Comparing Cloud Architectures: Monolithic, Microservices, and Serverless
 Daniel Her
Daniel Her
When building an e-commerce website, selecting the right cloud architecture can make or break your application's scalability, cost-efficiency, and ease of maintenance. Let's compare monolithic, microservices, and serverless architectures using an e-commerce platform as an example, focusing on the pros and cons of each.
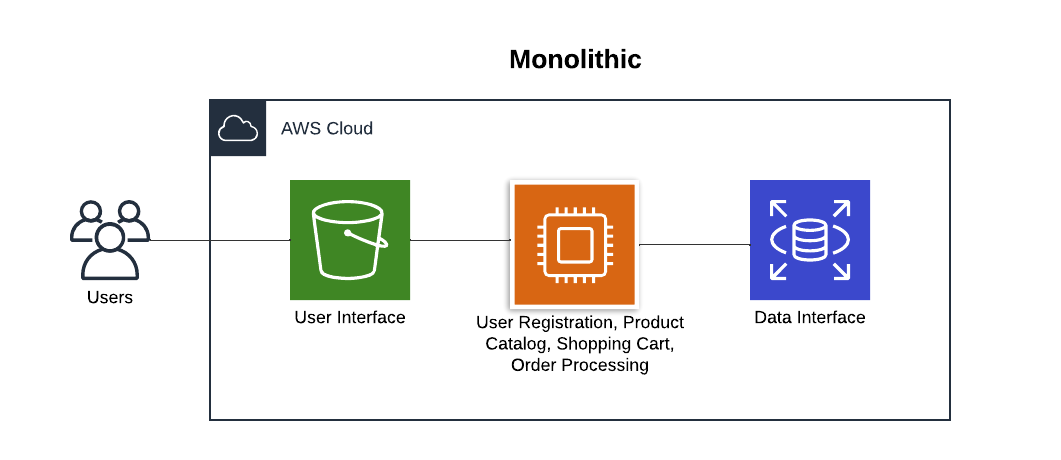
1. Monolithic Architecture: Simplicity First
A monolithic architecture combines all components—user interface, business logic, and database—into a single application. For an e-commerce site, some core components might include: user registration, product catalog, and a shopping cart.
Pros:
Simple to develop and deploy.
Great for small, consistent workloads.
Cons:
Difficult to scale; the entire app must scale together.
Inflexible; changes affect the whole application.
Risky deployments; even minor updates require redeploying the whole system.
Best For: Small, early-stage applications.
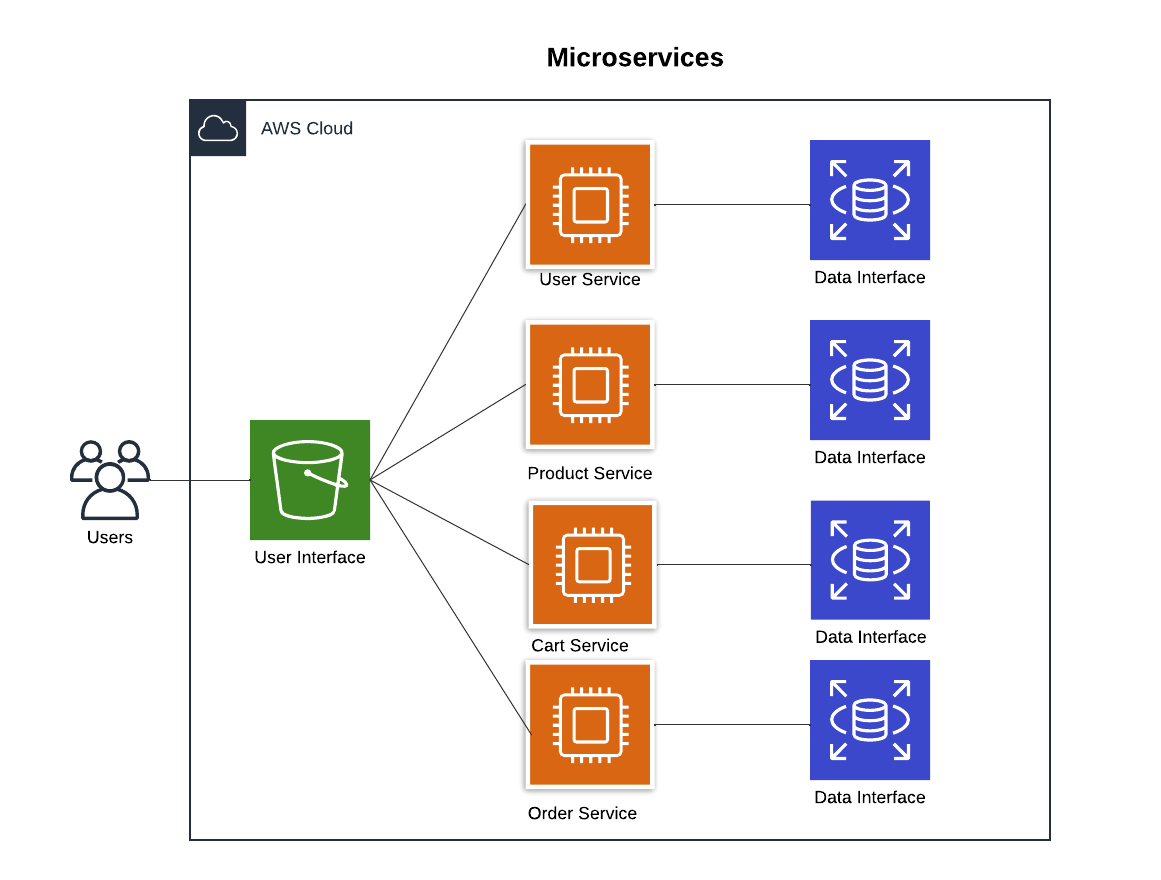
2. Microservices Architecture: Scalability with Independence
A microservices approach splits the application into independent services, each handling specific tasks like user authentication, shopping cart, or order management, often with its own database.
