How to Get Started with Jenkins and configure Docker as Agent for CI/CD: A Beginner's Guide
 Jerin Sebastian
Jerin Sebastian
What is Jenkins?
Jenkins is an open-source automation server widely used in software development to automate tasks related to building, testing, and deploying applications. It’s a cornerstone tool in DevOps practices, enabling Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD)..
How Jenkins Works
Master-Node Architecture
Master Node: Coordinates the build and deployment processes. It handles scheduling and monitoring jobs.
Worker Nodes: Execute the builds. You can scale Jenkins by adding more nodes to handle heavy workloads.
Job Configuration
Jobs define tasks like pulling code from a repository, running tests, and deploying applications.
Jobs can be triggered manually, on a schedule, or automatically (e.g., when code is pushed to GitHub).
Continuous Integration/Delivery
CI: Jenkins automatically builds and tests code whenever developers commit changes, ensuring issues are caught early.
CD: Jenkins deploys applications to production or staging environments in an automated, repeatable manner.
Setting up Jenkins on EC2 instance
Step 1: Launch an EC2 Instance
Launch EC2 instance and configure it as Jenkins Master. Edit the inbound traffic rule to only allow custom TCP port 8080
Step 2: Install Java
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jre
After running the commands, verify the Java version to ensure it’s installed correctly.
Step 3: Install Jenkins
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee \
/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian binary/ | sudo tee \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install jenkins
Downloads and store Jenkins' GPG key securely.
Configures your system to use the Jenkins repository, ensuring future package installations and updates are fetched from this source.
