Kubernetes Basics: Step-by-Step Creation of Pods, Namespaces, and Clusters + Key Interview Questions
 Chetan Mohanrao Mohod
Chetan Mohanrao Mohod
When planning to set up a cluster, you should first decide how many nodes you want to create.
The first should be the control plane and the worker nodes. We will create one control plane and two worker nodes.
By the way, the control plane includes the API server, etcd, Controller Manager, and Scheduler, which we cover in the K8S Architecture.
Before following the steps below, please install Kind and kubectl. Refer to this blog before continuing with the current one: Click Here
Steps to create a cluster: (For Only Master Node (Node’s is a server))
- Run this command:
kind create cluster --name=my-cluster
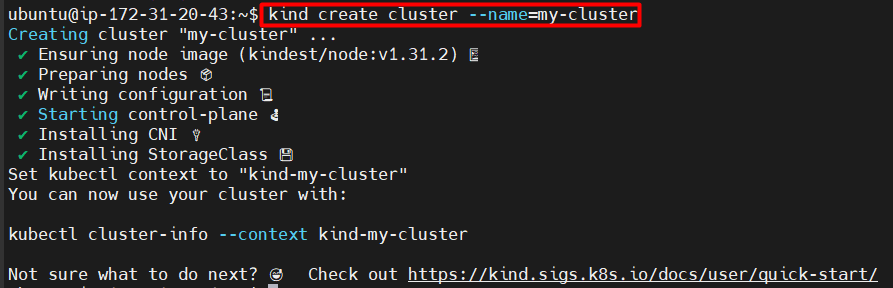
Q. What is v1.31.2? It is the K8s version.
The command will always create a cluster with the latest Kubernetes version. If you want to install a specific version, add the --version tag.
Q. What is CNI? The Container Network Interface allows the Master and Worker nodes to communicate with each other.
- To check how many clusters we have:
kind get clusters
- To check docker container:
docker ps

How to communicate with cluster?
Example: When you start a company, who is the first person to join? The CEO, right? In K8S, kubectl is like the CEO. Kubectl will ask the API server how many nodes we have.
kubectl get nodes
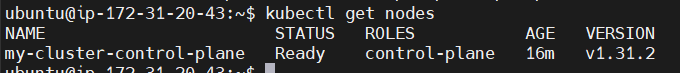
We have a Master Node (Control Plane).
Now we need to install the Worker Node with the Master Node, so we will delete our existing cluster.
Command to delete the cluster:
kind delete cluster --name=my-cluster
How it's Actually Created in Production:
We Will Write a Manifest File.
- We will create one separate directory:
mkdir k8s-practice
cd k8s-practice
- Create a
config.ymlfile (Manifest File): This will create both the Master and Worker Nodes at the same time.
kind: Cluster #This is a Type Kind, it is not K8S IN DOCKER Kind.
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane #Master Nodes
image: kindest/node:v1.31.2
- role: worker #Worker Node1
image: kindest/node:v1.31.2
- role: worker #Worker Node2
image: kindest/node:v1.31.2
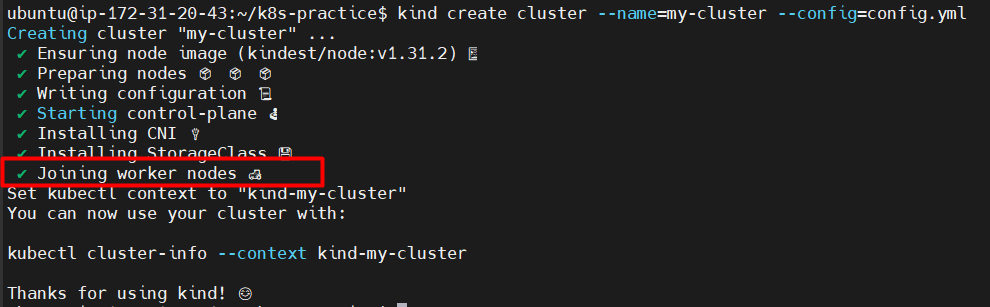
- Now we will run the kind command to execute config.yml.
kind create cluster --name=my-cluster --config=config.yml
- Check if the nodes are created by running
kubectl get nodes.
