Difference Between 4D and ActivePivot
 Abhijat Sarari
Abhijat Sarari
Introduction
Choosing the right database or analytical platform is crucial for business efficiency and data management. 4D and ActivePivot are two distinct technologies that cater to different needs. While 4D is a relational database and application development platform, ActivePivot is a real-time OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) engine designed for complex data analysis. This article provides an in-depth comparison of both, along with examples and use cases.
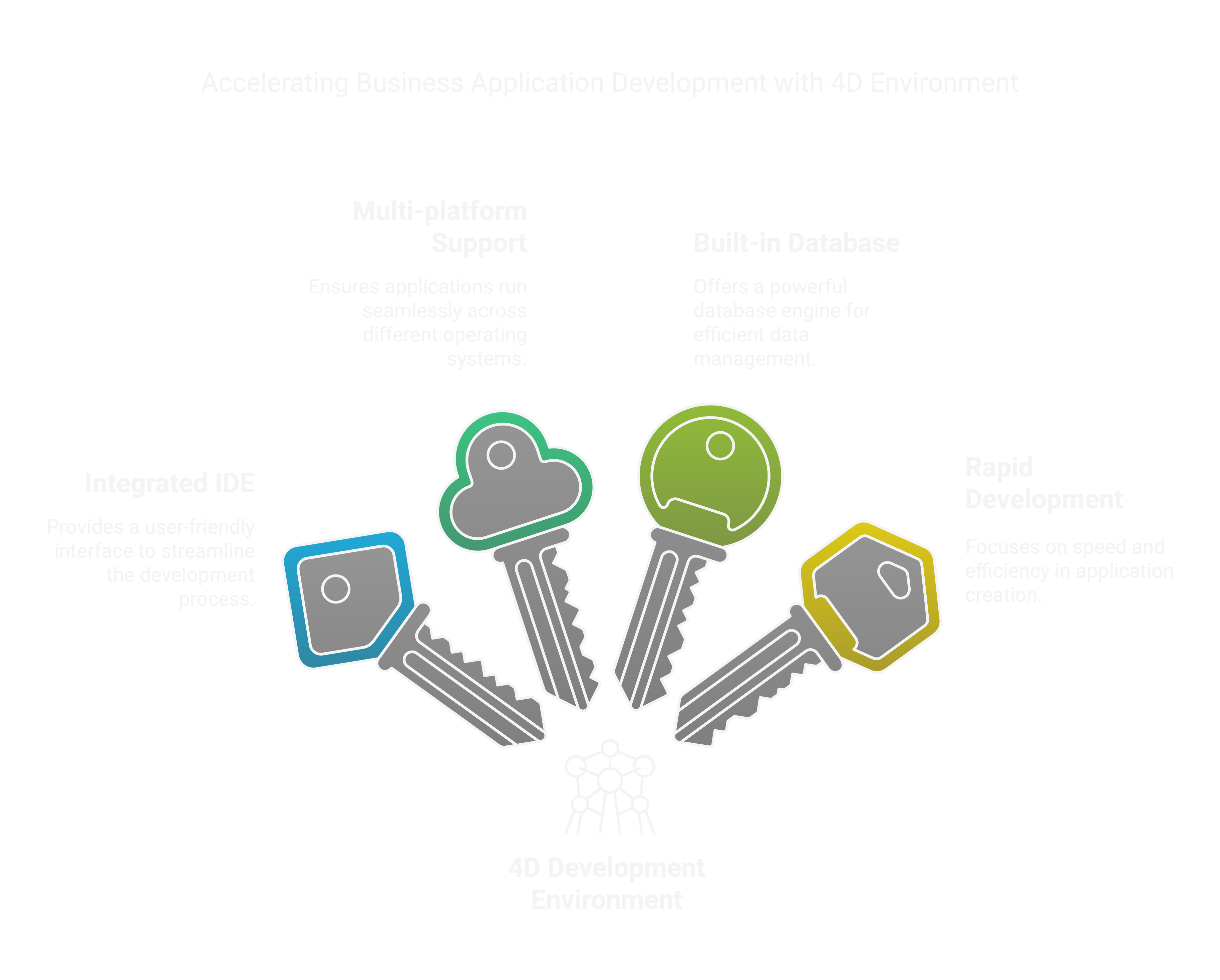
What is 4D?
4D is a relational database management system (RDBMS) with an integrated development environment (IDE). It is widely used for business applications, offering scalability, flexibility, and cross-platform support.
Key Features of 4D:
Relational Database: Supports SQL-based queries and structured data storage.
Integrated Development Environment: Facilitates application development and deployment.
Cross-Platform Support: Works on macOS and Windows.
Scalability: Suitable for small to medium-sized enterprises.
Built-in Web Server: Enables web application development.
