Understanding Daemon Sets and Replicasets in the World of Kubernetes
 Sachin Adi
Sachin Adi
A little story…
Two colleagues, Sachin and Rahul, are discussing Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets, crucial parts of Kubernetes.


Introduction to Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets
Kubernetes has revolutionized how we deploy and manage applications in the cloud, making container orchestration more efficient than ever. Among its many features, two concepts stand out: Daemon Sets and Replica Sets. While both play crucial roles in managing workloads within Kubernetes clusters, they serve different purposes that can dramatically impact your deployment strategy.
Imagine you are running a system where certain tasks need to be executed on every node while others require multiple instances spread across nodes for load balancing. This is where understanding these two powerful mechanisms becomes vital. Whether you're an experienced developer or just starting your journey with Kubernetes, grasping the differences between Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets will enhance your ability to optimize application performance effectively.
Ready to dive deeper into these essential components of Kubernetes? Let’s explore what makes Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets unique!
Understanding Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets in Kubernetes
In the Kubernetes ecosystem, Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets are vital for managing workloads efficiently. They serve distinct purposes that cater to different application needs.
Daemon Sets ensure that a specific pod runs on all or selected nodes in a cluster. This is ideal for tasks like logging, monitoring, or other node-specific services. With Daemon Sets, you can guarantee that critical services operate consistently across your entire infrastructure.
On the other hand, ReplicaSets focus on maintaining a defined number of pod replicas across the cluster. Their primary goal is to enhance availability and load balancing by ensuring multiple instances of an application run simultaneously.
By understanding these two concepts better, users can make informed decisions about deploying and scaling their applications effectively within a Kubernetes environment. Both provide unique capabilities that contribute significantly to operational efficiency and reliability.
The Purpose and Functionality of Daemon Sets
Daemon Sets in Kubernetes serve a crucial role by ensuring that specific pods are running on every node within a cluster. This is particularly beneficial for applications requiring access to the underlying hardware, such as logging agents or monitoring tools.
When you create a Daemon Set, Kubernetes automatically manages the deployment of these pods across all nodes. If a new node joins the cluster, the Daemon Set instantly provisions its corresponding pod on that node.
This functionality simplifies administration and provides consistent service availability throughout your environment. It allows for efficient resource utilization while maintaining uniformity in application behavior across different servers.
Moreover, Daemon Sets can be configured to run on selected nodes only, offering flexibility tailored to varying use cases. The inherent design facilitates seamless updates and scaling without affecting existing workloads drastically.
The Purpose and Functionality of ReplicaSets

ReplicaSets play a crucial role in Kubernetes by ensuring that a specified number of pod replicas are running at any given time. This is essential for maintaining application availability and reliability.
When you deploy an application, the ReplicaSet automatically creates and manages pods based on your defined specifications. If any pod fails or goes down, the ReplicaSet quickly spins up new instances to replace them.
This self-healing mechanism helps maintain a consistent user experience, even during unexpected issues. Additionally, it allows for seamless scaling; you can adjust the desired number of replicas according to demand with simple commands.
Moreover, ReplicaSets work hand-in-hand with Deployments, which provide a higher-level management approach for updates and rollbacks while leveraging the underlying functionality of ReplicaSets to ensure smooth operation.
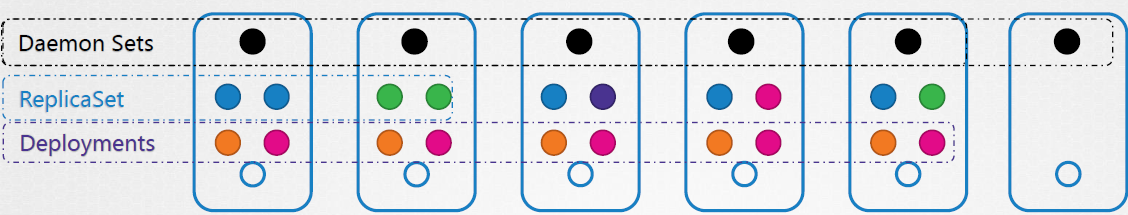
The architecture of Replicasets and DaemonSets

