Day 1 of 100 Days of DSA: Programming Fundamentals - Diving into the Basics
 Tushar Pant
Tushar Pant
Welcome to the start of my 100 Days of DSA challenge! Today, I tackled five foundational programming problems using Java to strengthen my understanding of basic algorithms and control structures. Here’s a detailed walkthrough of the problems and solutions:
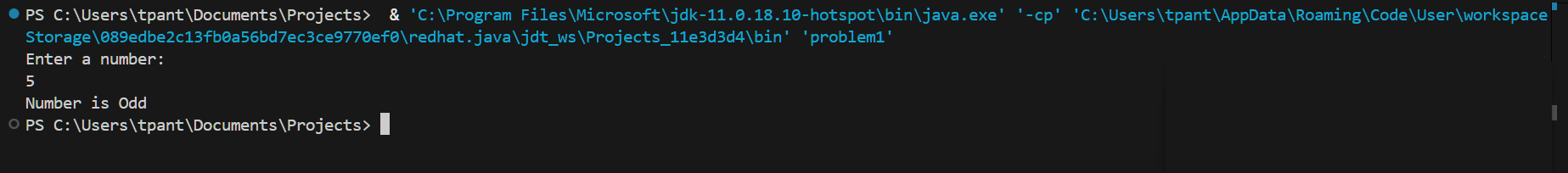
1. Check if a Number is Even or Odd
To determine if a number is even or odd, we use the modulus operator %. If the number is divisible by 2, it's even; otherwise, it's odd.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class EvenorOdd {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number:");
int num = sc.nextInt();
sc.close();
if(num%2==0)
System.out.println("Number is Even");
else
System.out.println("Number is Odd");
}
}
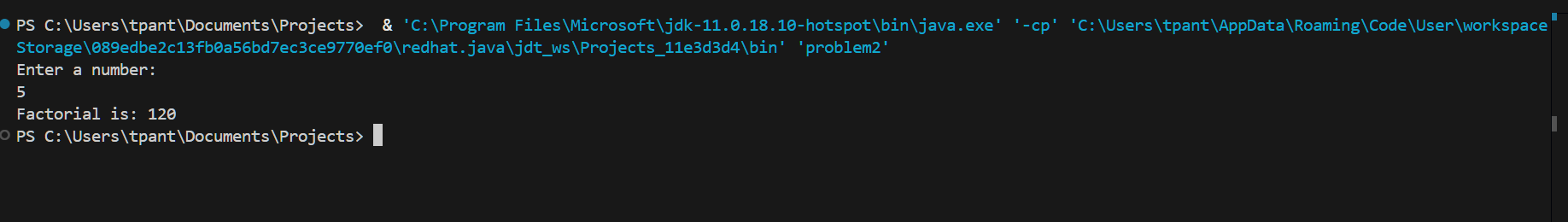
2. Find the Factorial of a Number
The factorial of a number ( n ) is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to ( n ). This can be calculated using a loop.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class Factorial {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number:");
int num = sc.nextInt();
int ans = 1;
sc.close();
if(num==0 || num==1)
ans = 1;
else{
while(num>1){
ans*=num;
num--;
}
}
System.out.println("Factorial is: "+ans);
}
}
3. Print the First n Fibonacci Numbers
The Fibonacci sequence is a series where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting with 0 and 1.
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Fibonacci {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the number of Fibonacci terms: ");
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int a = 0, b = 1;
System.out.print("Fibonacci Sequence: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(a + " ");
int next = a + b;
a = b;
b = next;
}
}
}

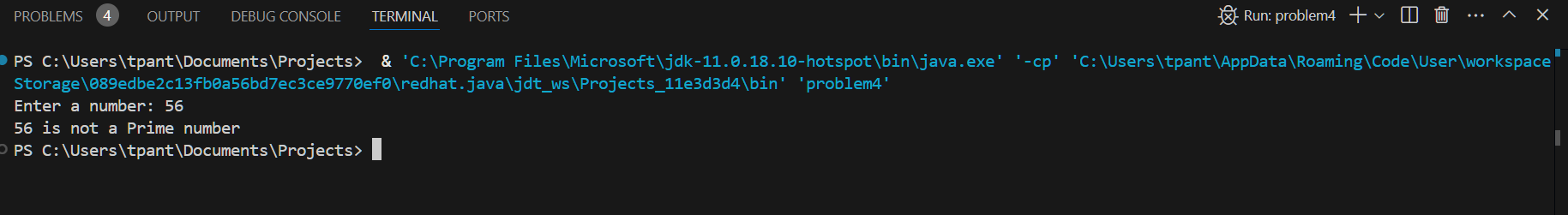
4. Check if a Number is Prime
A prime number is greater than 1 and divisible only by 1 and itself. We check divisors up to the square root of the number.
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrimeCheck {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = scanner.nextInt();
if (number > 1) {
boolean isPrime = true;
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(number); i++) {
if (number % i == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
if (isPrime) {
System.out.println(number + " is a Prime number");
} else {
System.out.println(number + " is not a Prime number");
}
} else {
System.out.println(number + " is not a Prime number");
}
}
}
5. Reverse a Number
To reverse a number, we repeatedly extract its last digit using the modulus operator and reconstruct it in reverse order.
Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReverseNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int number = scanner.nextInt();
int reversedNumber = 0;
while (number > 0) {
int digit = number % 10;
reversedNumber = reversedNumber * 10 + digit;
number /= 10;
}
System.out.println("Reversed Number is " + reversedNumber);
}
}
Reflection
Starting with programming fundamentals builds a strong base for tackling complex problems later. These exercises emphasized logic, loops, and conditionals—essential skills for any programmer. Stay tuned as I level up in this journey of solving Data Structures and Algorithms!
See you tomorrow with Day 2! 🚀
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Tushar Pant directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
