Understanding Lambda: A Step-by-Step Guide to Implementation
 Aditya Gadhave
Aditya Gadhave
What is Lambda?
Lambda is used to encapsulate Data centres, Hardware, Assembly code/Protocols, high-level languages, operating systems, AWS APIs.
Lambda is a compute service where you can upload your code and create the Lambda function.
Lambda takes care of provisioning and managing the servers used to run the code.
While using Lambda, you don't have to worry about scaling, patching, operating systems, etc.
Lambda can be used in the following ways:
It can be used as an event-driven compute service where AWS Lambda runs your code in response to events. These events could be changes to data in an Amazon S3 bucket or an Amazon DynamoDB table.
It can be used as a compute service to run your code in response to HTTP requests using Amazon API calls made using AWS SDKs.
How does Lambda work
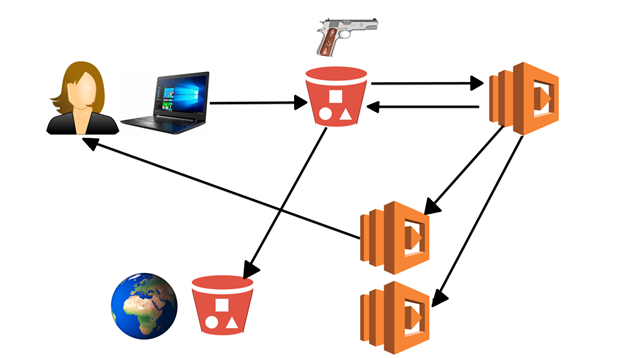
User uploads an image to S3.
S3 triggers an event, and this event is a Lambda function.
Lambda function takes this image, and then encode the image. When an image is encoded, it gets stored in S3.
The Lambda function might trigger other Lambda event which is returning image location back to the user.
The Lambda might trigger another Lambda event that takes the image from the S3 bucket and stores it in another S3 bucket located anywhere in the world.
From the above example, we conclude that Lambda event can trigger another Lambda event and they can communicate with other AWS resources.
An important feature of Lambda is that it scales automatically.
While using Lambda, you do not have to maintain Elastic Load Balancer.
It either scales up or scales out based on the condition.
Scaling up means increasing the resources in terms of RAM such as 8 GB to 12 GB.
Scaling out means adding more and more instances. For example, Load Balancer. If load increases, you scale out rather than scaling up the instances. Lambda function scales out automatically.
For example, if we have a two-line function, and millions of users hit the same function, millions of functions created to serve the millions of users.
How to create a Lambda function
Sign in to the AWS Management Console.
Click on the Lambda service.
Select the Northern Virginia region as it contains almost all AWS resources.
Click on the Function appearing on the left side of the console.
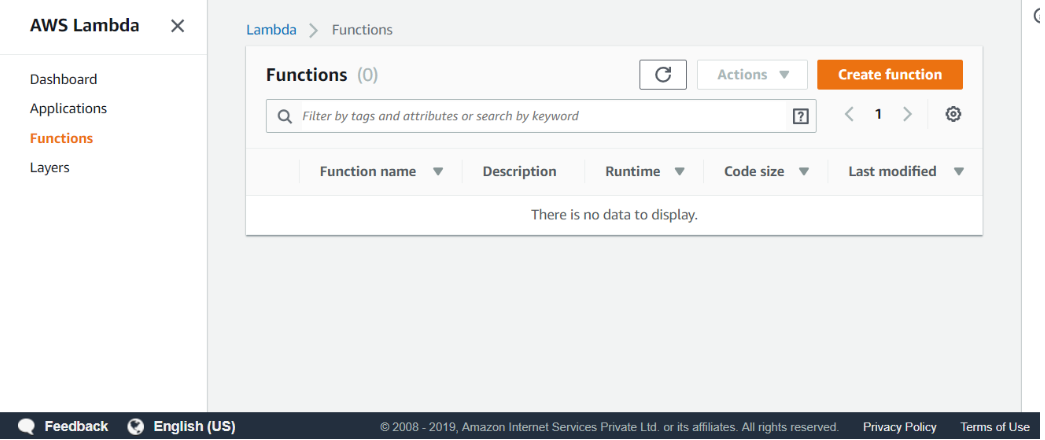
- Click on the Create function to create a new function.