Key Differences Between Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets

Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets serve distinct roles in Kubernetes, tailored for different scenarios. A Daemon Set ensures that a specific pod runs on every node within the cluster. This is crucial for workloads like logging or monitoring, where consistent access to all nodes is necessary.
In contrast, ReplicaSets focus on maintaining a defined number of identical pods across the cluster. They help ensure high availability and load balancing by automatically replacing any failed pod instances.
The key difference lies in their deployment strategy: while Daemon Sets are designed for single-instance tasks per node, ReplicaSets scale horizontally to meet demand. Understanding this distinction helps administrators optimize resource allocation effectively.
There is a simple diagram to show the key differences.
Source: Medium article reference from Taha Mashhadi
Use Cases for Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets in Kubernetes


Daemon Sets are particularly useful for running background services on every node in a Kubernetes cluster. Think of logging agents or monitoring tools that need to gather metrics from each machine. With Daemon Sets, you ensure these applications run consistently across all nodes.
On the other hand, ReplicaSets excel at maintaining the desired number of pod replicas for your application. They automatically handle scaling and failover scenarios. For example, if one pod crashes due to overload, a ReplicaSet will quickly spin up another instance to maintain resilience.
In high-traffic environments, using both can yield impressive results. A Daemon Set can manage log collection while ReplicaSets ensure your web servers remain responsive under load.
These concepts work together seamlessly, allowing developers flexibility in their deployments and ensuring optimal resource utilization throughout the cluster.
Implementation and Best Practices for Using Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets
When implementing Daemon Sets, ensure that you clearly define the node selectors. This helps to limit which nodes will run your pods, thereby optimizing resource usage.

