History of Android
 Dilip Patel
Dilip PatelTable of contents

Introduction
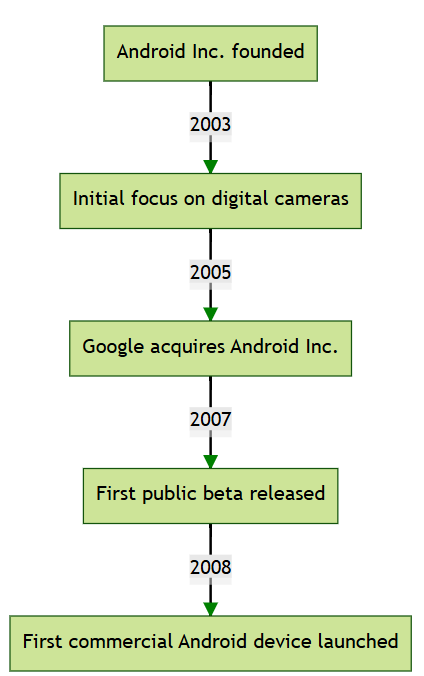
The history of Android begins in October 2003 when Android Inc. was founded by Andy Rubin, Rich Miner, Nick Sears, and Chris White in Palo Alto, California. Initially, the company aimed to develop an operating system for digital cameras, but soon shifted focus to mobile phones. In 2005, Google acquired Android Inc., and the team continued to develop the OS under Google's ownership. The first public beta of Android was released on November 5, 2007, and the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream (also known as the T-Mobile G1), was launched in September 2008.
Android version history
The version history of the Android mobile operating system began with the public release of its first beta on November 5, 2007. The first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released on September 23, 2008. The operating system has been developed by Google on a yearly schedule since at least 2011. New major releases are announced at Google I/O in May along with beta testing, with the stable version usually released to the public between August and October.
The first public release of Android 1.0 occurred with the release of the T-Mobile G1 (aka HTC Dream) in October 2008. Android 1.0 and 1.1 were not released under specific code names. The code names "Astro Boy" and "Bender" were tagged internally on some of the early pre-1.0 milestone builds and were never used as the actual code names of the 1.0 and 1.1 releases of the OS.
The project manager, Ryan Gibson, conceived using a confectionery-themed naming scheme for public releases, starting with Android 1.5 Cupcake. Google announced in August 2019 they were ending the confectionery theming scheme to use numerical ordering for future versions. The first release under the numerical order format was Android 10, which was released in September 2019.
| Name | Internal Codename | Version Number | API Level | Release Date | Latest Security Patch Date | Latest Google Play Services Version |
| Android 1.0 | — | 1.0 | 1 | September 23, 2008 | — | — |
| Android 1.1 | Petit Four | 1.1 | 2 | February 9, 2009 | — | — |
| Android Cupcake | Cupcake | 1.5 | 3 | April 27, 2009 | — | — |
| Android Donut | Donut | 1.6 | 4 | September 15, 2009 | — | — |
| Android Eclair | Eclair | 2.0 – 2.1 | 5 – 7 | October 27, 2009 | — | — |
| Android Froyo | Froyo | 2.2 – 2.2.3 | 8 | May 20, 2010 | October 2014 | — |
| Android Gingerbread | Gingerbread | 2.3 – 2.3.7 | 9 – 10 | December 6, 2010 | November 2016 | — |
| Android Honeycomb | Honeycomb | 3.0 – 3.2.6 | 11 – 13 | February 22, 2011 | — | — |
| Android Ice Cream Sandwich | Ice Cream Sandwich | 4.0 – 4.0.4 | 14 – 15 | October 18, 2011 | February 2019 | — |
| Android Jelly Bean | Jelly Bean | 4.1 – 4.3.1 | 16 – 18 | July 9, 2012 | September 2021 | — |
| Android KitKat | Key Lime Pie | 4.4 – 4.4.4 | 19 – 20 | October 31, 2013 | October 2017 | August 2023 |
| Android Lollipop | Lemon Meringue Pie | 5.0 – 5.1.1 | 21 – 22 | November 4, 2014 | November 2017 | August 2024 |
| Android Marshmallow | Macadamia Nut Cookie | 6.0 – 6.0.1 | 23 | September 29, 2015 | August 2018 | September 2024 |
| Android Nougat | New York Cheesecake | 7.0 – 7.1.2 | 24 – 25 | August 22, 2016 | October 2019 | — |
| Android Oreo | Oatmeal Cookie | 8.0 – 8.1 | 26 – 27 | August 21, 2017 | January 2021 | October 2021 |
| Android Pie | Pistachio Ice Cream | 9 | 28 | August 6, 2018 | January 2022 | — |
| Android 10 | Quince Tart | 10 | 29 | September 3, 2019 | February 2023 | — |
| Android 11 | Red Velvet Cake | 11 | 30 | September 8, 2020 | February 2024 | — |
| Android 12 | Snow Cone | 12 | 31 | October 4, 2021 | September 2024 | — |
| Android 12L | Snow Cone v2 | 12.1 | 32 | March 7, 2022 | — | — |
| Android 13 | Tiramisu | 13 | 33 | August 15, 2022 | — | — |
| Android 14 | Upside Down Cake | 14 | 34 | October 4, 2023 | — | — |
| Android 15 | Vanilla Ice Cream | 15 | 35 | October 15, 2024 | — | — |
Android has become the most popular mobile operating system globally, surpassing competitors like Symbian, BlackBerry, and Windows Phone. Its flexibility and open-source model have allowed it to dominate the smartphone market, with over 70% market share as of recent years.
