Cron Job in Linux
 Harshit Sahu
Harshit Sahu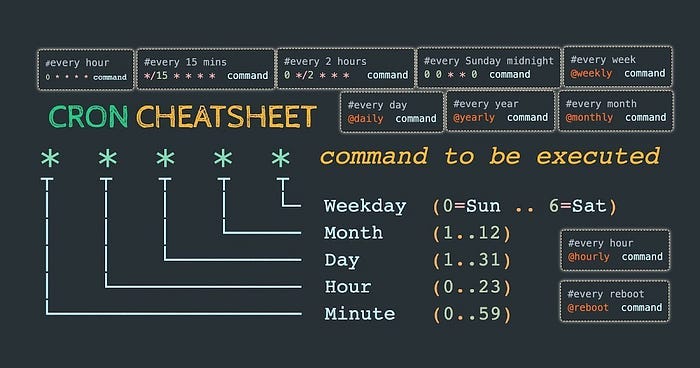
Understanding Cron, Crontabs, and Cron Jobs
1. Cron
Definition: Cron is a time-based job scheduler in Unix-like operating systems. It allows users to automate repetitive tasks by executing commands or scripts at specified times and intervals.
Usage: Commonly used for system maintenance, backups, sending emails, or running scripts.
2. Crontab (Cron Table)
Definition: Crontab is a file where the cron jobs (tasks) are defined. Each user, including the system, can have their own crontab file.
Command:
crontab -e: Edit the user's crontab.crontab -l: List the current user's crontab entries.crontab -r: Remove the current user's crontab.
To see more details, run
cat /etc/crontab
3. Cron Jobs
Definition: A cron job is a specific task or command scheduled to run at a particular time and interval using cron.
Syntax:
* * * * * /path/to/command_or_scriptThe
*symbols represent time fields in this order:Minute (0-59)
Hour (0-23)
Day of the Month (1-31)
Month (1-12 or names like Jan, Feb)
Day of the Week (0-6 or names like Sun, Mon)
Example Cron Job
Task: Run a script daily at 2:30 AM.
Create the script:
#!/bin/bash echo "Backup started at $(date)" >> /path/to/backup.log tar -czf /path/to/backup.tar.gz /important/directory echo "Backup completed at $(date)" >> /path/to/backup.logEdit the crontab: Open crontab using:
crontab -eAdd the cron job:
30 2 * * * /path/to/backup_script.sh
Advanced Example with Environment Variables
Task: Schedule a Python script to run every Monday at 9:00 AM.
MAILTO="admin@example.com" # Send output/errors via email 0 9 * * 1 python3 /path/to/script.py
Common Use Cases
System Cleanup:
Clear temporary files every hour:0 * * * * rm -rf /tmp/*Server Health Check:
Run a script to monitor CPU usage every minute:* * * * * /path/to/monitor_cpu.shDatabase Backup:
Backup a database weekly on Sunday at midnight:0 0 * * 0 /path/to/db_backup.sh # here last 0 = sunday
By leveraging cron, you can automate repetitive tasks, ensuring efficiency and reducing manual intervention.
Cron Job for Backup
First write a script
#!/bin/bash
alert = 90
backup_date = $(date +"%m-%d-%Y-%H-%M-%S")
df -h | awk '{print $5 " " $1}' | while read output;
do
usage = $(echo $ouput | awk '{print $1}' | cut -d'%' -f1)
file_sys = $(echo $ouput | awk '{print $2}')
if [ $usage -ge $alert ]
then
echo "CRITICAL for $file_sys on $backup_date"
fi
done
Then create crontab
crontab -e
* * * * * bash /home/ubuntu/backup.sh >> /home/ubuntu/backup.logs
Done now check in the specified path you will find that script…

Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Harshit Sahu directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Harshit Sahu
Harshit Sahu
Enthusiastic about DevOps tools like Docker, Kubernetes, Maven, Nagios, Chef, and Ansible and currently learning and gaining experience by doing some hands-on projects on these tools. Also, started learning about AWS and GCP (Cloud Computing Platforms).