How to use Tailwind CSS Flex
 Devwares
Devwares
Tailwind flex
Building responsive and flexible user interfaces is crucial in frontend development. Flexbox is an essential tool for this purpose, and Tailwind CSS flex simplifies its usage, allowing you to create complex layouts effortlessly.
Table of content
What is Flexbox ?
How to Use Tailwind CSS Flex
Flex Containers
Flex Items
Modifying Flex Direction
Controlling Flex Item Alignment
Adjusting Flex Item Sizing
Wrapping Flex Items
Conclusion
What is Flexbox ?
Flexbox, short for flexible box, is a layout mode in CSS that makes it easy to create flexible and responsive layouts. It consists of two main components: flex containers and flex items. It's perfect for building navigation bars, footers, and other components that need to adapt to different screen sizes.
How to Use Tailwind CSS Flex
Using Tailwind CSS flex is incredibly easy. Here are the basic classes you need to get started:
flex- enables flexbox layoutflex-wrap- wraps flex items to a new linejustify-center- centers flex items horizontallyjustify-space-between- distributes flex items evenlyitems-center- centers flex items verticallyself-center- centers a single flex item
Flex Containers
A flex container holds multiple flex items and defines the main axis and cross axis of the flex layout. To create a Tailwind flex container, simply apply the flex class to an element. By default, the flex-direction property is set to row, which means the flex items will be arranged horizontally.
Here's an example of creating a flex container:
<div class="flex"> <!-- Flex items go here --></div>
Preview

Flex Items
Flex items are the individual elements within a flex container. They can be manipulated and positioned within the container using flex utilities. By default, flex items will be arranged in the order they appear in the HTML markup.
Here's an example of creating flex items within a flex container:
<div class="flex">
<div class="flex-item">Item 1</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 2</div>
<div class="flex-item">Item 3</div>
</div>
Preview

Modifying Flex Direction
The flex-direction utility allows you to specify the direction in which flex items are arranged within the flex container. By default, the direction is set to row, which arranges the items horizontally. However, you can easily change it to column to arrange the items vertically.
Tailwind flex row
You can use the Tailwind flex row class to position flex items horizontally in the same direction as the text. It is one of the classes of Tailwind flex-direction utilities.
<div class="flex flex-row ...">
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">A</div>
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">B</div>
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">C</div>
</div>
The code above represents the flex-row class
Preview

Tailwind Flex row reverse
This Tailwind flex row reverses class positions the flex item horizontally in the opposite direction of the text:
<div class="flex flex-row-reverse.....">
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">
1
</div>
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">
2
</div>
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">
3
</div>
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">
4
</div>
</div>
</div>
Preview

Tailwind Flex column
The tailwind flex column is one of the flex-direction classes and its function is to position items vertically on the screen. You can see an example of the code below and its resulting image.
<div class="flex flex-col ...">
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">
A
</div>
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">
B
</div>
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">
C
</div>
</div>
</div>
Preview

Tailwind Flex Column Reverse
Another important property of the Tailwind flex column is the Tailwind flex column reverse. This uses the .flex-col-reverse class to position flex items vertically in the opposite direction on the screen.
<div class="flex flex-col-reverse...">
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">A</div>
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">B</div>
<div class="flex items-center justify-center bg-indigo-500...">C</div>
</div>
Preview

Controlling Flex Item Alignment
Tailwind CSS provides utilities to control the alignment of flex items along both the main axis and the cross axis. The justify-* utilities control the alignment along the main axis, while the items-* utilities control the alignment along the cross axis.
Here's an example of controlling flex item alignment:
<div class="flex justify-center items-center">
<!-- Flex items are centered both horizontally and vertically -->
</div>
Adjusting Flex Item Sizing
You can adjust the sizing of flex items using utilities such as flex-grow, flex-shrink, and flex-auto. These utilities allow you to control how flex items grow, shrink, or automatically adjust their size to fill the available space. These are the classes.
Tailwind Flex Auto
Tailwind Flex Grow
Tailwind Flex Shrink
Tailwind Flex-Auto
The Tailwind flex-auto class shows how much an item will grow relative to the content of the flexible items. Here, the initial size is ignored, and it grows and shrinks according to its need.
<div class="flex...">
<div class="flex-none...">A</div>
<div class="flex-auto...">B</div>
<div class="flex-auto...">C</div>
</div>
In the code above, we demonstrated how to use the flex-auto class in Tailwind CSS.
Preview