Android devices are an essential part of the mobile phone landscape today, especially as the world has increasingly embraced digital technology, particularly during the COVID-19 era. Android stands as the most widely used operating system in smartphones, playing a crucial role in this digital transformation. But when did Android first emerge, and how has it evolved over time? Let's explore these questions.
Android Version 1 Series
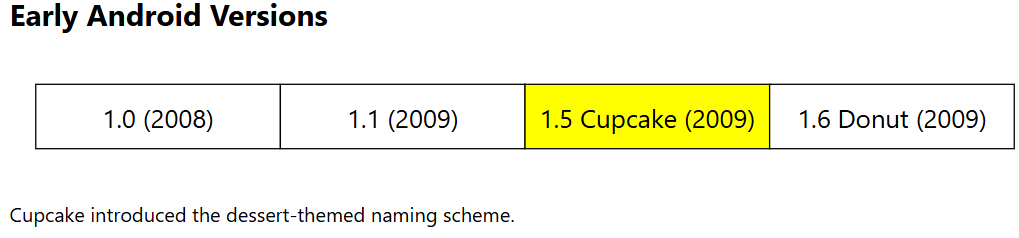
Android 1.0 (API 1) and 1.1 (API 2): Launched on September 23, 2008, Android 1.0 debuted on the HTC Dream (T-Mobile G1 in the US), featuring Google Maps, YouTube, an HTML browser, Gmail, and more. The Android Market (now Play Store) allowed users to download and update apps. Android 1.1, released in February 2009, improved user-friendliness and robustness with features like saving message attachments and enhanced Google Maps.
Android 1.5 Cupcake (API 3): Released in April 2009, Cupcake introduced the dessert-themed naming scheme and brought features like auto-rotation, third-party keyboard support, and video recording.
Android 1.6 Donut (API 4): Released in September 2009, Donut supported CDMA networks and various screen sizes, enhancing global compatibility.
Android Version 2 Series
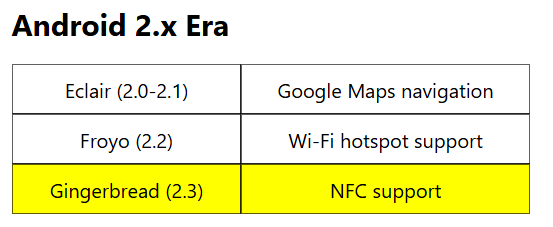
Android 2.0 to 2.1 Eclair (API 5-7): Released in October 2009, Eclair introduced Google Maps navigation, multiple account support, and live wallpapers. Subsequent updates focused on bug fixes and minor improvements.
Android 2.2 Froyo (API 8): Launched in May 2010, Froyo introduced Wi-Fi mobile hotspot support, push notifications, and Adobe Flash support.
Android 2.3 Gingerbread (API 9-10): Released in December 2010, Gingerbread refined the UI, added NFC support, and improved keyboard functionality.
Android Version 3 Series
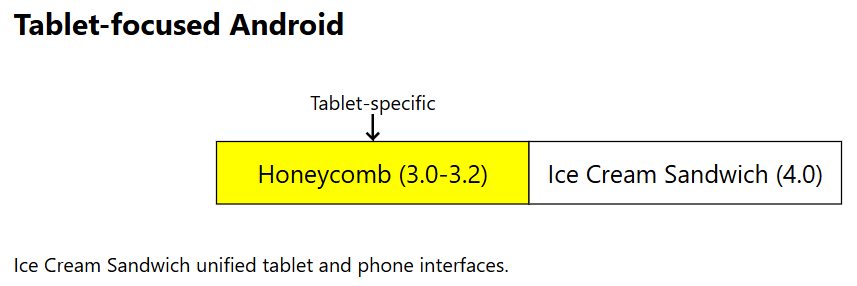
- Android 3.0 to 3.2 Honeycomb (API 11-13): Released in 2011, Honeycomb was designed for tablets, introducing virtual buttons and a holographic design.
