Understanding AWS CloudTrail: A Comprehensive Guide
 Aditya Gadhave
Aditya Gadhave
What is AWS CloudTrail?
WS CloudTrail is a service that enables governance, compliance, and operational and risk auditing of your AWS account.
It records and logs every API call made on your AWS account, capturing details such as the identity of the API caller, the time of the API call, the source IP address, the request parameters, and the response elements returned by the AWS service.
CloudTrail provides three ways to record events:
Event History:
Your AWS account has Cloud Trail activated by default, and you have immediate access to the Cloud Trail event history.
A viewable, searchable, printable, and immutable record of the last 90 days’ worth of management events in an AWS Region is available in the Event history.
The AWS Management Console, AWS Command Line Interface, and AWS SDKs and APIs are all used to perform the activities that these events record.
The AWS Region where the event occurred is documented in the Event history. The Event history can be seen for free on Cloud Trail.
Cloud Trail Lake:
A managed data lake called AWS Cloud Trail Lake is used to record, store, access, and analyze user and API activity on AWS for audit and security reasons.
Existing events in row-based json format are converted to Apache ORC format by Cloud Trail Lake.
A columnar storage format called ORC is designed for quick data retrieval.
Event data stores, which are immutable collections of events based on criteria you choose by using sophisticated event selectors, aggregate events into immutable collections.
The event data can be kept in an event data storage for a maximum of seven years (2557 days).
Trails:
In addition to delivering and storing events in an Amazon S3 bucket, Trails can also deliver events to Amazon Cloud Watch Logs and the Amazon Event Bridge.
These occurrences can be entered into your security monitoring programs.
You may also search and examine your Cloud Trail logs using custom third-party programs or programs like Amazon Athena.
AWS CloudTrail Architecture
AWS Account is created in the AWS environment in the diagram above. When a new account is created, Cloud Trail is activated. An API call is made in the Back End whenever we carry out any operation using an AWS account, such as signing in, creating and deleting EC2 instances**,** creating S3 buckets, and uploading data into them. An API request is made on the backend when the activity occurs.
The activities that we carry out with our AWS Account can be carried out in a variety of ways. For instance, we can use the account with the aid of the AWS CLI (AWS – Command-line Interface), and we can also carry out the activity using the SDK (Software Development Kit) or AWS Management Console.
We may use any method here, and by using that method, whenever we execute an activity from the account, the backend API is called. When the backend API is called, an event is generated, and the event log is saved in the Cloud Trail. Only when we carry out any activity using an AWS Account does an event get created in Cloud Trail.
The AWS account activity we perform lasts for 90 days in the same place. It is possible to keep event logs in an S3 bucket for longer than 90 days. SNS notification (Simple Notification Service) configuration is also possible in Cloud Trail.

How does AWS CloudTrail Work?
Your Amazon Web Services (AWS) account’s activity is tracked and recorded by the AWS CloudTrail service. It offers thorough logs of all API calls and operations made on your AWS resources. This is how AWS CloudTrail functions:
Data Collection: Activity in your AWS account is regularly monitored by CloudTrail. An API call is created whenever an AWS service or resource is used or updated.
Log Storage: You can define an Amazon S3 bucket where these log entries will be gathered and stored. For your CloudTrail logs, you may set the bucket’s location and retention time.
Access Control: Policies set forth by AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) govern who has access to CloudTrail logs. Who is permitted to read, write, or administer CloudTrail logs can be specified.
Alerting and Notifications: You can configure in-the-moment alerts based on particular occurrences or trends in your CloudTrail logs using CloudWatch Alarms. This enables you to react rapidly to operational or security incidents.
Log Generation: Each time an API is called, CloudTrail creates a log entry with information on the caller, the action taken, the resource used, and the timestamp.
AWS CloudTrail features
Comprehensive Logging: Captures detailed logs of API calls and activities across AWS services, providing visibility into actions taken by users, applications, or AWS services.
Audit and Compliance: Facilitates compliance auditing by tracking changes to resources and enabling forensic analysis of security incidents through comprehensive logging.
Integration with AWS Services: Integrates seamlessly with other AWS services like AWS Lambda**,** S3, CloudWatch Logs, and CloudWatch Events for advanced monitoring and automated responses to events.
