Streamline your Network Topology with AWS Transit Gateways
 Safeer C M
Safeer C M
AWS Network offerings started with the simple concept of VPC - a Virtual Private Cloud that isolates your workloads at a network level. Subnets, security groups, and network ACLS provided isolation and security. Over time, more services were added - VPN Gateways, Direct Connect, VPC Peering, Cloud WAN, and much more. As you increase the cloud footprint across VPCs, and geographies and/or adopt hybrid or multi-cloud architecture, managing the network architecture becomes overly complex. This is where VPC Transit Gateway comes to the rescue.
What is an AWS Transit Gateway?
AWS Transit Gateway is a service that is aimed at simplifying AWS network topologies. It functions as a managed transit hub that uses a hub-and-spoke model: VPCs, on-premises networks, data centers, or SD-WAN solutions can connect to the Transit Gateway. Instead of potentially managing dozens or hundreds of peering connections, tunnels, etc., engineers can now attach the relevant network entities and manage routing in a centralized place. AWS Transit Gateway provides a scalable, secure, and streamlined networking solution by eliminating the complexity of many point-to-point connections.
Key Components and Architecture
The key component is the Transit Gateway itself, which acts as the central hub and a virtual router for the VPCs and on-premise networks. In addition, the following components are part of the Transit Gateway Architecture.
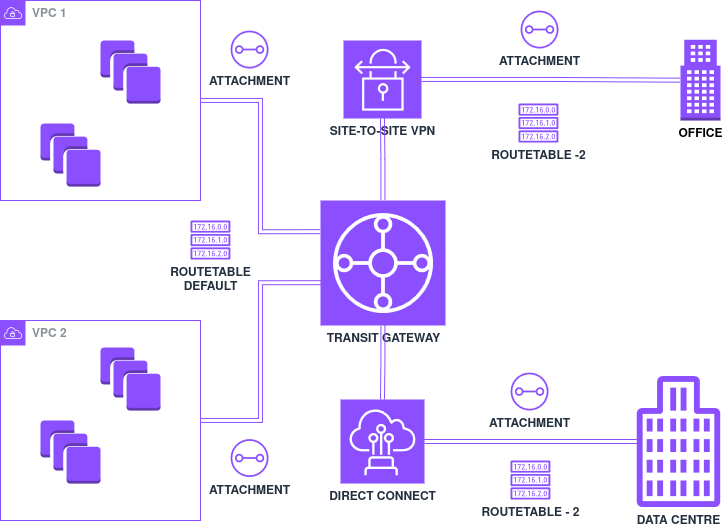
Attachments - Transit Gateway Attachments are connections that facilitate attaching different network entities like VPCs or VPNs to the transit gateway. Commonly supported attachments are:
VPCs
VPN Connections
Direct Connect Gateway
SD-WAN/Third-party Network Appliances
Another Transit Gateway
Route Tables - A transit gateway comes with a default route table, but can optionally have additional route tables. Like regular route tables, these route tables determine the next hop based on the destination IP address. Route tables can have static ( manual configuration ) or dynamic ( routing protocol-based) routes and the next hope in each route will be a Transit Gateway Attachment.
Routing Table Association - An attachment will be associated with exactly one route table. A route table within Transit Gateway might or might not be associated with an attachment
Route Propagation - Attachments can “advertise” routes to a Transit Gateway route table. If you enable route propagation for a VPC attachment, the subnet CIDRs of that VPC are automatically advertised to the associated Transit Gateway route table. Similarly, for on-premises connections, the CIDRs of on-premises networks can be automatically propagated to the Transit Gateway.
Transit Gateway is a regional resource, but it can have associations across regions or accounts. It can also peer with other Transit Gateways to segment or simplify network topologies. The following diagram provides a view of how Transit Gateway fits into AWS network architecture.
Advantages of Using AWS Transit Gateway
Centralized and Simplified Network Management - The biggest USPO of Transit Gateway is that it simplifies network management. Rather than handling a large number of point-to-point connections, TGW helps you centralize these connections with a hub and spoke architecture
Scalability and High Availability - TGW is a fully managed service and scales to handle your traffic automatically. There is no need to manually provision any network components or resize the SKUs as your network traffic needs evolve. The data plane traffic is distributed across multiple availability zones for high availability.
