Threat Modeling - Part 1
 Sukrit Dua
Sukrit Dua
What we will learn…
What is Threat modeling?
Threat modeling jargon - attack vectors, impact, severity, attack surface, and so on.
Threat Modeling
It’s simply a structured approach to pre-empt or identify risks that may exist in your system and you can build your security program around this instead of blindly following industry checklists. We try to answer questions such as what can go wrong, are we protected in that case, and how can we improve our security.
Our aim while building a threat model is to
Identify, Enumerate and Prioritize security risks
Identify Attack Vectors and Attack channels
Identify likelihood of risks identified
Identify controls and measures for addressing the risks
TM Jargon
Threat - Any potential danger or malicious action that can cause harm
Vulnerability - Any weakness that can be identified and exploited by a threat
Risk - Likelihood of the threat exploiting the vulnerability
Threat Actor - Agent that can identify and exploit the vulnerability
Threat Outcome - Result of a threat, C/I/A loss
Attack Surface - Self explanatory
Attack vector - Method/Technique used to perform an attack
Introduction of Vulnerabilities in our system
In a typical SDLC, if vulnerabilities are introduced during the initial design review phase is termed as a flaw.
The same vulnerabilities introduced in the Dev or deployment stage found are called Bugs.
Side note: As you can understand, findings issues as early as possible will save more money, time and effort. Threat modeling helps in exposing potential flaws in the early stages.
Impact and Likelihood
Our two favorite terms in cybersecurity!
Impact - Consequence of a threat identifying and exploiting a vulnerability (termed Severity as well)
Likelihood - Probability of a threat identifying and exploiting a vulnerability
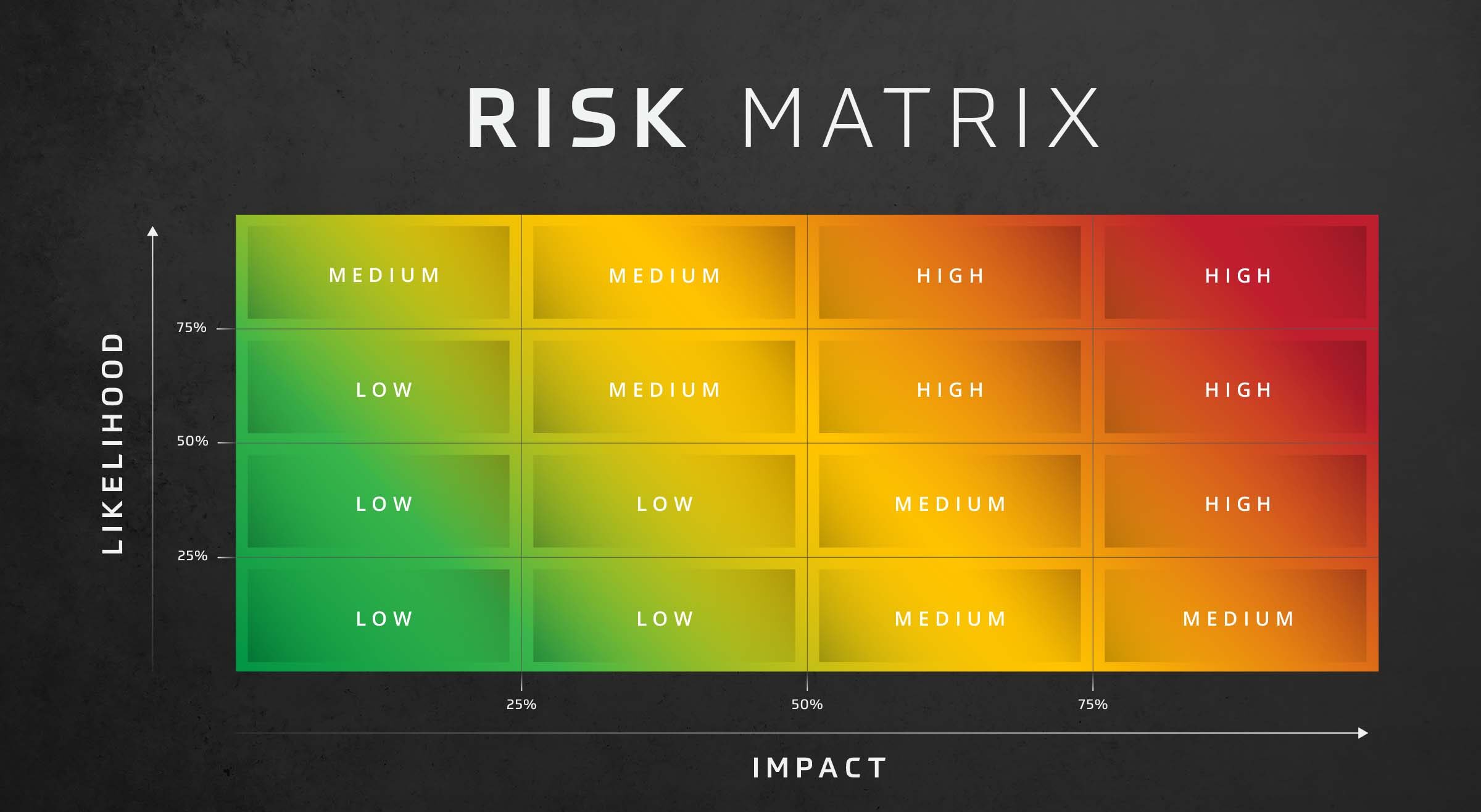
Risk is typically calculated by an Impact vs Likelihood matrix.
Source: HBS
Risk helps with assessing potential damage and ways to manage it.
Risk Management
The 4 Ts of Risk management are:
Treat it - Mitigation
Terminate it - Removal of source of risk
Transfer it - Transference (Insurance/Contracts etc)
Tolerate it - Acceptance
Treating and Transferring Risks
Preventive - Encryption, Access control etc.
Detective - Logging and Monitoring
Corrective - Backups
See you in the next one where we will talk about Trust Boundaries & Trust Zones.
Note: This threat modeling article series is a documentation of my learning from various sources including but not limited to AppSecEngineer, INE, OWASP, Youtube and more.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sukrit Dua directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by