Ensures package security by requiring signatures verified with the stored GPG key
Refresh Package Index using apt-get update: It downloads the latest lists of packages and their versions from the repositories specified in the
/etc/apt/sources.listfile and files in/etc/apt/sources.list.d/.Install Jenkins
Step 4
Login to Jenkins using below url
http://<ec2-instance-publicip>:8080 [You can get the ec2-instance-public-ip-address from your AWS EC2 console page]
After you login to Jenkins - Run the command to copy the Jenkins Admin Password - sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword - Enter the Administrator password
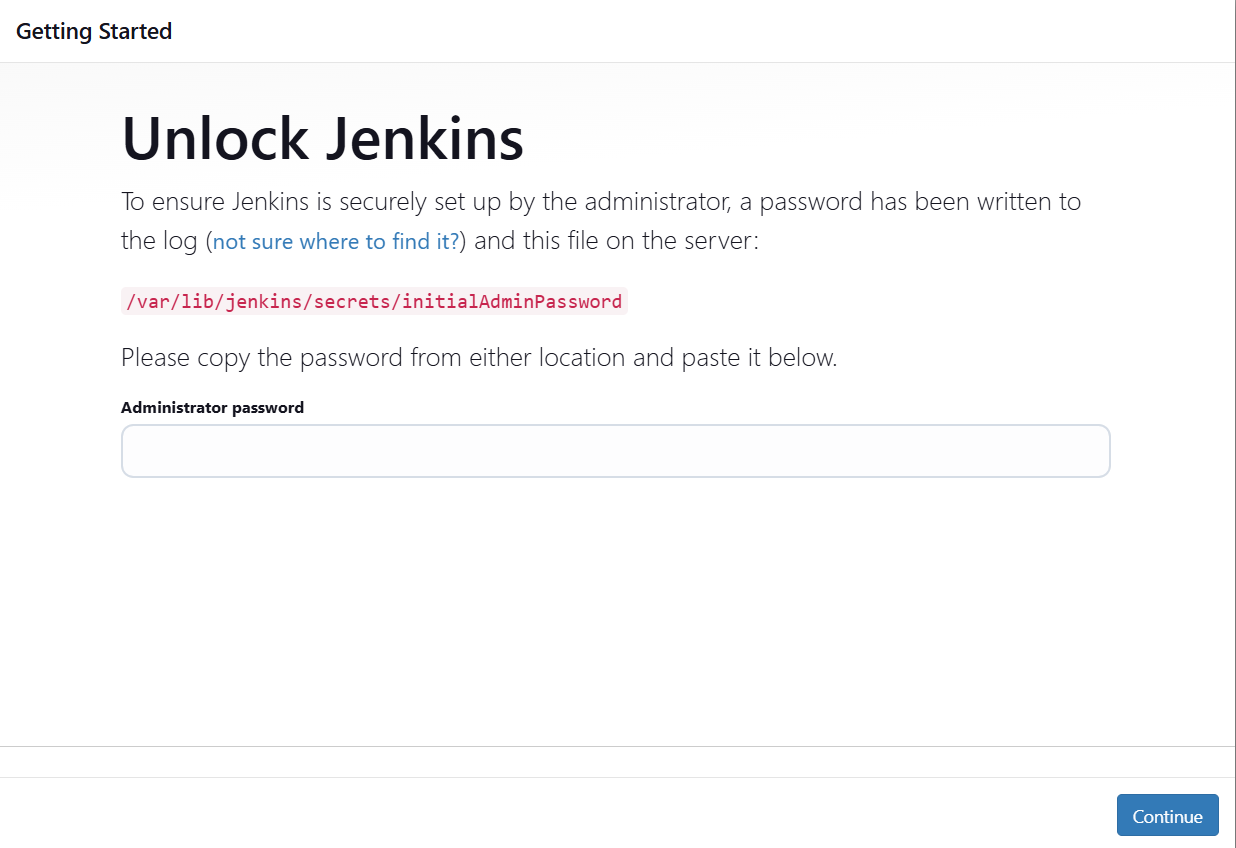
Step 5
Install Suggested plugins
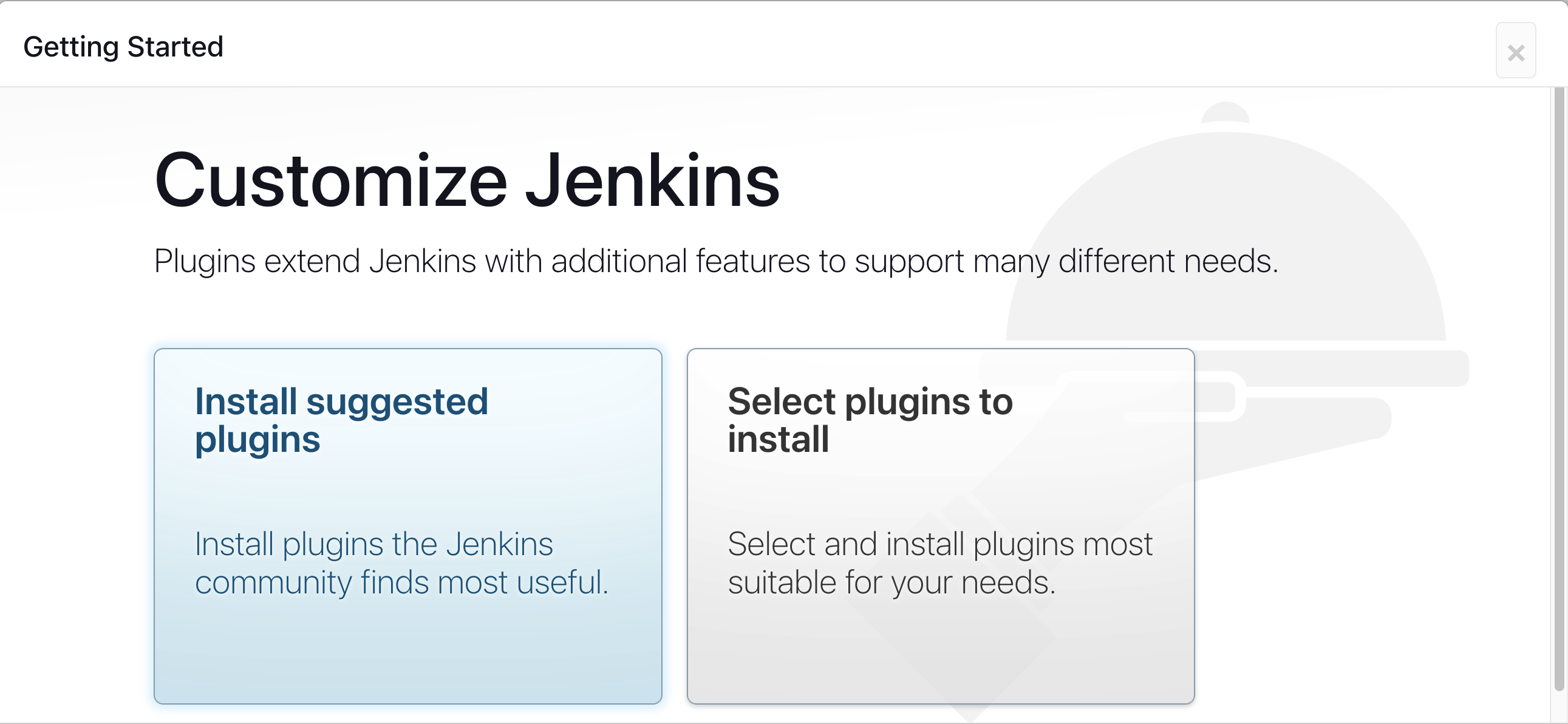
Step 6
Create Admin User
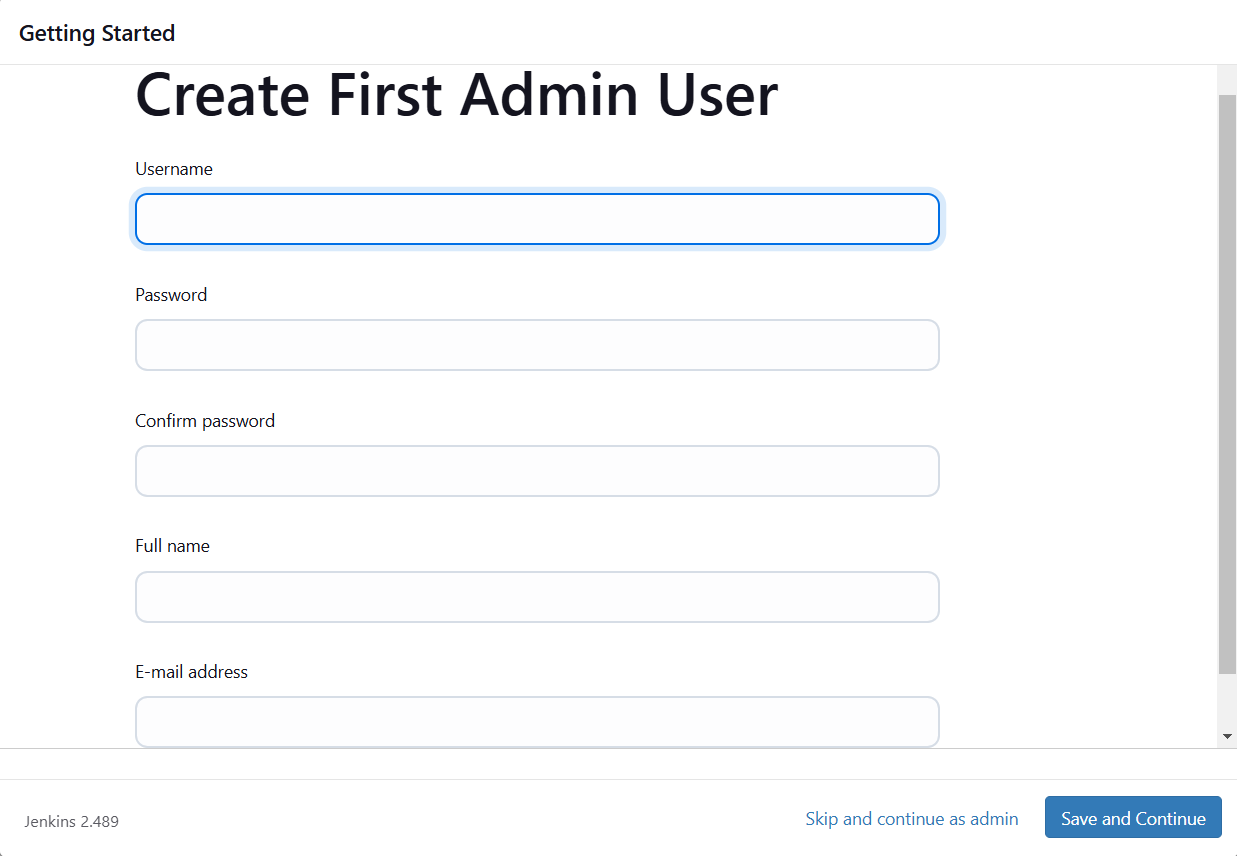
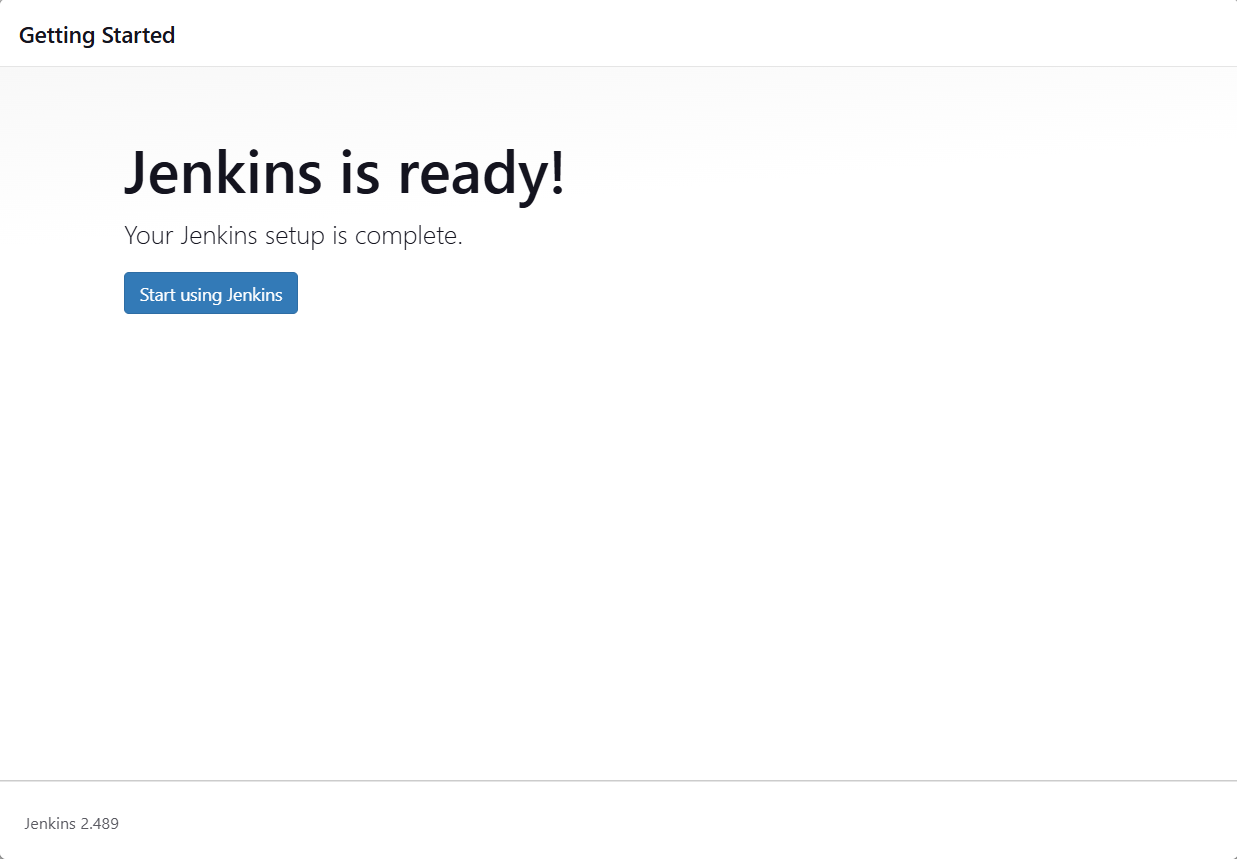
Jenkins Installation is Successful. You can now starting using the Jenkins
Step 7
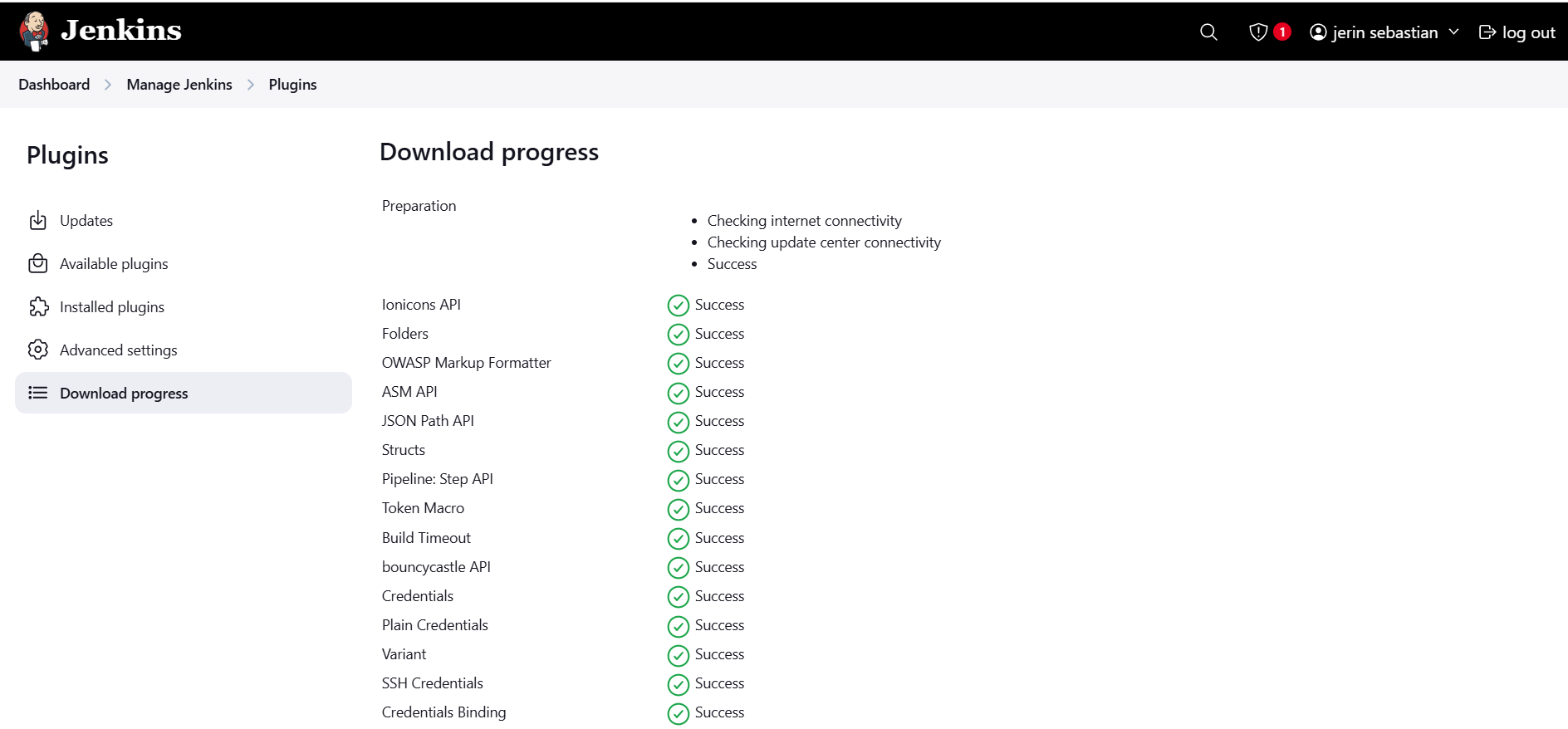