Multi-Account and Multi-Region Support: Supports logging and centralized management across multiple AWS accounts and regions, providing a unified view of activity across complex AWS environments.
Event History and Insights: Provides event history timelines and insights into API activity trends, enabling operational troubleshooting, security analysis, and operational intelligence.
Accessing CloudTrail
Accessing AWS CloudTrail Using These Methods:
AWS Management Console: Access via web browser, navigate to CloudTrail service, configure trails, view logs, and perform basic analysis.
AWS CLI: Use commands like aws cloudtrail create-trail, aws cloudtrail describe-trails, and aws cloudtrail lookup-events to manage trails, retrieve event history, and perform automated tasks.
AWS SDKs: Integrate CloudTrail into your applications using SDK functions to programmatically manage trails, retrieve and process event data, and incorporate CloudTrail insights into application logic.
AWS CloudTrail API: Develop custom applications or scripts that interact directly with CloudTrail API endpoints to automate tasks, perform complex queries, and integrate CloudTrail data into external systems or reporting tools.
AWS CloudTrail Use cases
Security and Compliance Monitoring: Monitor API calls and actions across AWS services to detect unauthorized access, changes to resources, and potential security breaches. CloudTrail logs provide detailed visibility for compliance audits and regulatory requirements.
Operational Troubleshooting: Investigate operational issues by reviewing CloudTrail logs to understand the sequence of events leading to errors or unexpected behavior in your AWS environment. Helps in identifying root causes and improving system reliability.
Change Management and Auditing: Track changes made to AWS resources over time, including configuration changes, deployments, and updates. CloudTrail logs enable auditing of resource history, aiding in change management and maintaining configuration integrity.
Incident Response and Forensics: Use CloudTrail logs during incident response to reconstruct events, analyze the scope of an incident, and identify impacted resources. Facilitates forensic investigation and timely resolution of security or operational incidents.
Governance and Accountability: Establish accountability by logging actions performed by users, applications, or AWS services. CloudTrail provides a trail of actions taken, helping organizations enforce governance policies and maintain accountability across AWS accounts.
Step by Step Implementation of AWS Cloudtrail :
Open CloudTrail Service
Click on Services and search for “CloudTrail
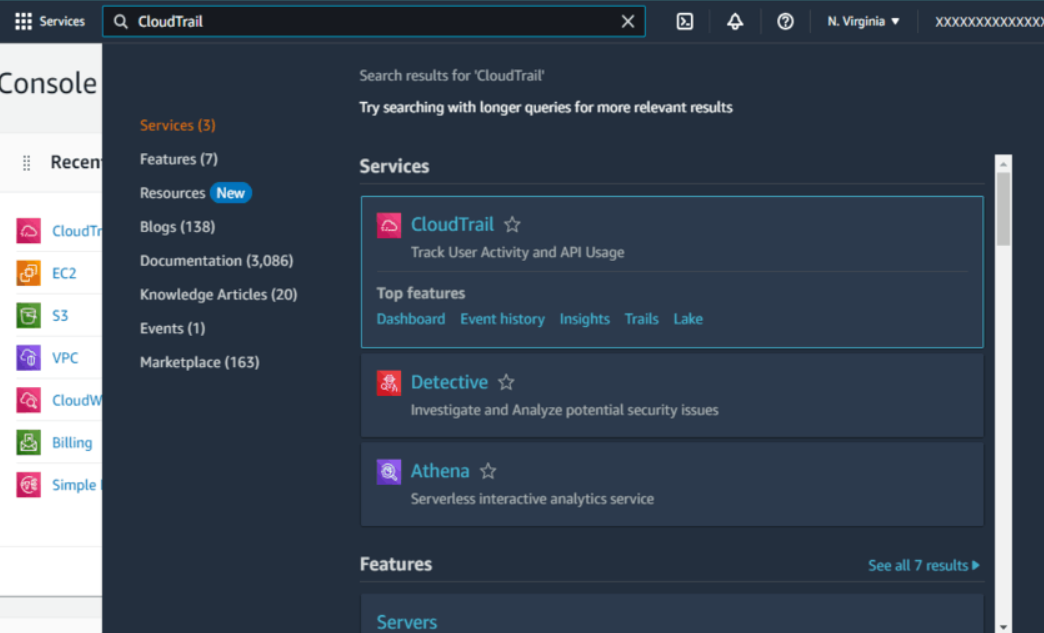
Create CloudTrail
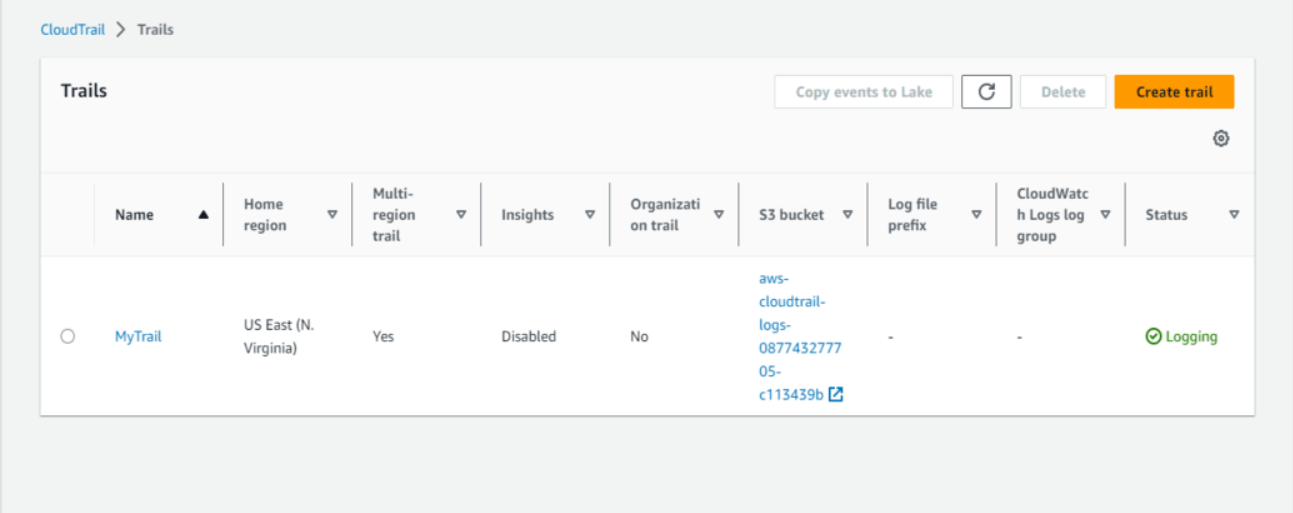
- Select “Create CloudTrail”, name it as “MyTrail”.
Edit Storage Location
- Click on the created “MyTrail” and edit the storage location. Choose “Create new S3 bucket” and save changes.
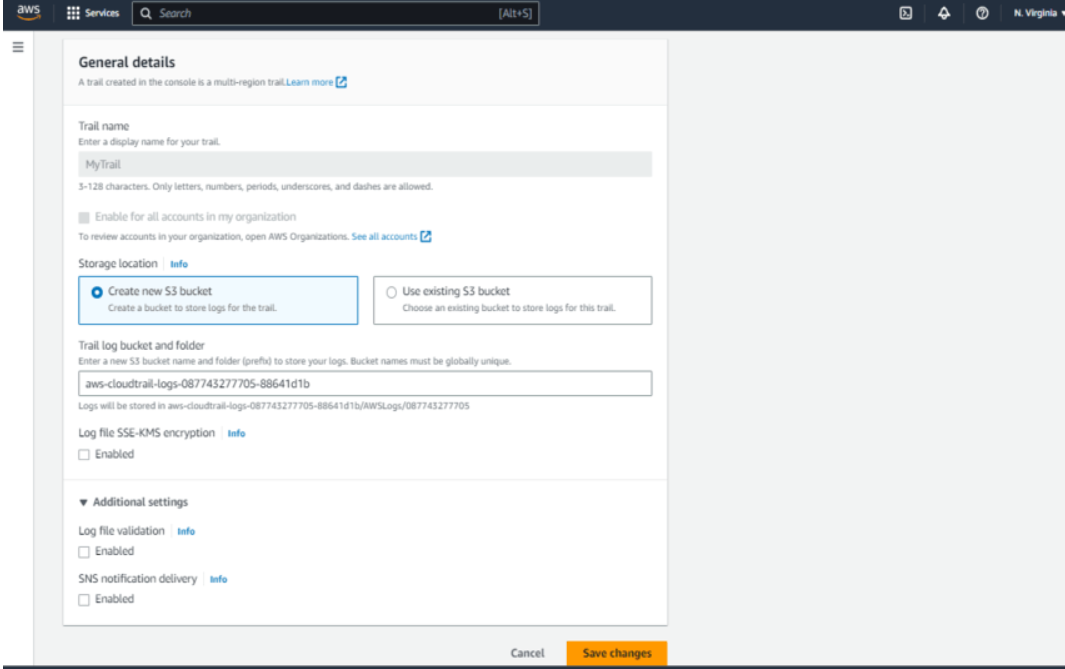
Save Changes
- Confirm and save changes to finalize the S3 bucket configuration.
