Geneve and AWS Gateway Load Balancer: Revolutionizing Cloud-Native Traffic Management
 Sourav Chakraborty
Sourav ChakrabortyIntroduction
As cloud workloads grow more complex, organizations demand efficient ways to manage and secure their network traffic. AWS Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) is a game-changer in this space, providing seamless scalability and integration for network appliances. At the heart of its innovation lies the Geneve protocol, a modern tunneling standard that elevates the capabilities of cloud-native networking.
In this blog, we’ll explore how GWLB leverages Geneve to redefine traffic management, dive into Geneve's architecture and use cases, and offer insights into GWLB’s subnet placement and routing configurations.
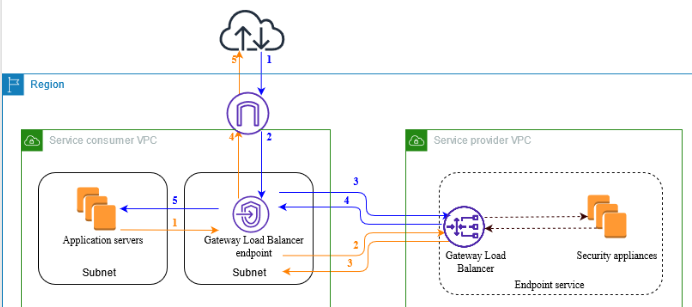
What is AWS Gateway Load Balancer?
AWS Gateway Load Balancer simplifies the deployment and scaling of virtual appliances, such as firewalls and intrusion prevention systems, across cloud environments. It combines a transparent network gateway with load balancing capabilities to distribute traffic efficiently while maintaining high availability.
Key Benefits of GWLB
Traffic Transparency: No need to modify routing configurations of backend appliances.
Health Monitoring: Directs traffic only to healthy instances.
Elastic Scalability: Grows with your traffic demands.
Built-in Redundancy: Ensures reliability with failover mechanisms.
By pairing GWLB with the Geneve protocol, AWS achieves an architecture that is both flexible and highly efficient.
The Geneve Protocol: A Foundation for Modern Networking
What is Geneve?
Geneve (Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation) is a protocol designed to address the limitations of older tunneling standards like VXLAN. Its dynamic and extensible framework makes it ideal for cloud-native applications. Defined in RFC 8926, Geneve is a cornerstone for scalable and adaptable traffic management.
Core Features of Geneve
Base Header: Defines the virtual network identifier (VNI) and other essential parameters.
Options Field: A flexible area for custom metadata, enabling advanced use cases like telemetry or service chaining.
UDP Transport: Ensures compatibility with existing network infrastructure.
Geneve Use Cases
Network Function Virtualization (NFV): Streamlines the management of virtualized network services.
Cloud Interoperability: Facilitates communication across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Traffic Analytics: Delivers granular insights with rich metadata.
Service Chaining: Simplifies sequencing and orchestration of network functions.
How AWS Gateway Load Balancer Uses Geneve
Geneve plays a pivotal role in GWLB’s architecture, enabling it to:
Encapsulate Traffic: Incoming packets are wrapped with a Geneve header, embedding metadata for routing and load balancing.
Distribute Traffic: Encapsulated packets are routed to virtual appliances in different subnets for processing.
Decapsulate Traffic: After processing, GWLB removes the Geneve header and forwards the traffic to its intended destination.
This model ensures a seamless and scalable approach to managing cloud traffic.
Subnet Placement in GWLB Deployment
Effective subnet design is essential for a robust GWLB setup.
Subnet Configuration
Dedicated GWLB Subnets: GWLB resides in distinct subnets in each Availability Zone (AZ).
Appliance Subnets: Virtual appliances are deployed in their own subnets, separate from GWLB.
Routing Connections: Traffic flows between application subnets, GWLB subnets, and appliance subnets seamlessly.
Routing Table Configuration for GWLB
Routing tables ensure proper traffic flow within the GWLB architecture:
Application VPC Route Table: Directs ingress traffic to the GWLB endpoint.
textCopy codeDestination Target 0.0.0.0/0 GWLB EndpointAppliance Subnet Route Table: Routes processed traffic back through GWLB for final delivery.
textCopy codeDestination Target 0.0.0.0/0 GWLB Endpoint
This routing ensures bi-directional traffic flow and robust failover.
Conclusion
The integration of Geneve with AWS Gateway Load Balancer transforms traffic management in cloud-native environments. With its extensibility, scalability, and ability to handle dynamic workloads, Geneve empowers GWLB to meet modern networking demands effortlessly.
By combining thoughtful subnet design, well-structured routing, and Geneve's advanced capabilities, AWS GWLB offers a future-proof solution for traffic management and security in the cloud.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sourav Chakraborty directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