Install the Docker Pipeline plugin in Jenkins
Log in to Jenkins.
Go to Manage Jenkins > Manage Plugins.
In the Available tab, search for "Docker Pipeline".
Select the plugin and click the Install button.
Restart Jenkins after the plugin is installed.
Step 8
Docker Slave Configuration
Run the below command to Install Docker
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker.io
Step 9
Grant Jenkins user and Ubuntu user permission to docker deamon
sudo su -
usermod -aG docker jenkins
usermod -aG docker ubuntu
systemctl restart docker
Once you are done with the above steps, restart Jenkins.
http://<ec2-instance-public-ip>:8080/restart
The docker agent configuration is now successful.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Jerin Sebastian directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Jerin Sebastian
Jerin Sebastian
🖋️As a professional specializing in Site Reliability Engineering (SRE), DevOps, and Performance Engineering, I thrive on designing and optimizing systems that are both reliable and scalable. My expertise lies in streamlining processes, driving automation, and ensuring high-performance infrastructure that meets modern business demands. I thrive on implementing best practices like observability, capacity planning to enhance system uptime and reliability. I believe in bridging the gap between development and operations by fostering a collaborative culture and aligning teams around shared goals for operational excellence. I am also exploring how predictive models and data-driven insights can enhance system reliability, automate troubleshooting, and optimize performance. Whether it’s building robust infrastructure, optimizing workflows, or leveraging cutting-edge tools, I am dedicated to delivering exceptional results that drive organizational success. Let’s connect to collaborate, share insights, and innovate together in the world of reliable, high-performing systems!🖋️