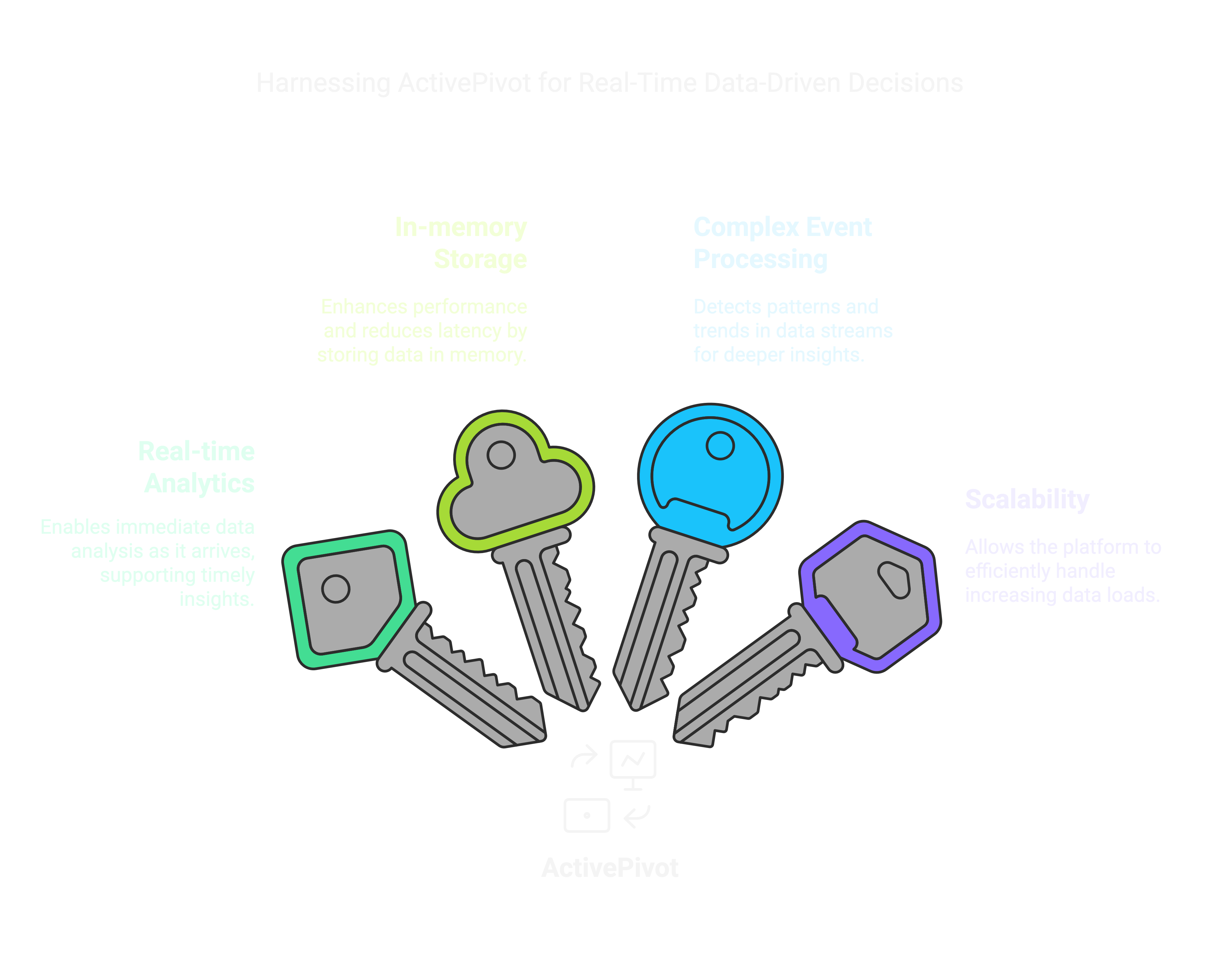
What is ActivePivot?
ActivePivot, developed by ActiveViam, is an in-memory OLAP engine designed for real-time data aggregation and analytics. It is primarily used in financial services, risk management, and supply chain analytics.
Key Features of ActivePivot:
Real-Time Data Processing: Enables instant data aggregation and analytics.
Multi-Dimensional Analysis: Supports complex queries on large datasets.
In-Memory Computation: Provides high-speed performance for analytics.
Scalable and Distributed: Can handle large-scale data environments.
Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics: Integrates with AI/ML workflows.
Comparison Table
| Feature | 4D Database | ActivePivot |
| Type | Relational Database | In-Memory OLAP Engine |
| Primary Use Case | Application development & data storage | Real-time analytics & business intelligence |
| Performance | Good for transactional applications | Extremely fast due to in-memory processing |
| Scalability | Moderate, suitable for SMBs | High, optimized for large-scale analytics |
| Data Model | Relational (SQL) | Multi-dimensional cubes |
| Querying Mechanism | SQL-based queries | MDX, Java, and custom APIs |
| Fault Tolerance | Replication & backups | Distributed fault-tolerant architecture |
| Integration | Web, mobile, desktop apps | AI, ML, financial applications |
Example Use Cases
Example: 4D for Business Application Development
Begin SQL
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Age > 30
End SQL;
This example demonstrates how 4D queries a customer database for users above 30 years old.
Example: ActivePivot for Real-Time Risk Analytics
ActivePivotManager manager = new ActivePivotManager();
manager.createCube("RiskAnalysis");
manager.aggregate("TotalRisk", "SUM");
This example showcases ActivePivot's real-time data aggregation for financial risk management.
When to Use 4D vs. ActivePivot
| Scenario | Best Choice |
| Building a business application with an embedded database | 4D |
| SQL-based relational data management | 4D |
| Real-time financial risk analytics | ActivePivot |
| Big data aggregation for instant insights | ActivePivot |
| Multi-dimensional OLAP analysis | ActivePivot |
Conclusion
4D and ActivePivot serve different purposes—4D is ideal for relational data storage and business application development, whereas ActivePivot excels in real-time, in-memory analytics for complex datasets. Selecting the right tool depends on the application's needs, whether it requires a traditional RDBMS or an advanced OLAP solution.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Abhijat Sarari directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