Always monitor the performance of each Daemon Set pod. Tools like Prometheus can be beneficial for tracking metrics and identifying bottlenecks in real-time.
For ReplicaSets, focus on setting an appropriate number of replicas based on traffic loads and application requirements. Start small and scale as needed; it’s easier than downscaling later.
Utilize health checks effectively to maintain reliability within your ReplicaSets. Liveness and readiness probes can automatically restart or manage pods that aren’t functioning optimally.
Version control is crucial for both concepts. Use annotations to track changes over time, making rollbacks smoother if necessary.
Some Sample scripts
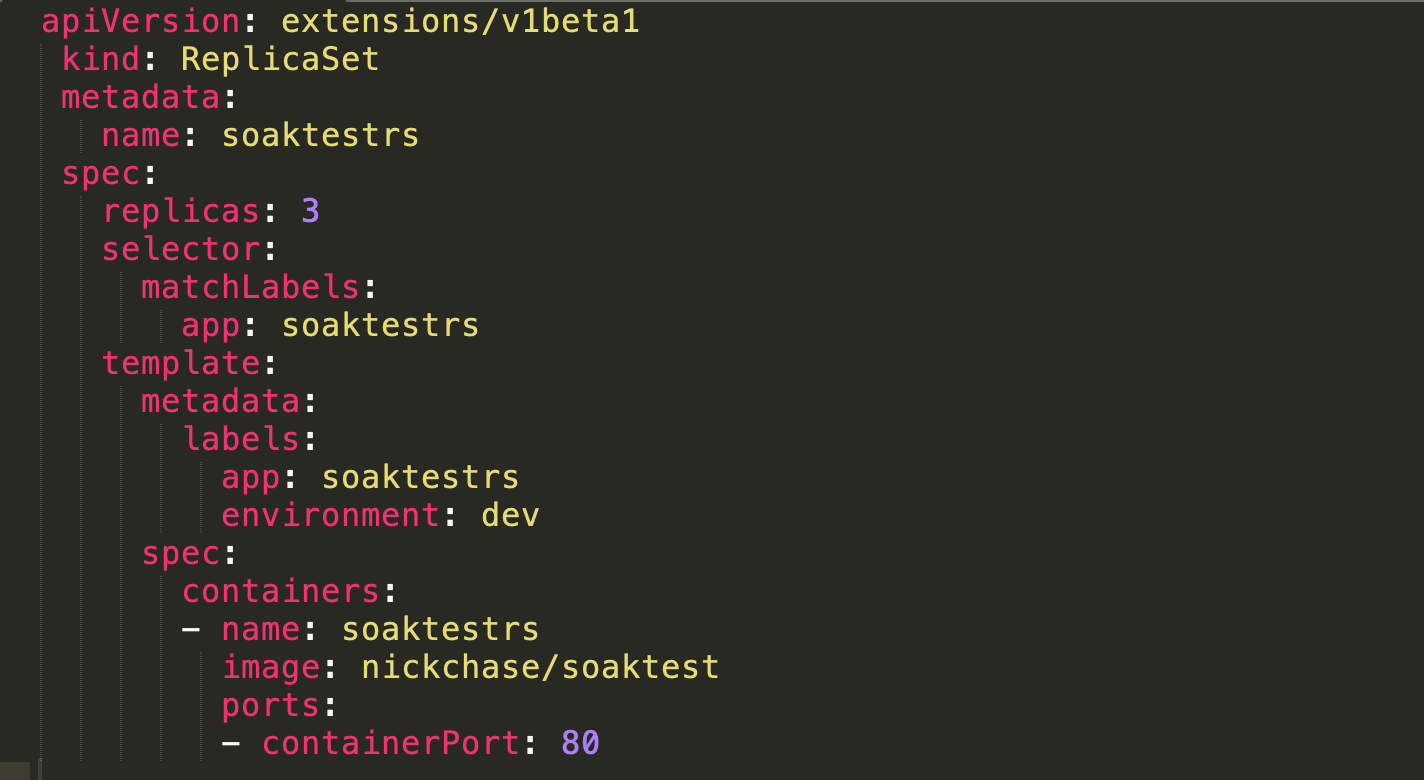
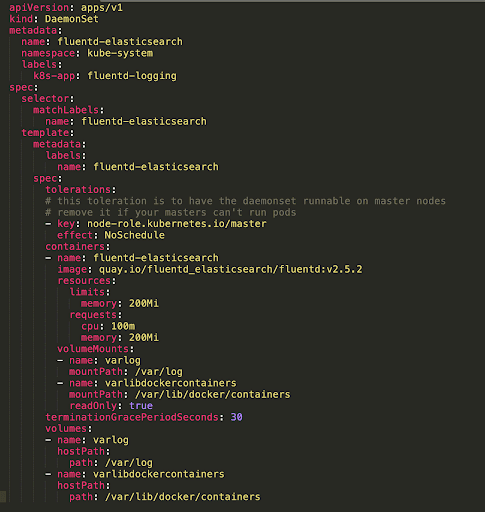
Future Developments in the World of Kubernetes with These Concepts
The future of Kubernetes is bright, especially when it comes to Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets. With the continuous evolution of cloud-native technologies, these concepts are set to become even more sophisticated.
Improvements in orchestration capabilities will enhance resource management across clusters. This means that Daemon Sets could see better optimization for specific node types, ensuring essential services run where they are needed most.
Meanwhile, ReplicaSets may evolve with smarter scaling options. Integrating machine learning algorithms can help predict workload fluctuations and adjust pod counts dynamically.
As security becomes a priority, enhancements around access controls for both Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets will likely emerge. This focus can offer tighter integration with existing security frameworks within Kubernetes.
Innovations in observability tools promise deeper insights into how these sets function within complex environments. Real-time analytics will empower developers to make informed decisions quickly.
Conclusion
Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets are essential components of Kubernetes, each serving unique purposes. Understanding their functionalities can significantly enhance the efficiency of your containerized applications.
When you need to run a specific pod on every node, Daemon Sets come into play. They ensure that necessary services like logging or monitoring agents are consistently available across all nodes in the cluster. This capability makes them invaluable for maintaining system-wide operations.
On the other hand, ReplicaSets provide redundancy by ensuring a specified number of identical pods are running at any given time. This is particularly useful for load balancing and scaling applications seamlessly without downtime.
The differences between these two concepts lie not only in their operational focus but also in their use cases. While Daemon Sets cater to node-specific tasks, ReplicaSets manage application availability more broadly across multiple instances.
Both have distinct roles within Kubernetes environments but often complement one another effectively. As organizations continue to adopt Kubernetes for managing microservices architectures, understanding when and how to implement these resources will become increasingly critical.
Looking ahead, advancements in Kubernetes may lead to even more refined ways of managing workloads with Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets. Staying informed about emerging trends will help teams make better decisions regarding deployment strategies and resource management.
Embracing both Daemon Sets and ReplicaSets empowers developers to create resilient applications capable of meeting various demands within dynamic environments like Kubernetes. Their effective implementation is key to achieving optimal performance while maximizing resource utilization throughout your infrastructure.


As I always say, these articles can be basic or be written for understanding. If you have any feedback, feel free to share them so that I can better the articles and my knowledge too.. Happy learning!!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sachin Adi directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