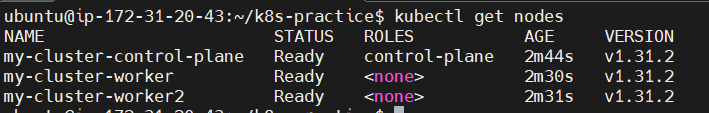
This is how K8S Multi Nodes are created!
What is Namesapce?
In Kubernetes, a namespace is a way to separate resources within a single cluster, like creating mini-clusters for different teams or projects.
Isolation: Keeps resources separate for each team or environment (e.g., dev, test).
Organization: Avoids name conflicts and simplifies resource management.
Resource Limits: Controls CPU and memory per namespace.
Key Commands
Create a namespace:
kubectl create namespace my-namespaceList pods in a namespace:
kubectl get pods -n my-namespaceDelete a namespace:
kubectl delete ns devList namespace:
kubectl get ns
Namespaces help manage multiple teams and apps in one Kubernetes cluster.
How to create a POD?
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx #This will create NGINX Container
kubectl get pods
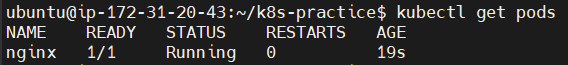
To know more details about this POD, run:
kubectl describe pod/nginx
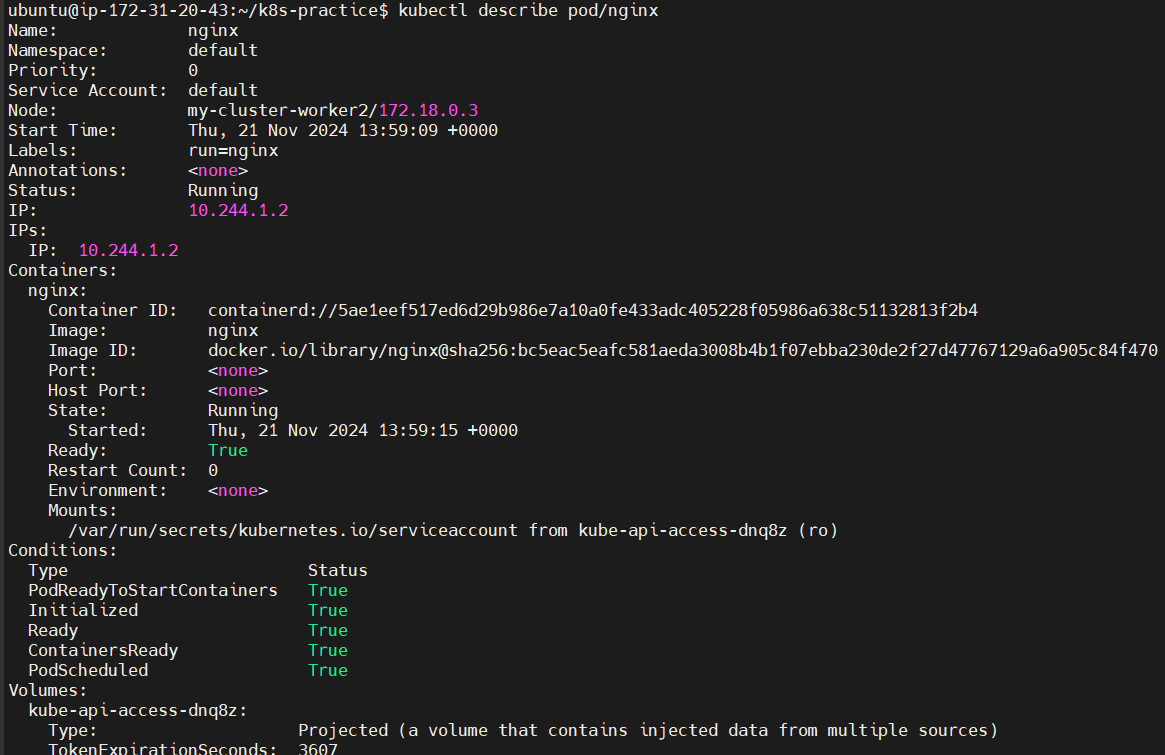
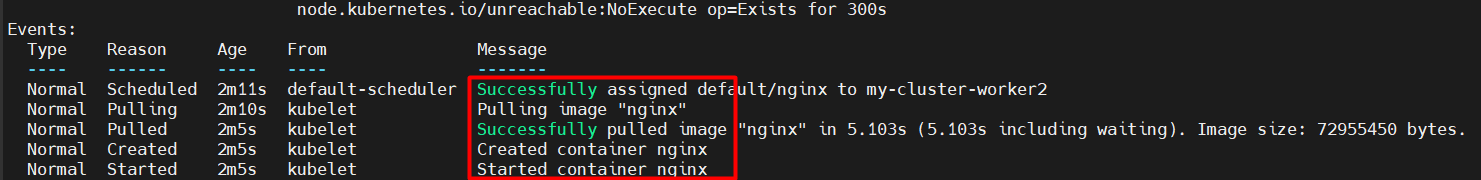
Internally, this process involves executing docker pull to download the image and docker run to start the container.
That's it. This is how Pods and Clusters are created. Now you can delete your cluster.
kind delete cluster --name=my-cluster
Note: Kind clusters operate only when Docker containers are running. Kind is a tool that creates a Kubernetes architecture within Docker using Docker containers.
Interview Questions:
Here are some common Kubernetes interview questions covering key topics like Pods, Namespaces, Clusters, Master Node, and Worker Node:
1. Pods
What is a Pod in Kubernetes? Why is it the smallest deployable unit?
How do Pods differ from containers?
What happens to a Pod when a container inside it fails?
How do you scale applications with Pods?
How can you expose a Pod to make it accessible outside the cluster?
