Breaking Down Complexity: Forming Analytical Questions for Problem Solving
 Queen Carine
Queen Carine

Forming practical analytical questions is a cornerstone of impactful decision-making in the data-driven world. Analytical questions guide data analysts in extracting meaningful insights from raw data, shaping the direction of their analysis, and ensuring that their work aligns with business objectives. Crafting these questions is both an art and a science, requiring a deep understanding of the problem, available data, and decision-making context. This article will discuss how to focus on the right areas by forming the right analytical questions.
The “Value from Analytics” Workflow
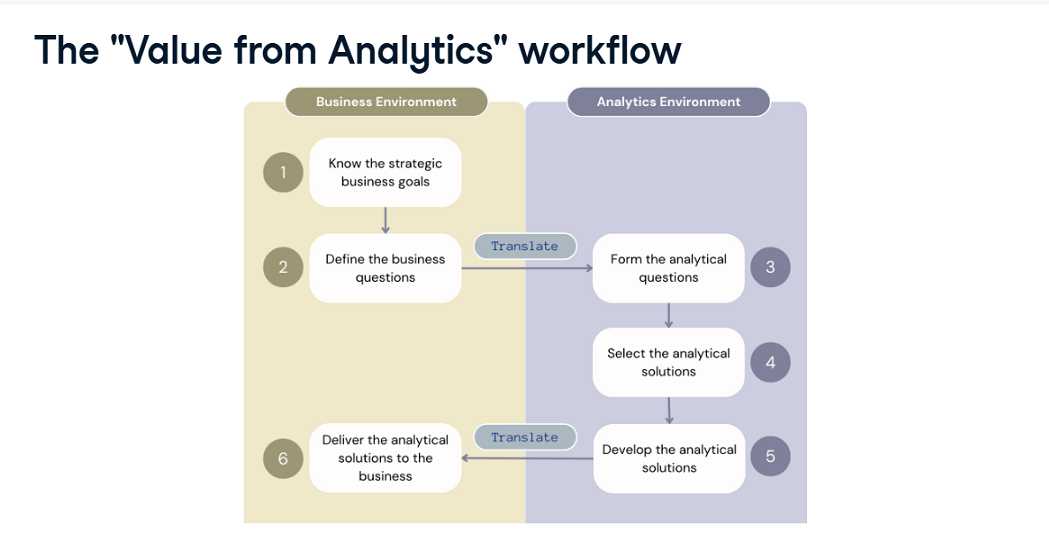
Strategic business goals are predetermined targets companies want to achieve over time. Knowing these goals gives teams direction and purpose.
Business teams define team-level goals based on strategic business goals. This results in business goals that need to be answered or questions that need to be solved. Example: How can we increase the product sales?
Analytical questions that require the use of data and analytics to be answered. Example: Based on past sales data, what are the main drivers of customer churn?
What customer segments have experienced the most significant purchase decline over the last quarter?
What product categories are most associated with high-value customer churn?
Select the right analytical solution to answer the analytical questions: Regression analysis, Time series analysis, etc.
Develop the analytical solution. Key Activities:
Clean and preprocess data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Apply the chosen analytical model or technique to the dataset.
Validate the results through testing or by comparing them against known benchmarks.
Refine the solution as needed to improve its reliability and relevance to the question.
Purpose: To translate raw data into actionable insights, ensuring the analysis directly addresses the business's needs and questions.
- Deliver the analytical solution to the business. This is the final and crucial step, where the developed solution is presented to the stakeholders in an understandable and actionable format.
Key Activities:
Create visualizations, dashboards, or reports to showcase the findings.
Communicate the insights effectively, highlighting how they answer the analytical and business questions.
Provide actionable recommendations based on the analysis, such as strategies for improving sales or reducing customer churn.
Facilitate discussions to align insights with the organization's goals and decision-making processes.
Purpose: To ensure the insights generated are understood and can be practically applied by business teams to meet their strategic goals.
Difference between business and analytical questions.
| Business Questions | Analytical Questions |
| The methodology used to answer is data analytics, intuition, experience, or expert opinion | The methodology to answer is data analytics, statistical techniques. |
| They are qualitative | They are quantitative |
| They have a broad scope and are open-ended | Are very specific and to the point |
| This may be answered using assumptions and intuition | This can only be answered using data and analytics |
Adopting the SMART Framework
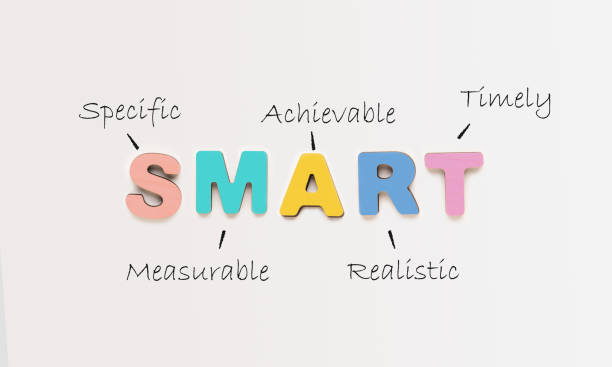
Analytical questions should be:
Specific: Focused on a particular aspect of the problem.