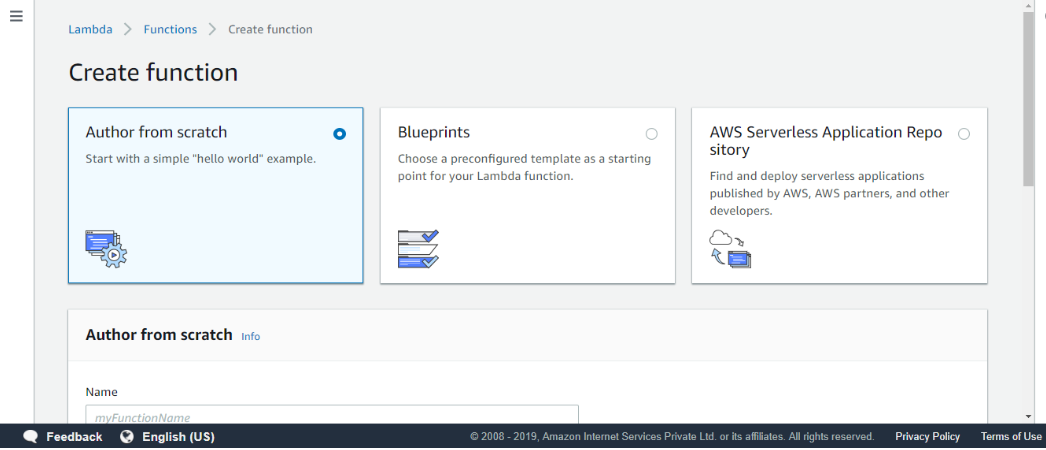
From the above screen, we observe that we have three ways of the authoring Lambda function, i.e., Author from scratch, Blueprints, and AWS Serverless.
- Now, we create the Lambda function by using the Author from scratch.

Name: It defines the name of the Lambda function.
Runtime: You can select an appropriate Lambda runtime or create your runtime as a part of your function deployment package.
Name: It defines the name of the Lambda function.
Runtime: You can select an appropriate Lambda runtime or create your runtime as a part of your function deployment package.
Click on the Create function.

The above screen shows that the function has been successfully created.
How is Lambda Priced?
Lambda is priced in the following ways:
Number of Requests: It is priced based on the number of requests. First 1 million requests are free. $0.20 per 1 million requests thereafter.
Duration: Duration is calculated from the time your code begins executing until it returns or otherwise terminates rounded up to the nearest 100ms. The price depends on the amount of money you allocate to your function. You are charged $0.00001667 for every GB-second used.
Use Cases Of AWS Lambda Functions
You can trigger the lambda in so many ways some of which are mentioned below.
File Processing: AWS lambda can be triggered by using simple storage services (S3). Whenever files are added to the S3 service Lambda data processing will be triggered.
Web Applications: You can combine both web applications and AWS lambda which will scale up and down automatically based on the incoming traffic.
IoT (Internet of Things) applications: You can trigger the AWS lambda based on certain conditions while processing the data from the device which are connected to the IOT applications. It will analyze the data which are received from the IOT application.
Stream Processing: Lambda functions can be integrated with the Amazonn kinesis to process real-time streaming data for application tracking, log filtering, and so on.
Features Of AWS Lambda Functions
The following are the some features which are provided by the AWS (Amazon Web Services):
AutoScaling and High Availability: AWS lambda will make sure that your application was highly available to the end users when there is sudden incoming traffic. High availability can be achieved by scaling the application.
