain directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
