Simplifying Kubernetes with Kubestellar
 Pratik Mahalle
Pratik Mahalle
Introduction to Kubestellar: Simplifying Multi-Cluster Kubernetes Management
Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for container orchestration. However, managing multiple clusters across different environments can be complex. This is where Kubestellar comes in—a powerful open-source tool that simplifies multi-cluster Kubernetes management.
What is Kubestellar?
Kubestellar is an open-source framework designed to manage and synchronize configurations across multiple Kubernetes clusters efficiently. It extends KubeFed (Kubernetes Federation) concepts to make multi-cluster deployments seamless, scalable, and declarative.
Kubestellar is a Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) Sandbox project that simplifies the deployment and configuration of applications across multiple Kubernetes clusters. It provides a seamless experience akin to using a single cluster, integrating with familiar tools, and eliminating the need to modify existing resources.
Why Use Kubestellar?
Multi-Cluster Management: Easily distribute workloads and configurations across clusters.
Policy-Driven Synchronization: Define policies for deploying applications and services across clusters.
Scalability: Works well in cloud, hybrid, and on-premise environments.
Declarative Configuration: Uses Kubernetes-native YAML manifests for managing clusters.
Enhanced Security: Fine-grained access control to manage cluster permissions.
Kubestellar is particularly beneficial if you are:
Deploying in a single cluster but planning to expand to multiple clusters.
Using multiple clusters but seeking a more streamlined developer experience.
How Does Kubestellar Work?
Kubestellar operates by synchronizing resources across multiple clusters through declarative policies. It uses Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) to define multi-cluster deployments.
Key Components
Kubestellar Hub - The central control plane where all cluster configurations are managed.
Cluster Agents - Agents running on managed clusters that apply configurations from the Hub.
Synchronization Policies - Define how and where configurations should be deployed across clusters.
Spaces - Abstract API services that function like Kubernetes API servers to manage workloads.
Binding Policies - Define cluster and resource relationships to automate multi-cluster operations.
Kubestellar Architecture
Kubestellar follows a modular architecture that enables multi-cluster management efficiently. Below are the key components and their roles:
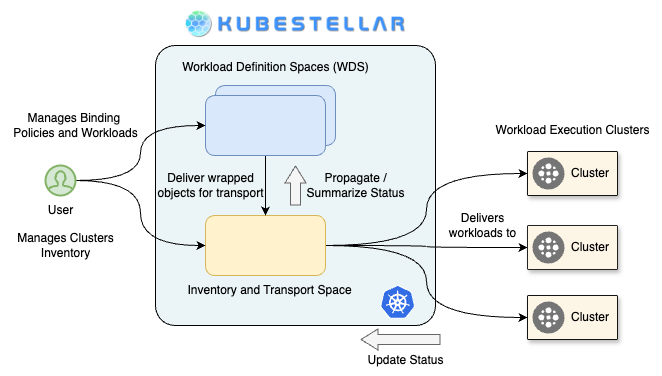
1. Kubestellar Hub
The central control plane for managing configurations and policies.
Stores metadata and synchronization rules.
Communicates with all connected clusters to apply configurations.
2. Cluster Agents
Run on each managed cluster.
Ensure configurations from the Kubestellar Hub are applied correctly.
Provide feedback to the Hub on the cluster's status and synchronization state.
3. Synchronization Policies
Define which resources should be synchronized and where they should be deployed.
Enable declarative configuration management.
Allow selective application of policies to different clusters.
4. Spaces
Spaces are Kubernetes-like API services used to manage workloads efficiently.
These include Workload Definition Spaces (WDS) and Inventory and Transport Spaces (ITS).
WDS stores workload definitions, while ITS manages cluster inventory and workload transport.
5. Binding Policies
Help in defining rules for distributing workloads.
Specify where resources should be applied and managed.
Enable workload placement decisions based on specific criteria.
Step by Step Setup
This walks you through the steps to produce the same configuration as the automated setup script, making it suitable for study but not production usage. For general setup information, see the full documentation.
Install Software Prerequisites
The following command will check for the prerequisites needed for installation. For more details, refer to the prerequisites documentation.
bash <(curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubestellar/kubestellar/v0.25.1/hack/check_pre_req.sh) kflex ocm helm kubectl docker kind
Cleanup from Previous Runs
If you have run this setup before, clean up any residual configurations using:
kind delete cluster --name kubeflex
kind delete cluster --name cluster1
kind delete cluster --name cluster2
kubectl config delete-context cluster1
kubectl config delete-context cluster2
Set the Version
kubestellar_version=0.25.1
Create a Kind Cluster to Host KubeFlex
bash <(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubestellar/kubestellar/v0.25.1/scripts/create-kind-cluster-with-SSL-passthrough.sh) --name kubeflex --port 9443
Use Core Helm Chart to Initialize KubeFlex
helm upgrade --install ks-core oci://ghcr.io/kubestellar/kubestellar/core-chart \
--version $kubestellar_version \
--set-json='ITSes=[{"name":"its1"}]' \
--set-json='WDSes=[{"name":"wds1"}]' \
--set-json='verbosity.default=5'
Wait for ITS to Initialize
kubectl --context kind-kubeflex wait controlplane.tenancy.kflex.kubestellar.org/its1 --for 'jsonpath={.status.postCreateHooks.its}=true' --timeout 90s
kubectl --context kind-kubeflex wait -n its1-system job.batch/its --for condition=Complete --timeout 150s
Create and Register Workload Clusters
clusters=(cluster1 cluster2);
for cluster in "${clusters[@]}"; do
kind create cluster --name ${cluster}
kubectl config rename-context kind-${cluster} ${cluster}
clusteradm --context its1 get token | grep '^clusteradm join' | sed "s/<cluster_name>/${cluster}/" | awk '{print $0 " --context '${cluster}' --singleton '"}' | sh
done
Approve Cluster Registration
clusteradm --context its1 accept --clusters cluster1
clusteradm --context its1 accept --clusters cluster2
Verify and Label Clusters
kubectl --context its1 get managedclusters
kubectl --context its1 label managedcluster cluster1 location-group=edge name=cluster1
kubectl --context its1 label managedcluster cluster2 location-group=edge name=cluster2
Now that your system is running, you can try some example scenarios to test Kubestellar’s multi-cluster workload deployment capabilities.
Additional Resources
For more details, refer to the official Kubestellar website for documentation, tutorials, and best practices.
Conclusion
Kubestellar is a game-changer for Kubernetes multi-cluster management. With its declarative, policy-driven approach, it significantly simplifies workload distribution, synchronization, and automation across clusters. Whether you're running a hybrid cloud setup, managing disaster recovery, or deploying globally distributed applications, Kubestellar provides the flexibility and scalability needed to streamline your operations.
Would you like to try Kubestellar in your Kubernetes setup? Get started today and unlock the full potential of multi-cluster management!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Pratik Mahalle directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Pratik Mahalle
Pratik Mahalle
A second year computer engineering student who is seeking to learn the devops.