How SIM Cards Work: The Technology Behind Mobile Connectivity
 Ayan
Ayan
A SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module) is a small but essential component of modern mobile communication. It allows your phone to connect to a cellular network, enabling services like calls, texts, and internet access. But how exactly does this tiny card make such critical functions possible? Let’s explore the technology behind SIM cards and their role in mobile connectivity.
What Is a SIM Card?
A SIM card is a portable, integrated circuit that stores unique information about a subscriber on a cellular network. It acts as a digital passport, identifying the user to the network and granting access to mobile services.
Key Features:
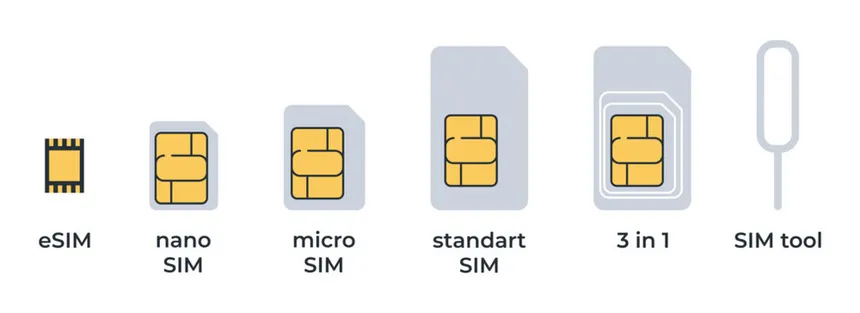
Size Variants: SIM cards come in different sizes: Standard SIM, Micro SIM, Nano SIM, and eSIM (embedded SIM).
Unique Identification: Each SIM card has a unique International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI), which identifies the user to the network.
Storage: SIM cards can store contacts, SMS messages, and minimal user data.
How SIM Cards Work
1. Identification and Authentication
When you insert a SIM card into your phone and power it on:
The SIM communicates with the network by sending its IMSI.
The network cross-checks this IMSI with its database to verify that the subscriber is authorized to use its services.
To ensure security, the SIM uses encryption methods to authenticate with the network.
2. Network Connection
Once authenticated:
The network assigns the SIM a temporary identifier called the TMSI (Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) to enhance privacy.
The phone establishes a connection with the nearest cellular tower, enabling communication with the broader network.
3. Data Storage
SIM cards store critical information, including:
IMSI: Identifies the subscriber globally.
Ki (Authentication Key): A secret key shared between the SIM and the network for secure authentication.
Phonebook and Messages: Limited space for storing contacts and SMS (mostly outdated with modern smartphones).
4. Roaming and International Use
SIM cards allow roaming by connecting to partner networks when the user travels outside their home network’s coverage area. The IMSI helps the roaming network identify the subscriber and coordinate billing with the home network.
Types of SIM Cards
1. Physical SIM
- Standard, Micro, and Nano SIMs: Differ in size but work similarly. Nano SIMs are the most common in modern smartphones.
2. eSIM (Embedded SIM)
Built directly into a device, eSIMs can be programmed remotely, eliminating the need for a physical card.
Common in newer smartphones, smartwatches, and IoT devices.
Security Features of SIM Cards
1. Encryption
SIM cards use encryption protocols to secure communication between the phone and the network. This prevents eavesdropping and fraud.
2. PIN and PUK Codes
PIN (Personal Identification Number): Protects the SIM from unauthorized use.
PUK (Personal Unblocking Key): Used to unlock the SIM if the PIN is entered incorrectly multiple times.
3. Authentication Algorithms
Modern SIM cards use advanced algorithms like MILENAGE to verify identity and encrypt data.
Why Are SIM Cards Important?
1. Global Connectivity
SIM cards enable seamless communication across the globe by standardizing mobile network access.
2. Flexibility
With a SIM card, users can switch between devices while keeping their phone number and network access.
3. Privacy and Security
SIM cards protect user data with encryption and secure authentication protocols.
Future of SIM Technology
As technology evolves, traditional SIM cards are being replaced by eSIMs and even iSIMs (integrated SIMs embedded in the processor). These advancements promise:
Better space utilization in devices.
Simplified carrier switching.
Enhanced compatibility with IoT devices.
Conclusion
SIM cards are the backbone of mobile communication, bridging the gap between users and cellular networks. They authenticate subscribers, enable secure connections, and store critical information. While they may seem like simple pieces of plastic, the technology behind them is sophisticated, ensuring seamless and secure global connectivity. As we move towards eSIMs and beyond, the evolution of SIM technology will continue to shape the future of mobile communication.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ayan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Ayan
Ayan
"I post blogs here in a simple way, so that a 5-year-old can read and understand them."