2. Namespace
What is a Kubernetes Namespace, and why is it used?
How does a Namespace provide isolation within a cluster?
How can you switch between Namespaces in your Kubernetes environment?
How would you set resource limits or quotas on a Namespace?
What are the default Namespaces in Kubernetes, and what is their purpose?
3. Cluster
What is a Kubernetes cluster?
How does a Kubernetes cluster achieve high availability?
Explain the relationship between nodes, clusters, and Pods.
What are some best practices for managing clusters in Kubernetes?
How do you monitor the health of a Kubernetes cluster?
4. Master Node
What is a Master Node in Kubernetes, and what components does it contain?
Explain the role of the API server on the Master Node.
How does the Scheduler work on the Master Node?
What role does the Controller Manager play in a Master Node?
Why is etcd important, and where is it located?
5. Worker Node
What is a Worker Node in Kubernetes, and what role does it play?
Describe the main components of a Worker Node.
What is the role of kubelet on a Worker Node?
How does kube-proxy function within a Worker Node?
What happens when a Worker Node fails?
6. General Questions on Architecture and Concepts
Explain the Kubernetes control plane.
How do Master and Worker Nodes communicate in Kubernetes?
How does Kubernetes handle load balancing for services?
What are the different types of services in Kubernetes, and when would you use each?
How can you secure communication between Master and Worker Nodes?
Happy Learning :)
Chetan Mohod ✨
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Chetan Mohanrao Mohod directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Chetan Mohanrao Mohod
Chetan Mohanrao Mohod
DevOps Engineer focused on automating workflows, optimizing infrastructure, and building scalable efficient solutions.