Pros:
Each service can scale independently.
Easier to innovate; teams can deploy updates without affecting other services.
Resilient; a failure in one service won’t bring down the entire application.
Cons:
Operationally complex.
Higher costs from managing multiple services and databases.
Best For: Large, high-traffic applications with diverse features (think Netflix).
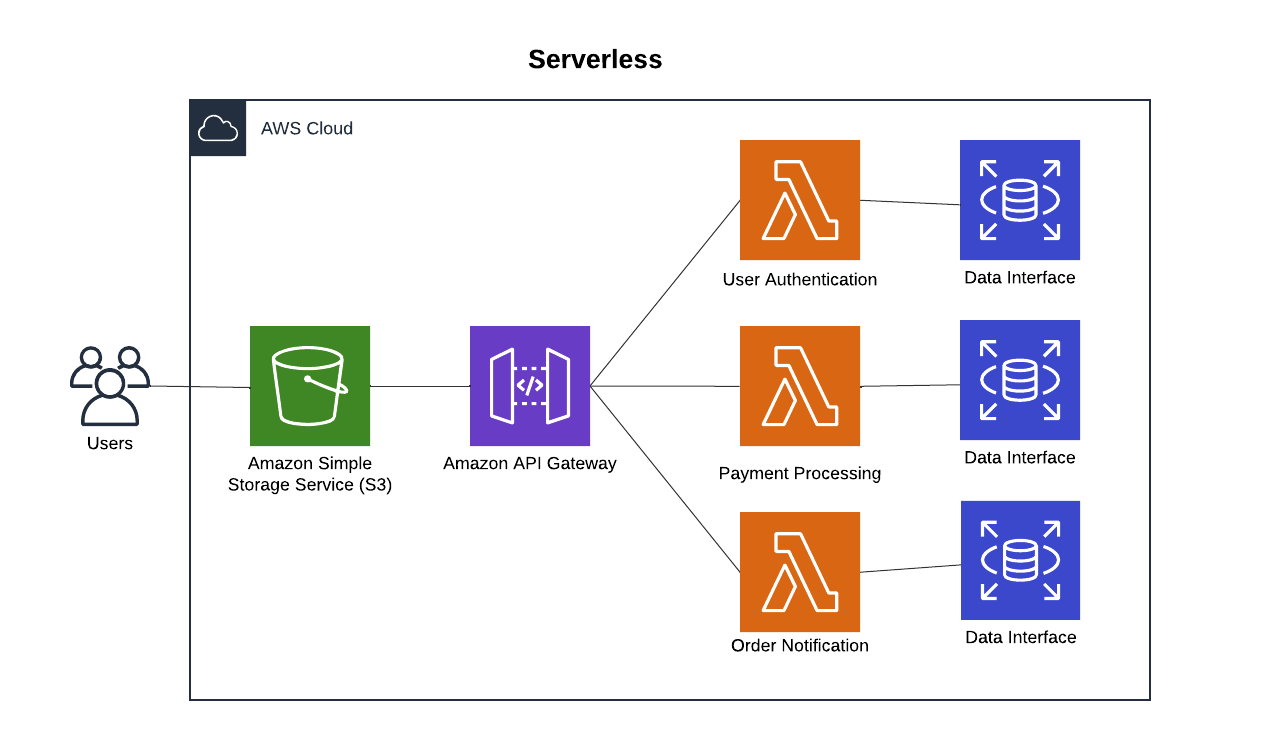
3. Serverless Architecture: Pay-As-You-Go Efficiency
Serverless designs use event-driven functions, such as AWS Lambda, to execute specific tasks like processing payments or querying the product catalog.
Pros:
Scales automatically to meet demand.
Cost-effective; pay only for what you use.
No server management required.
Cons:
Cold starts can introduce slight delays.
Requires rethinking workflows for an event-driven model.
Best For: Applications with variable traffic or event-driven workloads.
Conclusion
Each architecture has its strengths and trade-offs. Monolithic designs are ideal for simplicity and small workloads, microservices shine for complex systems, and serverless is perfect for cost-effective scalability. The choice ultimately depends on the application's size, traffic, and operational needs.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Daniel Her directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
