Day-01 Introduction: Machine Learning
 Mohit Meshram
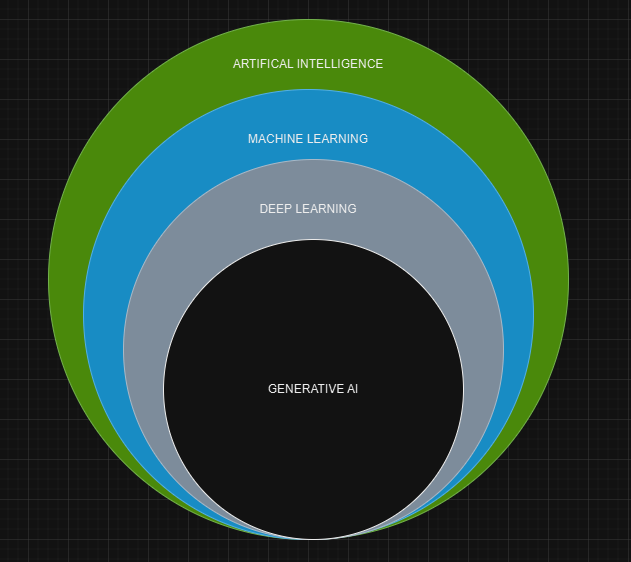
Mohit MeshramMachine learning is a type of artificial intelligence that allows computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. It's like teaching a computer to learn from experience, just like humans do.
How does it work?
Data Collection: Gather a large amount of data relevant to the task you want the machine to learn.
Data Preparation: Clean and organize the data to make it suitable for analysis.
Model Selection: Choose an appropriate machine learning algorithm based on the nature of the problem and the data.
Model Training: Feed the prepared data into the chosen algorithm, allowing it to identify patterns and relationships.
Model Evaluation: Assess the model's performance on a separate set of data to measure its accuracy.
Model Deployment: Once satisfied with the model's accuracy, deploy it to make predictions or decisions on new, unseen data.
Types of Machine Learning:
Supervised Learning: The algorithm is trained on labeled data, where the correct output is provided for each input.
Unsupervised Learning: The algorithm learns patterns from unlabeled data without explicit guidance.
Reinforcement Learning: The algorithm learns by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties for its actions.
Generative Learning: Generative learning is a type of machine learning approach focused on modeling the underlying distribution of data to generate new, synthetic examples that resemble the original dataset.
Unlike discriminative models, which focus on distinguishing between classes (e.g., determining if an image is a cat or dog), generative models aim to understand the full distribution of the data, allowing them to create new samples from scratch.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mohit Meshram directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
