AWS CodeDeploy
 Ashwin
Ashwin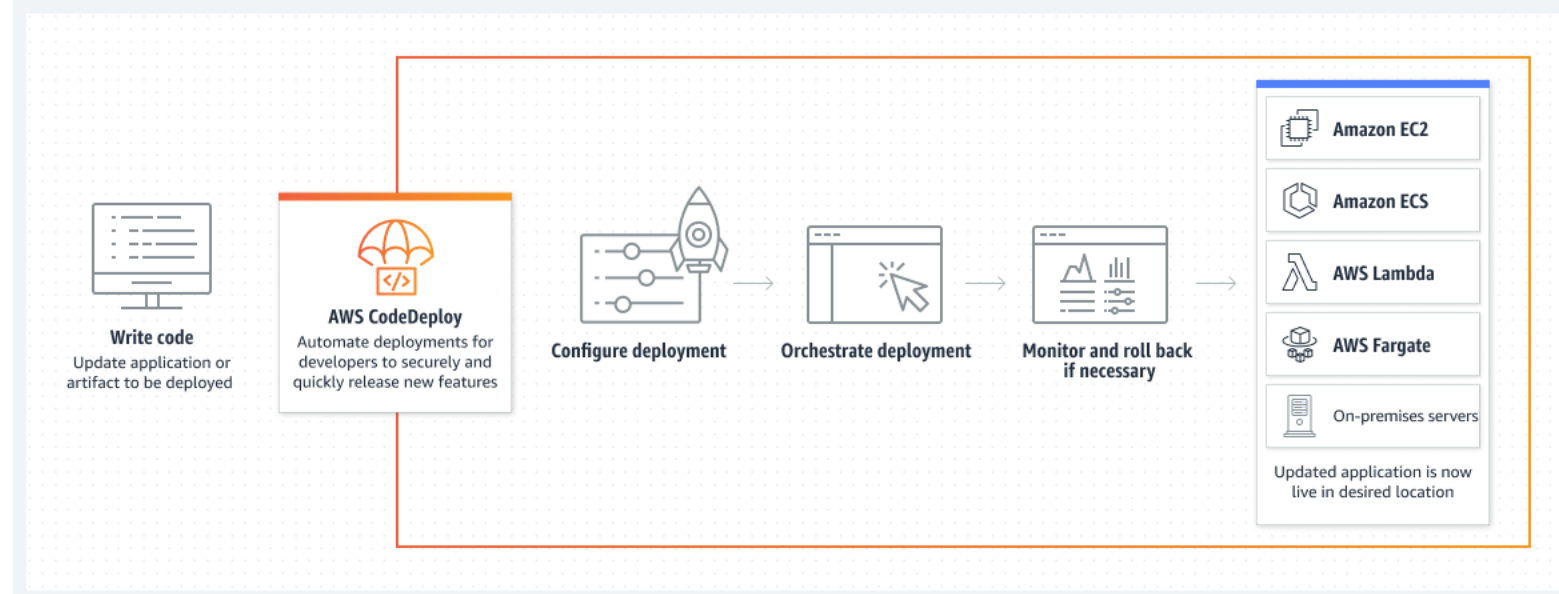
AWS CodeDeploy is a service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that automates the deployment of applications to instances, allowing for updates to be quickly and reliably pushed out to your infrastructure.
Here's a brief overview of how AWS CodeDeploy works:
1. Deployment Groups:
- Applications are organized into deployment groups within CodeDeploy. These groups can contain instances (virtual machines) or tags associated with instances in your AWS environment.
2. Deployment Configurations:
- CodeDeploy provides deployment configurations that specify how deployments should be executed, like the order of deployments, the number of instances to deploy simultaneously, and the actions to take during deployment.
3. Application Revisions:
- The deployment process in CodeDeploy relies on application revisions, which are sets of files and configuration settings for your application. These revisions are typically stored in Amazon S3 buckets or GitHub repositories.
4. Deployment Process:
When you initiate a deployment, CodeDeploy retrieves the application revision from the specified source (S3, GitHub, etc.).
Then it deploys the revision to the instances within the deployment group according to the specified deployment configuration.
5. Deployment Status:
- Throughout the deployment process, CodeDeploy monitors the instances, tracks the deployment progress, and reports the status back to the user.
Benefits of AWS CodeDeploy:
Automated Deployments: Reduces the manual effort required for deploying applications.
Rollback Functionality: Provides the ability to roll back to a previous version in case of issues.
Integration with Other AWS Services: Works seamlessly with other AWS tools like AWS CodePipeline, allowing for a more comprehensive CI/CD pipeline.
Deployment Flexibility: Supports deploying applications to various environments, including EC2 instances, AWS Lambda functions, on-premises servers, etc.
Use cases:
Automate deployments to remove manual operations
Repeat an application deployment across different groups or instances using a file and command-based install model.
Deploy to many hosts
Manage deployments to thousands of hosts with advanced monitoring and traffic shifting.
Use advanced deployment techniques
Support multiple deployment types, including in-place, canary, and blue/green deployments.
Monitor health and rollback
Configure alarms that will initiate rollbacks, and stop application deployments in progress.
Usage:
Console: AWS Management Console provides a graphical user interface to manage deployments.
CLI: AWS CLI allows users to perform CodeDeploy actions through command-line interfaces.
SDKs: AWS CodeDeploy provides SDKs for various programming languages to interact programmatically.
Example of code deployment:
Let's go through a simple example of deploying a web application using AWS CodeDeploy.
Pre-requisites:
AWS Account: You'll need an AWS account to access AWS services.
CodeDeploy IAM Role: Ensure you have the necessary IAM roles with appropriate permissions for CodeDeploy.
