AWS Storage Deep Dive: Unlocking the Power of EBS, EFS & S3
 Aman Patel (Amansdlc)
Aman Patel (Amansdlc)
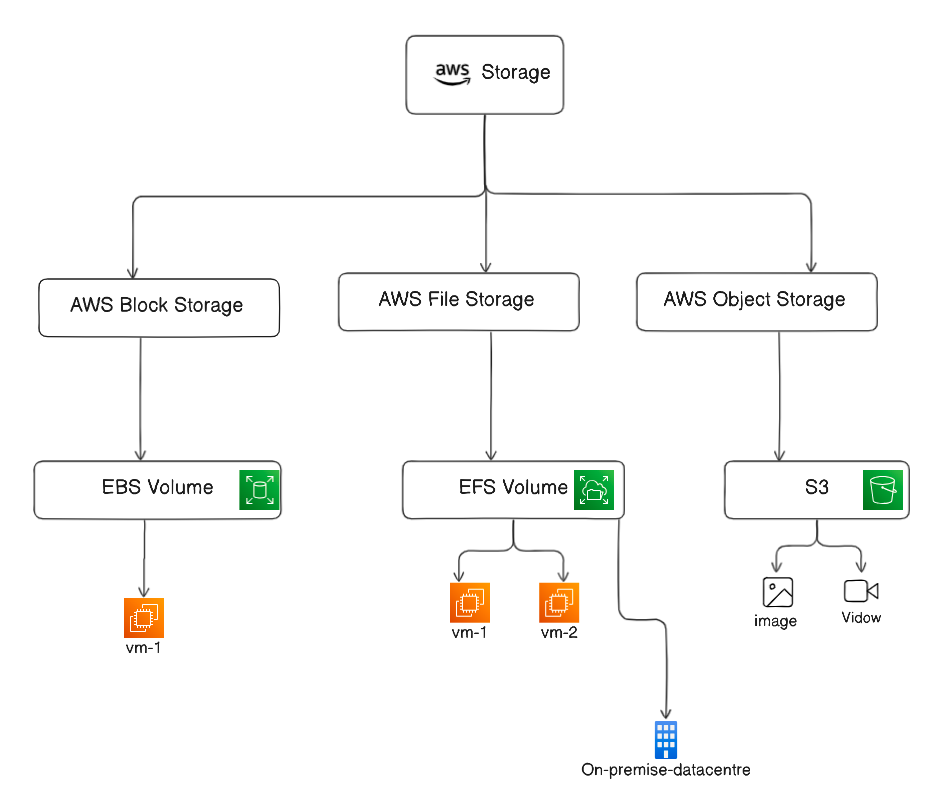
AWS provides several storage services designed to meet different use cases for scalability, security, performance, and cost efficiency. Here are the main AWS storage services:
1. Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service)
Use Case: Object storage for unstructured data like documents, images, backups, logs, etc.
Features:
Scalability: Virtually unlimited storage.
Durability: 99.999999999% durability.
Different storage classes (Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, One Zone-IA, Glacier, etc.)
Versioning and lifecycle management.
Data security features like encryption and access control.
2. Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store)
Use Case: Block storage for EC2 instances (like hard drives).
Features:
Persistent storage that remains available even if EC2 instance is terminated.
Suitable for databases, file systems, and applications requiring low-latency storage.
Different volume types: General Purpose (SSD), Provisioned IOPS (SSD), and Magnetic.
Snapshots for backup.
3. Amazon EFS (Elastic File System)
Use Case: Scalable file storage for use with EC2 instances.
Features:
Network file system (NFS) protocol support.
Can be mounted by multiple EC2 instances.
Scalable and automatically grows and shrinks as files are added or removed.
Supports file-based storage.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aman Patel (Amansdlc) directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aman Patel (Amansdlc)
Aman Patel (Amansdlc)
I am a DevOps/Cloud Engineer who likes to work on Cloud Infrastructure & Automation, CI/CD, Systems Administration, and Monitoring/Observability. I am an Open Source enthusiast and like to contribute back to the community whenever possible.