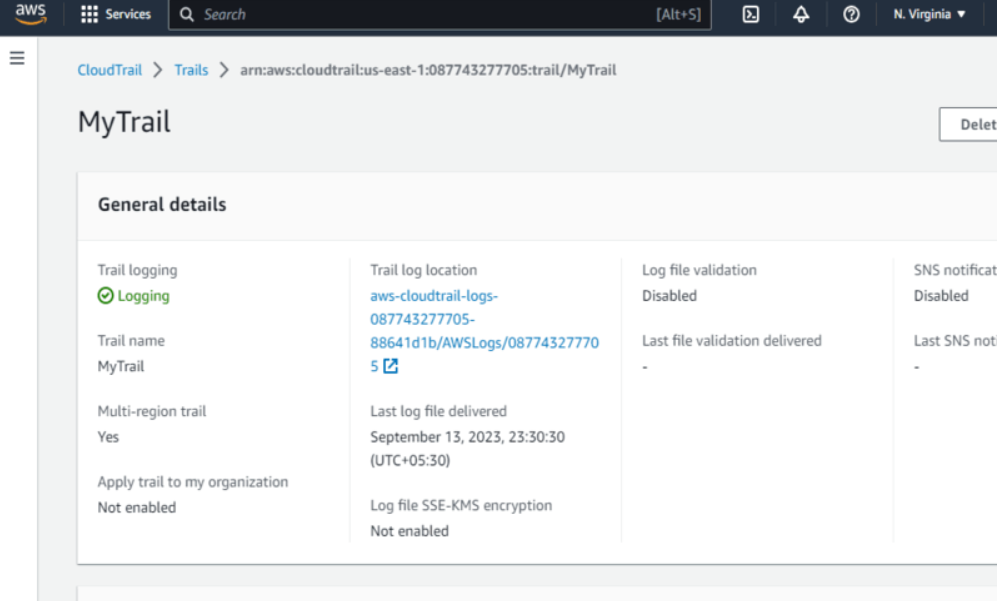
Confirm Settings
- Ensure data events are configured to deliver to the AWS CloudTrail console, Amazon S3 buckets, and optionally Amazon CloudWatch Logs.
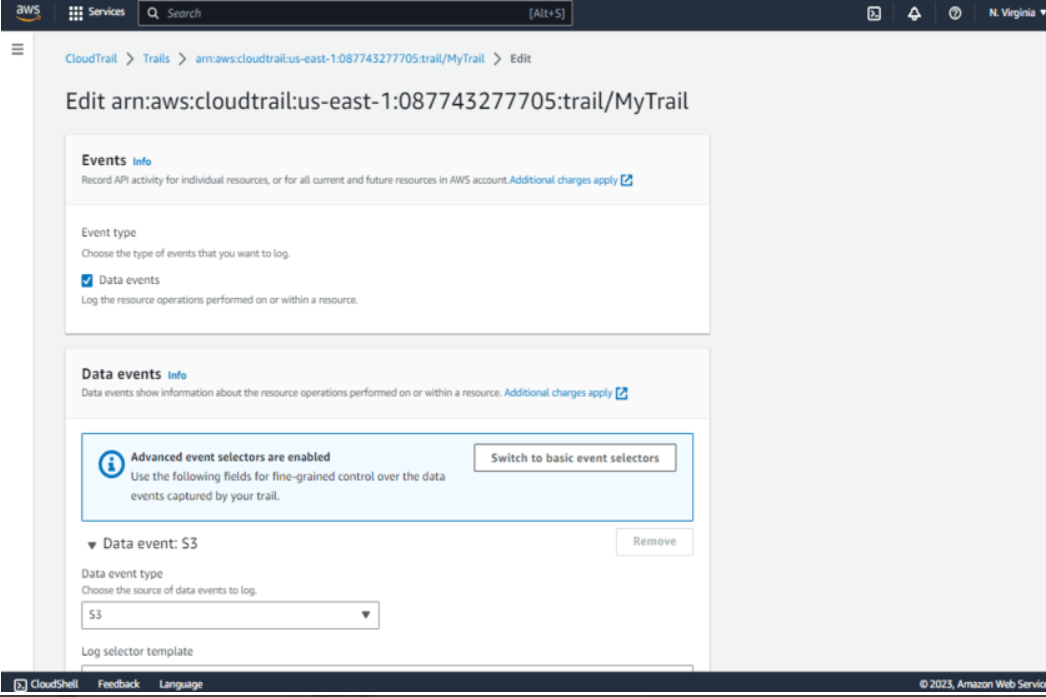
Monitor Data Events
- Data events are automatically stored in the designated S3 bucket.