Serverless Execution: There is no need for provisioning the servers manually in AWS. AWS lambda will provision the underlying infrastructure based on the triggers you are mentioned whenever a new file uploaded to a particular then AWS lambda will automatically trigger and takes care of the infrastructure.
Pay-per-use-pricing: AWS will charge you only for the time that time compute engine was active. AWS bills you based on the time taken to execute the code.
Supports different programming languages: AWS lambda function will support different programming languages. You can build the function with the language at your convenience. Following are some languages supported by AWS lambda
Advantages of AWS Lambda Function
The following are the advantages of AWS Lambda function
Zero Server Management: Since AWS Lambda automatically runs the user’s code, there’s no need for the user to manage the server. Simply write the code and upload it to Lambda.
Scalability: AWS Lambda runs code in response to each trigger, so the user’s application is automatically scaled. The code also runs in parallel processes, each triggered individually, so scaling is done precisely with the size of the workload.
Event-Driven Architecture: AWS Lambda function can be triggered based on the events happing in the aws other service like when the file or video is added to the S3 bucket you can trigger the AWS Lambda function.
Automatic High Availability: When there is high demand or high incoming traffic aws lambda function will automatically scale the servers.
Affordable: With AWS Lambda, one doesn’t pay anything when the code isn’t running. The user has to only be charged for every 100ms of code execution and the number of times his code is actually triggered.
Disadvantages of AWS Lambda Function
The following are the disadvantages of AWS Lambda function:
Latency while starting: While aws lambda is going to be activated after a long gap it will take some time to initialize the service which is required to deploy the application at that time end users will face latency issues.
Limited control of infrastructure: Behalf of your lambda function is going to take of underlying infrastructure so you will have very limited control over undelaying infrastructure.
Time Limit: AWS Lambda enforces a maximum execution time limit for functions, which is currently set to 900 seconds (15 minutes). If your function exceeds this time limit, it will be forcibly terminated.
Vendor Lock-In: If you want to execute the lambda function then you need the support of any cloud provider as here we are using AWS because it is widely used in the market.
Limited Computing and Memory Options: Limited configuration is there on the memory and CPU configuration. The predefined memory configuration was 120 MB to 120 GB and memory configuration determines the corresponding CPU power.
Benefits of AWS Lambda Functions
The following are the benefits of AWS Lambda Functions:
Cost Efficiency: It only charges for the compute that is only for running known as pay-as-you-go model.
Automatic Scaling: AWS Lambda automatically helps in scaling your applications by running code in response to each trigger.
Reduced Operational Compliance: It allows the developers to focus on building your logic, the aws itself while take care of the infrastructure.
Integration with AWS Services: It provides a seamlessly integration with other AWS services, enabling strong and scalable applications.
Best practices of using AWS Lambda Functions
The following are the best practices of using AWS Lambda functions:
Optimzing function performance: By minimizing the cold starts by keeping the functions warm and reduce the execution time by optimizing your code and dependencies.
Efficient Resource Management: Through allocating the appropriate amount of memory to your function based on performance needs and cost considerations.
Implement Error Handling and Retries: By using try-catch blocks, AWS SDK retries and dead letter queues (DLQs), we handle the errors gracefully.
Secure Your Functions: By applying the principles of least privilege for IAM roles, using environment variables securely enhance the security.
Conclusion :
AWS Lambda provides a scalable, serverless compute solution that automatically runs code in response to various triggers without requiring server management. It’s ideal for microservices, automation, and data processing tasks, making it a core component of modern, event-driven applications.
If you have any questions, need clarifications, or want to discuss anything related to AWS technologies, feel free to reach out to me on LinkedIn. Connect with me at Aditya Gadhave, and I'll be more than happy to assist you. 😊
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aditya Gadhave directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aditya Gadhave
Aditya Gadhave
👋 Hello! I'm Aditya Gadhave, an enthusiastic Computer Engineering Undergraduate Student. My passion for technology has led me on an exciting journey where I'm honing my skills and making meaningful contributions.