Consistent Performance - Transit Gateway traffic flows through the AWS backbone and that provides consistent performance for inter-VPC and hybrid connectivity. When you peer multiple Transit Gateways across Regions, traffic stays on AWS’s global private network, avoiding the unpredictable nature of the public internet.
Centralized Security and Monitoring - Since the transit gateway consolidates network traffic across your cloud infrastructure, it is easy to apply managed policies and network ACLs on it. As of September 2024, security group referencing is also enabled on Transit Gateways. The centralized nature also makes it easy to have network analysis, packet inspection, firewall capabilities, etc to be implemented in a centrally dedicated infrastructure. The VPC Flow Logs for TGW can be used for packet analysis across the AWS network infrastructure connected to it.
Flexible and Granular Routing Policies - The Transit gateway enables you to enforce granular control over routing. The ability to associate specific routing tables on individual attachments makes it easy to control routing. Transitive routing which was not possible between three or more VPCs is now possible with TGW. It is also possible to segment the network by controlling which parts of the network should and should not communicate with each other.
Cost-Effectiveness Over Large-Scale Deployments - While there is a cost associated with AWS Transit Gateway attachments and data processing, the service can be more cost-effective compared to managing a large mesh of VPC peering connections or multiple VPNs. The fewer network endpoints you have to configure, monitor, and secure, the lower your total administrative overhead. Many organizations also see cost savings by consolidating connectivity through Transit Gateway, particularly when egress or data transfer charges in multi-VPC environments are taken into account.
Common use cases of Transit Gateways
TGWs are used to centralize networking and ease management burden. But let us look at some of the use cases of how customers can make use of TGW in their infrastructure.
Interconnecting Multiple VPCs - A fundamental use case for AWS Transit Gateway is interconnecting multiple VPCs. In a complex cloud infrastructure, organizations will maintain 100s of VPCs. The regular VPC peering is one-to-one in nature and handling a large number of VPCs would require a large mesh of peer connections. TGW simplifies this mesh by providing a Hub-and-Spoke architecture for managing network infrastructure.
Hybrid Connectivity with On-Premises Data Centers - AWS Transit Gateway offers a cohesive way to connect on-premises data centers to AWS. Enterprises can use Site-to-Site VPN for smaller or less latency-sensitive workloads or opt for Direct Connect for more demanding, data-intensive applications. Once the on-premises networks are attached to the Transit Gateway, each VPC that is also attached can communicate as needed, all managed from a single routing domain
Multi-Region High-Availability and Disaster Recovery - For High Availability and business continuity plans, businesses invest in multi-region infrastructure. Reliable cross-connectivity between infrastructure in different regions is critical for such plans. Transit gateways can act as the central hub that facilitates the traffic routing between these regions.
Shared Services with central control and security - Create a hub of shared services/offerings that can be accessed from customer networks by integrating with the transit gateway. This will allow businesses to offer private/dedicated services to customers while maintaining control and ensuring security. A SaaS provider with tenant VPCs for each customer would be a good example of such a case.
SD-WAN Integration - A lot of organizations use traditional SD-WAN services from telecom/network vendors. Utilizing a transit gateway, this kind of infrastructure can be migrated to integrate with AWS, allowing for better management and security.
Additional Networking Features of Transit Gateways
Some of the additional features of the transit gateways that are worth mentioning are:
Larger MTU - The maximum transmission unit is the size of the largest packet that can go through a network. A larger MTU means better bandwidth and faster communication. While a lot of traditional networks have an MTU of 1500 bytes, TGW offers 8500 bytes MTU for many of its attachments.
ECMP - Equal cost multipathing is a network-level load balancing method that allows sending traffic to the same destination through multiple routes. The transit gateway supports ECMP for different types of attachments.
Multicast support - Multicast is a network protocol that allows sending the same message to a selected set of network destinations. The transit gateway supports multicast and provides options to configure multicast groups and destinations.
Transit gateways are a game changer in simplifying cloud network architecture, eliminating the need for complex mesh topologies and legacy hub and spoke networks. It is the key to maintaining a secure and efficient network topology with simplified management. This is very critical as your cloud footprint and complexity grow.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Safeer C M directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