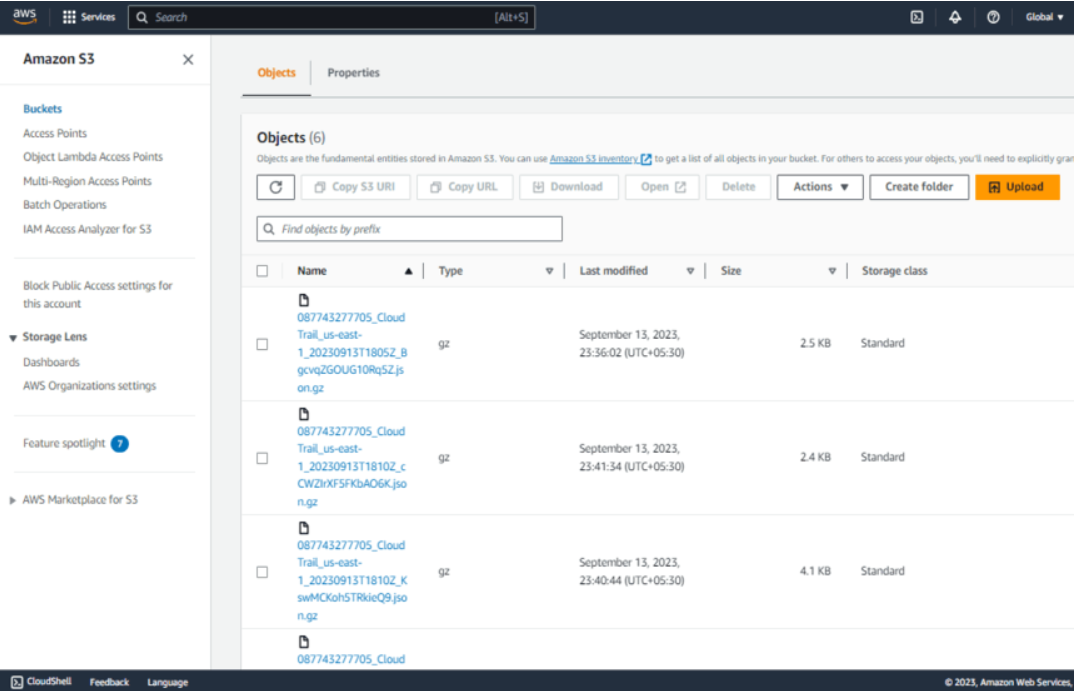
Conclusion:
AWS CloudTrail is a key service for governance, compliance, and auditing within AWS. By recording API calls and user activity, CloudTrail provides a history of account actions, which can be essential for identifying security issues, managing risk, and ensuring compliance.
If you have any questions, need clarifications, or want to discuss anything related to AWS technologies, feel free to reach out to me on LinkedIn. Connect with me at Aditya Gadhave, and I'll be more than happy to assist you. 😊
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aditya Gadhave directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aditya Gadhave
Aditya Gadhave
👋 Hello! I'm Aditya Gadhave, an enthusiastic Computer Engineering Undergraduate Student. My passion for technology has led me on an exciting journey where I'm honing my skills and making meaningful contributions.