Android Version 4 Series
Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich (API 14-15): Released in October 2011, it unified tablets and phones with a single UI, introducing features like Face Unlock and data usage monitoring.
Android 4.1 to 4.3 Jelly Bean (API 16-18): Released in 2012, Jelly Bean enhanced performance and introduced Google Now and expandable notifications.
Android 4.4 KitKat (API 19-20): Launched in 2013, KitKat introduced "OK, Google" voice activation and a lighter UI.
Android Version 5 Series
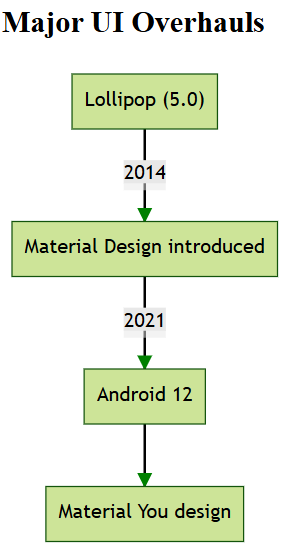
- Android 5.0 to 5.1 Lollipop (API 21-22): Released in 2014, Lollipop introduced Material Design, transforming Android's look and feel.
Android Version 6 Series
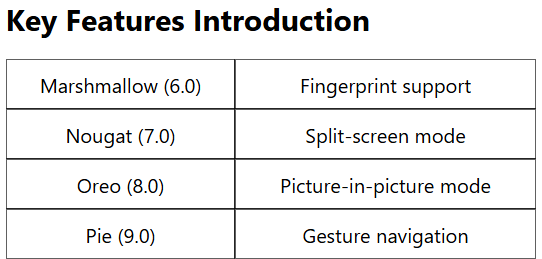
- Android 6.0 Marshmallow (API 23): Launched in 2015, Marshmallow introduced Now On Tap, app permissions, and fingerprint support.
Android Version 7 Series
- Android 7.0 to 7.1 Nougat (API 24-25): Released in 2016, Nougat brought split-screen mode, bundled notifications, and Google Assistant.
Android Version 8 Series
- Android 8.0 to 8.1 Oreo (API 26-27): Released in 2017, Oreo introduced picture-in-picture mode and notification channels.
Android Version 9 Series
- Android 9 Pie (API 28): Launched in 2018, Pie introduced gesture-based navigation and Digital Wellbeing controls.
Android Version 10

- Android 10 (API 29): Released in 2019, Android 10 focused on privacy, introducing a system-wide dark theme and gesture navigation.
Android Version 11
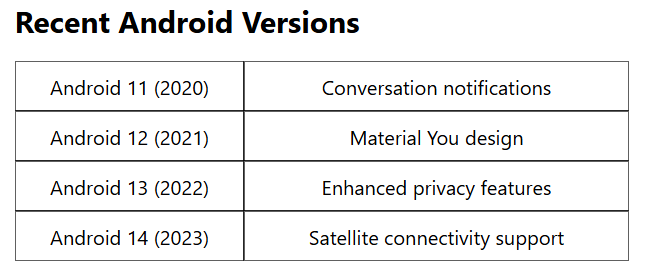
- Android 11 (API 30): Released in 2020, Android 11 enhanced privacy controls and introduced conversation notifications.
Android Version 12
- Android 12 (API 31): Released in 2021, Android 12 introduced Material You, allowing dynamic theming based on wallpaper colors.
Android Version 13
- Android 13 (API 33): Released in 2022, Android 13 focused on large-screen enhancements and improved privacy features.
Android Version 14
- Android 14 (API 34): Released in 2023, Android 14 introduced lock screen customization and satellite connectivity support.
Android Version 15
- Android 15 (API 35): Released in 2024, Android 15 added a Private Space for sensitive apps and multitasking improvements.
Conclusion
Android 1.5 Cupcake (April 2009): Introduced features like video uploads to YouTube and support for third-party keyboards.
Android 2.0 Eclair (October 2009): Added text-to-speech support and Google Maps navigation.
Android 3.0 Honeycomb (February 2011): Designed specifically for tablets with larger screens.
Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich (October 2011): Combined features from Honeycomb and Gingerbread, introducing face unlock and data usage monitoring.
Android 5.0 Lollipop (November 2014): Introduced Material Design and improved notifications.
Android 6.0 Marshmallow (October 2015): Brought fingerprint support and Doze mode for battery saving.
Android 8.0 Oreo (August 2017): Introduced picture-in-picture mode and notification channels.
Android 10 (September 2019): Marked a shift from dessert names and introduced a system-wide dark mode.
Android 11 (September 2020): Focused on improving messaging and privacy features.
Android 12 (October 2021): Featured a major UI overhaul with Material You design.
Android 13 (August 2022): Continued to refine the user experience with incremental updates.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Dilip Patel directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
Dilip Patel
Dilip Patel
Software Developer