Micro Frontends in React: A Simple Guide
 Saurav Kumar
Saurav Kumar
What are Micro Frontends?
Modern web apps are big and complex. Managing one huge codebase can be tough. Micro Frontends break a frontend into smaller, independent parts, making development and deployment easier.
Why Use Micro Frontends?
✅ Scalability – Teams can build and deploy independently. ✅ Flexibility – Different technologies can coexist. ✅ Better Maintenance – Smaller, focused codebases. ✅ Faster Deployments – Reduces risk in updates.
📌 Think of it like a car dashboard: Each section (speedometer, fuel gauge, music controls) is separate but works together.
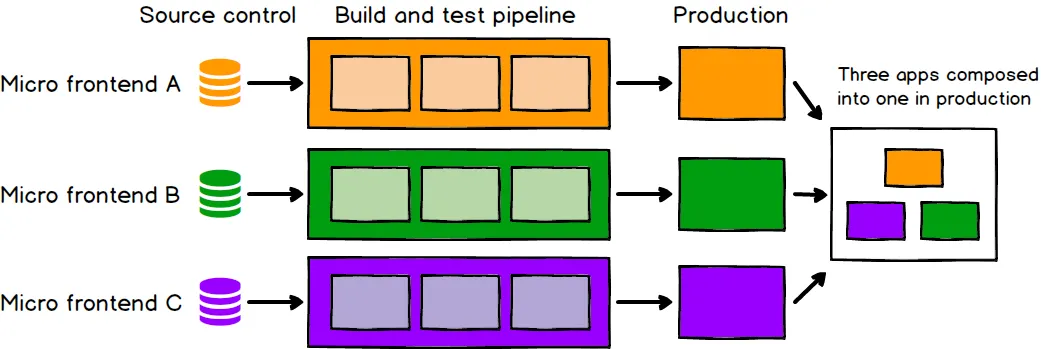
How Micro Frontends Work
A host app integrates multiple micro frontends, each handling different UI sections. Common methods include:
Iframe-Based – Simple but limited.
Webpack Module Federation (Recommended) – Dynamic imports.
Single SPA – Supports multiple frameworks.
Component-based (NPM packages) – Ideal for UI libraries.
📌 Diagram: Micro Frontend Architecture
+----------------------------+
| Host App |
|----------------------------|
| [Micro Frontend A] [B] |
| [Micro Frontend C] [D] |
+----------------------------+
Setting Up Micro Frontends in React with Webpack
Step 1: Create the Host App
npx create-react-app host-app
cd host-app
npm install webpack webpack-cli module-federation-plugin
Add to webpack.config.js:
const ModuleFederationPlugin = require("webpack/lib/container/ModuleFederationPlugin");
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: "host",
remotes: { microfrontend: "microfrontend@http://localhost:3001/remoteEntry.js" },
}),
],
};
Import Micro Frontend:
import React, { Suspense } from 'react';
const MicroFrontend = React.lazy(() => import('microfrontend/App'));
function App() {
return <Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}><MicroFrontend /></Suspense>;
}
export default App;
Step 2: Create the Micro Frontend
npx create-react-app microfrontend-app
cd microfrontend-app
Edit webpack.config.js:
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: "microfrontend",
filename: "remoteEntry.js",
exposes: { "./App": "./src/App" },
}),
],
};
Run both apps and see them work together.
Best Practices
🔹 Use events or global state (Redux, Zustand) for communication.
🔹 Keep dependencies isolated to avoid conflicts.
🔹 Lazy load micro frontends for better performance.
🔹 Use shared UI libraries for consistency.
📌 Diagram: Micro Frontends interacting with shared state.
Where Are Micro Frontends Used?
✅ E-commerce (e.g., Amazon): Separate cart, products, payments.
✅ Dashboards (e.g., Analytics tools): Different widgets.
✅ Enterprise Apps: Different teams handling separate features.
📌 Example: Spotify uses micro frontends for Home, Search, Library.
Common Issues & Fixes
🔴 Version conflicts – Use singleton in Webpack settings.
🔴 Micro Frontend not loading – Check CORS and publicPath.
🔴 Performance issues – Ensure shared dependencies.
Conclusion
Micro Frontends in React help make apps modular, scalable, and easier to maintain. Webpack Module Federation is a great way to implement them. Try tools like Bit.dev for sharing components and Nx for managing multiple apps.
🚀 What’s next? Build your own Micro Frontend project and see how it works!
Happy coding! 🎉
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Saurav Kumar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Saurav Kumar
Saurav Kumar
Build WebApps | Powered by Next.js, Node.js, Express.js, MongoDB & many more Styling, Auth, Db, Security, Deployment Tools & Techs