What is DNS and Why is it Important?
 Lovely Sharma
Lovely Sharma
Introduction: Why Your Browser Needs DNS
When you type a website like chaicode.com into your browser, your browser doesn’t automatically know where to go. Websites aren’t recognized by their names alone—they’re tied to unique numbers called IP addresses, which are like the "phone numbers" of websites. This is where DNS (Domain Name System) steps in. It’s like your phone’s contact list, translating human-friendly domain names into machine-friendly IP addresses.
Without DNS, you’d need to remember and type in long, complex strings of numbers just to visit a website. DNS makes the internet accessible and user-friendly by handling this translation behind the scenes.
What is DNS?
DNS, or Domain Name System, is the internet’s translator. It turns easy-to-remember names like google.com into the IP addresses that computers use to find and connect to websites.
Think of it as the internet’s GPS, helping your browser navigate to the correct destination.
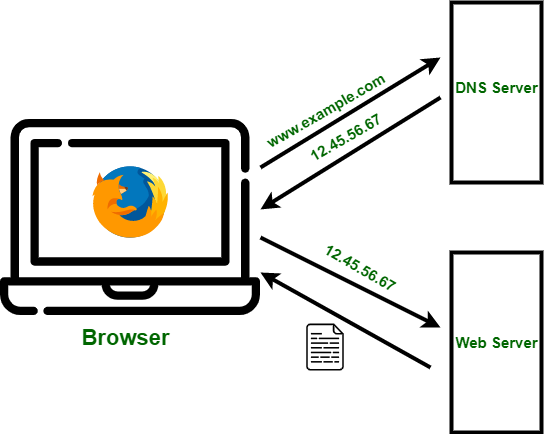
How DNS Works (In Simple Steps)
Here’s how DNS works when you try to visit a website like chaicode.com:
Your Computer Checks the Cache:
- First, your computer looks in its local DNS cache to see if it already knows the IP address of the website. If it does, it skips the rest of the process and connects directly to the site.
It Asks the DNS Resolver:
- If the IP address isn’t in your cache, your computer asks a DNS resolver for help. This resolver is usually run by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or a public service like Google (8.8.8.8) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1).
The Resolver Checks the DNS Hierarchy:

If the resolver doesn’t have the answer, it climbs the DNS hierarchy to find it:
Step 1: Root Servers: These servers direct the resolver to the correct Top-Level Domain (TLD) servers based on the domain extension (like
.comor.org).
Step 2: TLD Servers: These servers point the resolver to the authoritative DNS server for the specific domain (like chaicode.com).
Step 3: Authoritative DNS Server: This server holds the exact IP address of the domain you’re trying to visit.

DNS Resolution Complete flow
Your Computer Gets the IP Address:
- Once the resolver has the IP address, it sends it back to your computer. Now your browser knows where to go and connects you to the website.
Future Visits Are Faster:
- Your computer saves the IP address in its cache, so the next time you visit the same website, the process is quicker.
Why DNS Matters
Imagine trying to browse the internet without DNS. You’d have to memorize and type in long, confusing numbers like 104.18.40.2139 for every website you visit. Sounds impossible, right? DNS simplifies everything by letting you type easy-to-remember names instead.
But DNS does more than just make browsing easier:
It Powers the Internet: Every website, app, and online service relies on DNS to function. Without it, the internet would grind to a halt.
It Saves Time: DNS caches speed up your browsing experience by remembering the IP addresses of websites you visit often.
It Handles Traffic: DNS routes internet traffic efficiently, ensuring you get connected to the right server, even for global websites.
It Supports Email and Subdomains: DNS doesn’t just connect websites; it also manages email routing (via MX records) and subdomains (like chaicode.com).
DNS in Action: A Real-Life Analogy
Think of DNS as your favorite pizza delivery app. When you’re craving pizza, you don’t call the restaurant by their phone number; you search for their name in the app. The app finds the number for you, places the order, and your pizza shows up. DNS does the same for websites—it finds their “number” (IP address) so your browser can connect to them. Without it, you’d be stuck guessing numbers and missing out on pizza—or the internet.
Risks and the Importance of Secure DNS
While DNS is amazing, it has its flaws. Most DNS queries are sent in plain text, meaning anyone watching your network can see which websites you’re visiting. Hackers can exploit this by redirecting you to fake websites in a type of attack called DNS spoofing.
How to Keep DNS Secure
To protect your online activity, you can use secure DNS protocols like DNS over HTTPS (DoH) or DNS over TLS (DoT). These encrypt your DNS queries, making it harder for hackers or snoops to intercept them. Tools like Cloudflare DNS and Quad9 not only enhance privacy but also block malicious websites.
Conclusion
DNS is the unsung hero of the internet, quietly working behind the scenes to connect you to the websites you love. It simplifies your online experience, powers the web, and keeps things running smoothly. By understanding how DNS works and securing your DNS traffic, you can browse the internet confidently and safely. So next time you visit a website, take a moment to appreciate the magic of DNS—the internet’s ultimate translator.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Lovely Sharma directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Lovely Sharma
Lovely Sharma
Hello! I'm Lovely, an undergraduate B.Tech student with a knack for exploring the world of technology and engineering. Through my blog, I document my learnings, experiences, and insights as I navigate my academic journey. Join me as I delve into the fascinating realms of tech, share my projects, and reflect on the lessons learned along the way. Let's embark on this adventure of growth and discovery together!