Sample Application: For this example, let's assume you have a simple web application stored in an Amazon S3 bucket as a
.zipfile.
Steps for Deployment:
1. Prepare Your Application
- Store your application code (e.g., a web app) in an S3 bucket, and create a
.zipfile containing the application code and necessary configuration files.
2. Create an Application in CodeDeploy Console
Go to the AWS Management Console > CodeDeploy.
Create a new application and deployment group.
Define the deployment configuration, specifying the S3 location of your application revision.
3. Set Up CodeDeploy Agent on Instances
Ensure your EC2 instances have the CodeDeploy agent installed and configured.
The agent is responsible for receiving deployment instructions from CodeDeploy and executing them on the instances.
4. Initiate Deployment
In the CodeDeploy console, select the deployment group and initiate the deployment.
CodeDeploy will pull the application revision from S3 and deploy it to the instances in the deployment group.
5. Monitor Deployment
Monitor the deployment progress in the CodeDeploy console.
You can check the status of the deployment and view logs to troubleshoot any issues.
Using AWS CLI:
Here's a simplified example of deploying an application using AWS CLI (assuming you have the necessary permissions and a prepared application revision in S3):
- Create Deployment:
aws deploy create-deployment --application-name MyApp --deployment-group-name MyDeploymentGroup --s3-location bucket=my-bucket,key=my-app.zip,bundleType=zip
- Monitor Deployment:
aws deploy get-deployment --deployment-id <DEPLOYMENT_ID>
Please note that this is a basic example, and actual deployments might involve more configurations, such as hooks for deployment validation, scripts for pre/post-deployment tasks, custom configurations, etc.
Some Important Questions
What is AWS CodeDeploy?
AWS CodeDeploy is a fully managed deployment service that automates software deployments to a variety of compute platforms, including Amazon EC2 instances, AWS Lambda functions, and on-premises servers.
How does CodeDeploy work?
CodeDeploy coordinates application deployments by pushing code changes to instances, managing deployment lifecycle events, and rolling back deployments if necessary.
What are the deployment strategies supported by CodeDeploy?
CodeDeploy supports various deployment strategies, including Blue-Green, In-Place, and Canary. Each strategy determines how new code versions are rolled out to instances.
Explain the Blue-Green deployment strategy in CodeDeploy.
In Blue-Green deployment, two identical environments (blue and green) are set up. New code is deployed to the green environment, and after successful testing, traffic is switched from the blue to the green environment.
How does CodeDeploy handle rollbacks?
If a deployment fails or triggers alarms, CodeDeploy can automatically roll back to the previous version of the application, minimizing downtime and impact.
Can you use CodeDeploy for serverless deployments?
Yes, CodeDeploy can be used to deploy AWS Lambda functions. It facilitates smooth updates to the Lambda function code without service interruption.
What is an Application Revision in CodeDeploy?
An Application Revision is a version of your application code that is deployed using CodeDeploy. It can include application files, configuration files, and scripts necessary for deployment.
How can you integrate CodeDeploy with your CI/CD pipeline?
CodeDeploy can be integrated into your CI/CD pipeline using services like AWS CodePipeline. After successful builds, the pipeline triggers CodeDeploy to deploy the new version.
What is a Deployment Group in CodeDeploy?
A Deployment Group is a set of instances or Lambda functions targeted for deployment. It defines where the application should be deployed and how the deployment should be executed.
How can you ensure zero downtime during application deployments?
Zero downtime can be achieved by using strategies like Blue-Green deployments or Canary deployments. These strategies allow you to gradually shift traffic to the new version while testing its stability.
Explain how you can manage deployment configuration in CodeDeploy.
Deployment configuration specifies parameters such as deployment style, traffic routing, and the order of deployment lifecycle events. It allows you to fine-tune deployment behavior.
How can you handle database schema changes during deployments?
Database schema changes can be managed using pre- and post-deployment scripts. These scripts ensure that the database is properly updated before and after deployment.
Describe a scenario where you would use the Canary deployment strategy.
You might use the Canary strategy when you want to gradually expose a new version to a small portion of your users for testing before rolling it out to the entire user base.
How does CodeDeploy handle instances with different capacities?
CodeDeploy can automatically distribute the new version of the application across instances with varying capacities by taking into account the deployment configuration and specified traffic weights.
What are hooks in CodeDeploy?
Hooks are scripts that run at various points in the deployment lifecycle. They allow you to perform custom actions, such as validating deployments or running tests, at specific stages.
How does CodeDeploy ensure consistent deployments across instances?
CodeDeploy uses an agent on each instance that manages deployment lifecycle events and ensures consistent application deployments.
What is the difference between an EC2/On-Premises deployment and a Lambda deployment in CodeDeploy?
An EC2/On-Premises deployment involves deploying code to instances, while a Lambda deployment deploys code to Lambda functions. Both utilize CodeDeploy's deployment capabilities.
How can you monitor the progress of a deployment in CodeDeploy?
You can monitor deployments using the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or AWS SDKs. CodeDeploy provides detailed logs and metrics to track the status and progress of deployments.
Can CodeDeploy deploy applications across multiple regions?
Yes, CodeDeploy can deploy applications to multiple regions. However, each region requires its own deployment configuration and setup.
What is the role of the CodeDeploy agent?
The CodeDeploy agent is responsible for executing deployment instructions on instances. It communicates with the CodeDeploy service and manages deployment lifecycle events.

Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ashwin directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Ashwin
Ashwin
I'm a DevOps magician, conjuring automation spells and banishing manual headaches. With Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes in my toolkit, I turn deployment chaos into a comedy show. Let's sprinkle some DevOps magic and watch the sparks fly!