Smart Contracts: Transforming Traditional Contracts
 Kehinde Sodiq
Kehinde SodiqTHE IMPACT OF SMART CONTRACTS ON THE INDUSTRIES LIKE FINANCE, REAL ESTATE AND SUPPLY CHAINS.
What are Smart Contracts?
A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement written directly into code. It operates on blockchain technology, automatically enforcing and executing transactions without intermediaries.
Objective:
Explore how smart contracts are revolutionizing industries by providing transparency, efficiency, and automation.
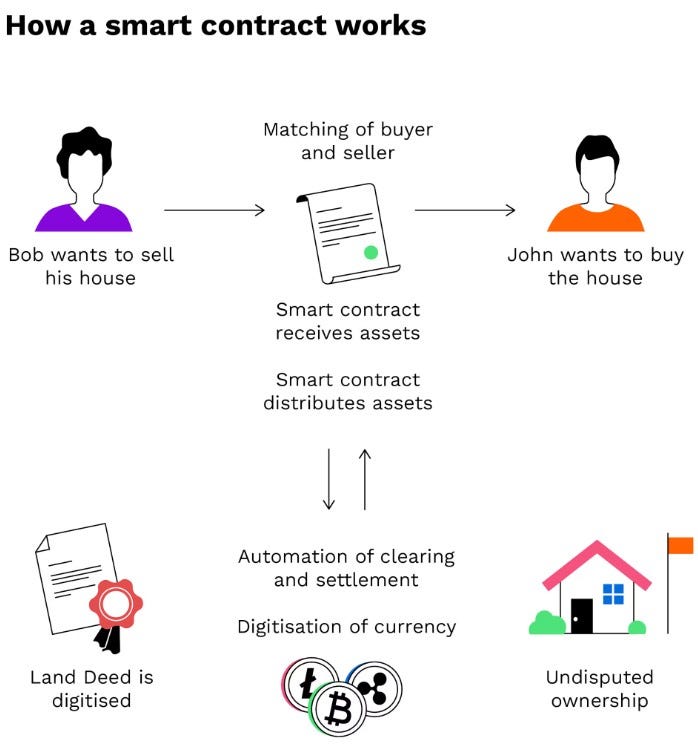
Traditional Contracts vs. Smart Contracts
Traditional Contracts:
<> Relies on manual processes and intermediaries (lawyers, banks).
<> Prone to delays, human errors, and high costs.
<> Requires trust between parties.
Smart Contracts:
<> Code-based, decentralized, and self-executing.
<> Faster, transparent, and cost-effective.
<> Reduces the need for intermediaries and minimizes risks of fraud or dispute.

Impact on Finance
Key Features:
<> Automated Payments & Settlements: Faster, real-time execution of financial transactions.
<> Reduced Costs: Eliminates middlemen like banks, lowering fees.
<> Increased Security: Transactions are encrypted and immutable on the blockchain.
Examples in Finance:
<> Peer-to-peer lending platforms
<> Decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems
<> Insurance claim automation
Impact on Real Estate
Key Features:
<> Property Ownership: Smart contracts enable digital title transfers and ownership tracking.
<> Escrow Automation: Funds are held in escrow and released automatically when conditions are met.
<> Faster Transactions: Real estate transactions are streamlined, reducing time for property sales.
Examples in Real Estate:
<> Tokenization of property assets
<> Digital contracts for rent agreements
<> Automated escrow services
Impact on Supply Chains
Key Features:
Enhanced Traceability: Tracks goods in real time from manufacturer to end-user.
Automated Payments: Payments are released automatically when delivery conditions are met.
Improved Transparency: All participants can see the status of goods and transactions.
Examples in Supply Chains:
Food safety tracking
Anti-counterfeiting measures for luxury goods
Reducing paperwork and manual processes

Case Study: Smart Contracts in Supply Chains
Example:
Walmart’s Food Safety Initiative: Smart contracts used to track the provenance of food products, ensuring safety and transparency in the supply chain.
Outcome: Faster recall processes, improved food safety, and reduced inefficiencies.
Challenges and Considerations
Legal and Regulatory Challenges: How do existing legal frameworks accommodate smart contracts?
Security Risks: Smart contracts are immutable, so coding errors can be exploited.
Adoption Barriers: Industries with established traditional systems may resist switching to blockchain solutions.
Conclusion
Summary:
Smart contracts are transforming industries by automating processes, reducing costs, and enhancing transparency. Their potential is vast, but legal and adoption challenges remain.
Call to Action:
For businesses, exploring the adoption of smart contracts could lead to greater efficiency, security, and innovation in their operations.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Kehinde Sodiq directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Kehinde Sodiq
Kehinde Sodiq
Software Developer | | Blockchain Developer | | Web3 Technical Writer | | DLTAfrica | | Coding enthusiast | | Lifelong learner