Tailwind Flex Grow
The flex-grow utility controls the ability of a flex item to grow and take up additional space if available. By default, it is set to 0, meaning the flex item will not grow. You can adjust the value to control the growability of a flex item.
<div class="flex...">
<div class="flex-none... ">A</div>
<div class="flex-grow...">B</div>
<div class="flex-none...">C</div>
</div>
The code above shows flex-grow class.
Preview

Tailwind Flex Shrink
The flex-shrink utility controls the ability of a flex item to shrink if necessary. By default, it is set to 1, meaning the flex item can shrink to fit the available space.
<div class="flex...">
<div class="flex...">A</div>
<div class="flex-shrink...">B</div>
<div class="flex...">C</div>
</div>
The code above shows flex-shrink class.
Preview

Wrapping Flex Items
By default, flex items will try to fit in a single line within the flex container. However, you can enable wrapping using the flex-wrap utility. These are the classes used to achieve this
Tailwind Flex Wrap
Tailwind Flex Wrap-reverse
Tailwind Flex No-Wrap
Tailwind Flex Wrap
Tailwind Flex Wrap class makes it possible for flex items to wrap onto multiple lines if needed, instead of being forced into a single line.
Here's an example of wrapping flex items:
<div class="flex flex-wrap">
<!-- Flex items wrap onto multiple lines if needed -->
</div>
<div
class="flex flex-wrap..."
>
<div class="flex...">
A
</div>
<div class="flex...">
B
</div>
<div class="flex...">
C
</div>
</div>
</div>
The code above represents the flex-wrap class.
Preview

Tailwind Flex Wrap Reverse
Flex wrap reverse is a utility class that reverses the wrap flex items.
<div
class="flex flex-wrap-reverse..."
>
<div class="flex...">
A
</div>
<div class="flex...">
B
</div>
<div class="flex...">
C
</div>
</div>
</div>
The code above represents the flex-wrap-reverse class.
Preview
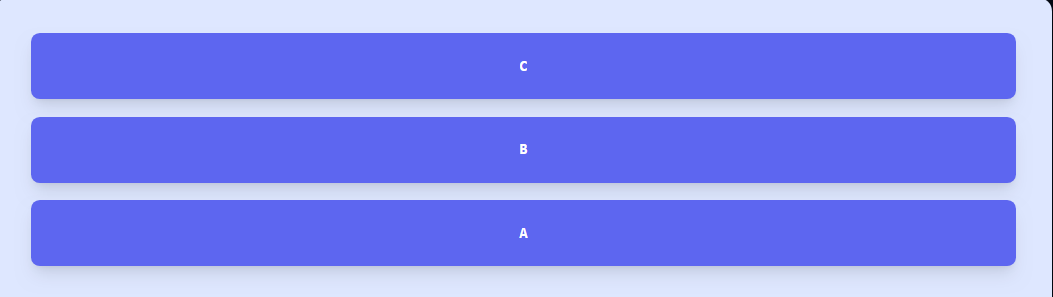
Tailwind CSS Flex-no-wrap
This Tailwind class doesn't allow flex items to wrap. This makes these flex items overflow the container. It doesn't regulate flex items to a box.
<div class="flex flex-nowrap...">
<div class="flex...">A</div>
<div class="flex...">B</div>
<div class="flex...">C</div>
</div>
The code above represents the flex-nonwrap class.
Preview

Conclusion
Tailwind CSS Flex makes it easy to create flexible and responsive layouts with just a few classes. By mastering the basics of flexbox and using Tailwind CSS Flex, you can build complex user interfaces with ease.
Resources
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Devwares directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