Measurable: The answer can be derived from data.
Achievable: Within the scope of your resources and data.
Relevant: Aligned with business goals.
Time-bound: Linked to a specific time frame, if applicable.
Example: What percentage of customers churned within 30 days after signing up in Q3 2024?
Understanding the Business Question
A clearly defined problem will have clarity on the following:
What the business wants to know
What decisions need to be made
Who will use the results?
Any other information that is important to know?
Steps to forming analytical questions
Extract the key information from the business question
Break down the business question:
-What do we need to know from the data to answer the business question?
Refine the analytical question:
-Make the question specific and focused
-Consider what data is required to answer the questions
Review relevance: Confirm that the analytical questions formed can address the business question.
Types of Analytical Questions and their Solutions Techniques
Descriptive Questions: Focus on what happened and what the current situation is. Example: "What was the average customer retention rate in the last six months?"
The main techniques used to form these questions are:
-Data aggregation: Mean, Median, and percentiles
-Data visualization: Line charts, bar charts, and histograms
-Cluster analysis: Clustering(grouping similar data) and hierarchical clustering
They are answered using descriptive analytics.
Descriptive analytics
- Tracking trends
-Figuring out what works and what doesn’t
-Overview of the business performance
Diagnostic Questions: Aim to understand why something happened.
Example: "What factors contributed to the decrease in user engagement last month?"
The main techniques used to form these questions are:
-Regression analysis: Identifying the relationship between one or more independent variables.
-Hypothesis testing: Testing a hypothesis to determine whether a particular variable has a statistically significant impact or outcome.
-Root cause analysis: Identifying the underlying causes of a particular problem
-Correlation analysis
They are answered using diagnostic analytics.
Diagnostic analytics
- Identify root causes of the problem
-Make data-driven decisions to:-Optimize processes, improve efficiency and reduce costs
Predictive Questions: Explore what is likely to happen.
Example: "Which customers are most likely to churn in the next quarter?"
The main techniques used to form these questions are:
-Time series forecasting: Analyzing patterns in historical data over time to make predictions about future trends.
-Machine learning: Training models to make predictions based on input variables.
-Predictive text analytics: Predicting the next word, phrase, or sentence in a given text.
-Regression prediction algorithm
-Classification predicting algorithm
-Logistic regression
They are answered using predictive analytics.
Predictive analytics
- Analyzing past data to make predictions
-Predicting what will happen
Prescriptive Questions: Offer guidance on what actions to take.
Example: "What promotions are most effective in retaining high-value customers?"
The main techniques used to form these questions are:
-Recommendation engines: Analyzing behaviors and preferences to provide personalized recommendations to users.
-Optimization: Finding the best solution to a problem, subject to certain constraints or limitations.
-Decision trees: Maps out different possible decisions and outcomes, based on certain criteria or parameters
They are answered using prescriptive analytics.
Prescriptive analytics
- It goes a step further to prescribe the course of action
- What should be done?
-What can we do to make something happen?
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Being Too Vague: Avoid general questions that lack focus, like "How can we improve?"
Ignoring Data Limitations: Don't ask questions that your data can't answer.
Overloading Questions: Keep questions concise and focused on one aspect at a time.
Conclusion
Forming practical analytical questions is essential for driving meaningful insights and aligning data analysis with business objectives. Organizations can translate raw data into actionable strategies by understanding the differences between business and analytical questions, applying frameworks like SMART, and leveraging appropriate analytical techniques for each question type. Avoiding common pitfalls such as vagueness and data limitations ensures the analytical process remains focused and effective. Ultimately, mastering the art of crafting precise and relevant analytical questions empowers decision-makers to confidently address challenges, seize opportunities, and achieve strategic goals.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Queen Carine directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Queen Carine
Queen Carine
As a Data Analyst, I'm passionate about turning data📊📈 into actionable insights that drive smarter decisions. On this journey, I share my experiences, challenges, and the tools I’m learning along the way. Join me as I explore the world of data analytics and uncover new ways to make data work for you.