Data Warehousing with AWS Redshift
 Avinash Reddy
Avinash ReddyBusinesses these days require efficient ways to query and analyze vast amounts of data quickly. AWS Redshift is one way to fully manage your data warehouse, along with scalability, speed and integration with AWS services.
In my recent Proof of Concept (POC), I demonstrated how to set up and use AWS Redshift to query large datasets remotely with speed and efficiency.
By the end of this blog, you will understand:
How to set up an AWS Redshift cluster
How to integrate Redshift with SQL Workbench
How to store and retrieve large datasets from Amazon S3
How to use AWS QuickSight for designing dashboards out of raw data
Let’s go!
Prerequisites
An AWS account with appropriate permissions
Basic knowledge of SQL
SQL Workbench and Java Development Kit (JDK 8)
An Amazon S3 bucket for data storage
Step 1: Launching a Windows EC2 Instance
Since we’ll be using SQL Workbench to interact with Redshift, we need an environment.
Create a Windows instance from EC2, with at least 4GB RAM.
Connect to the instance via RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol).
Download and install SQL Workbench.
Install JDK 8 to enable the Redshift JDBC driver.
Step 2: Setting Up an AWS Redshift Cluster
Now, let’s create a Redshift cluster to handle our data warehousing needs.
Create a subnet group in a VPC as you wish.
Open the AWS Redshift console.
Click Create Cluster and configure the following:
Cluster Type: Single Node (for POC, use a free-tier eligible option)
Node Type: dc2.large
Database Name:
redshift_pocMaster Username:
adminMaster Password:
yourpassword
Click Create Cluster and wait for it to be available.
Once the cluster is running, copy the Endpoint URL from the cluster’s details.
Step 3: Connecting SQL Workbench to Redshift
To query Redshift, we need to connect it with SQL Workbench.
From the windows instance that is setup, open SQL Workbench
Download the AWS Redshift JDBC driver and configure it.
Create a new connection and enter the following details:
Driver: Select Redshift JDBC
Get the jar file from Redshift
URL:
jdbc:redshift://your-cluster-endpoint:5439/redshift_pocUsername:
adminPassword:
yourpassword
Click Test Connection to ensure connectivity.
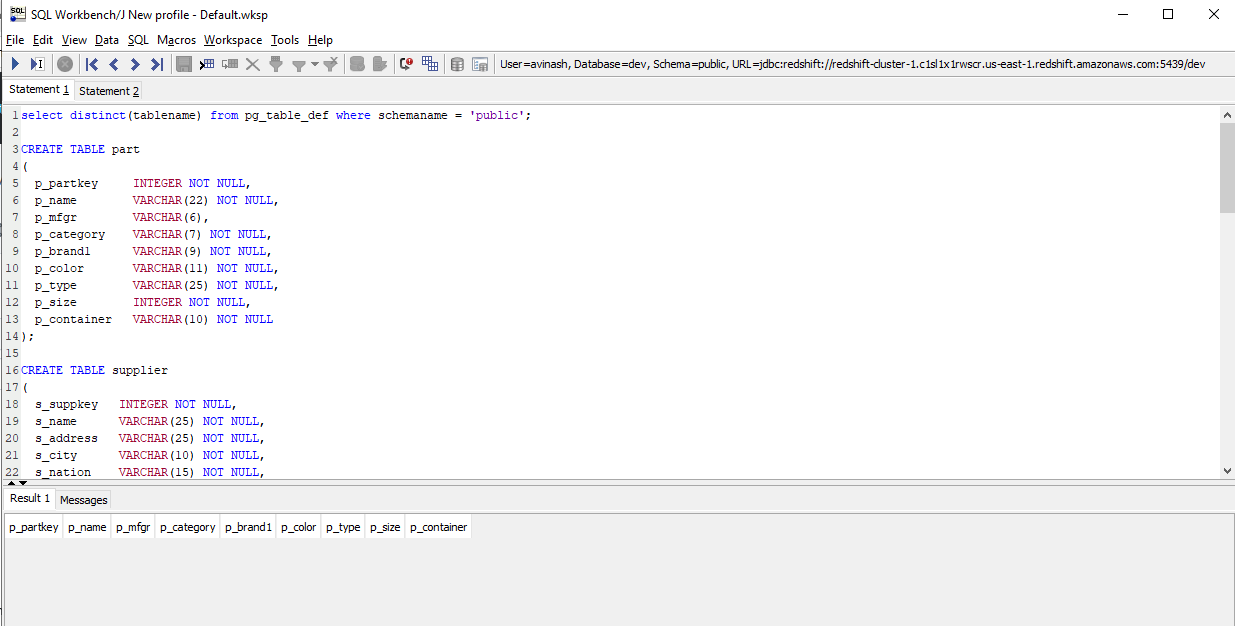
Step 4: Creating a Table in Redshift
We will create a table in Redshift and later load data from an Amazon S3 backup. You can checkout my Github repo for the script.
select distinct(tablename) from pg_table_def where schemaname = 'public';
CREATE TABLE part
(
p_partkey INTEGER NOT NULL,
p_name VARCHAR(22) NOT NULL,
p_mfgr VARCHAR(6),
p_category VARCHAR(7) NOT NULL,
p_brand1 VARCHAR(9) NOT NULL,
p_color VARCHAR(11) NOT NULL,
p_type VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
p_size INTEGER NOT NULL,
p_container VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL
);
select * from part
CREATE TABLE supplier
(
s_suppkey INTEGER NOT NULL,
s_name VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
s_address VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
s_city VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
s_nation VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
s_region VARCHAR(12) NOT NULL,
s_phone VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE customer
(
c_custkey INTEGER NOT NULL,
c_name VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
c_address VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
c_city VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
c_nation VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
c_region VARCHAR(12) NOT NULL,
c_phone VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
c_mktsegment VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE dwdate
(
d_datekey INTEGER NOT NULL,
d_date VARCHAR(19) NOT NULL,
d_dayofweek VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
d_month VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
d_year INTEGER NOT NULL,
d_yearmonthnum INTEGER NOT NULL,
d_yearmonth VARCHAR(8) NOT NULL,
d_daynuminweek INTEGER NOT NULL,
d_daynuminmonth INTEGER NOT NULL,
d_daynuminyear INTEGER NOT NULL,
d_monthnuminyear INTEGER NOT NULL,
d_weeknuminyear INTEGER NOT NULL,
d_sellingseason VARCHAR(13) NOT NULL,
d_lastdayinweekfl VARCHAR(1) NOT NULL,
d_lastdayinmonthfl VARCHAR(1) NOT NULL,
d_holidayfl VARCHAR(1) NOT NULL,
d_weekdayfl VARCHAR(1) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE lineorder
(
lo_orderkey INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_linenumber INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_custkey INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_partkey INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_suppkey INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_orderdate INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_orderpriority VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
lo_shippriority VARCHAR(1) NOT NULL,
lo_quantity INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_extendedprice INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_ordertotalprice INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_discount INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_revenue INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_supplycost INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_tax INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_commitdate INTEGER NOT NULL,
lo_shipmode VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL
);
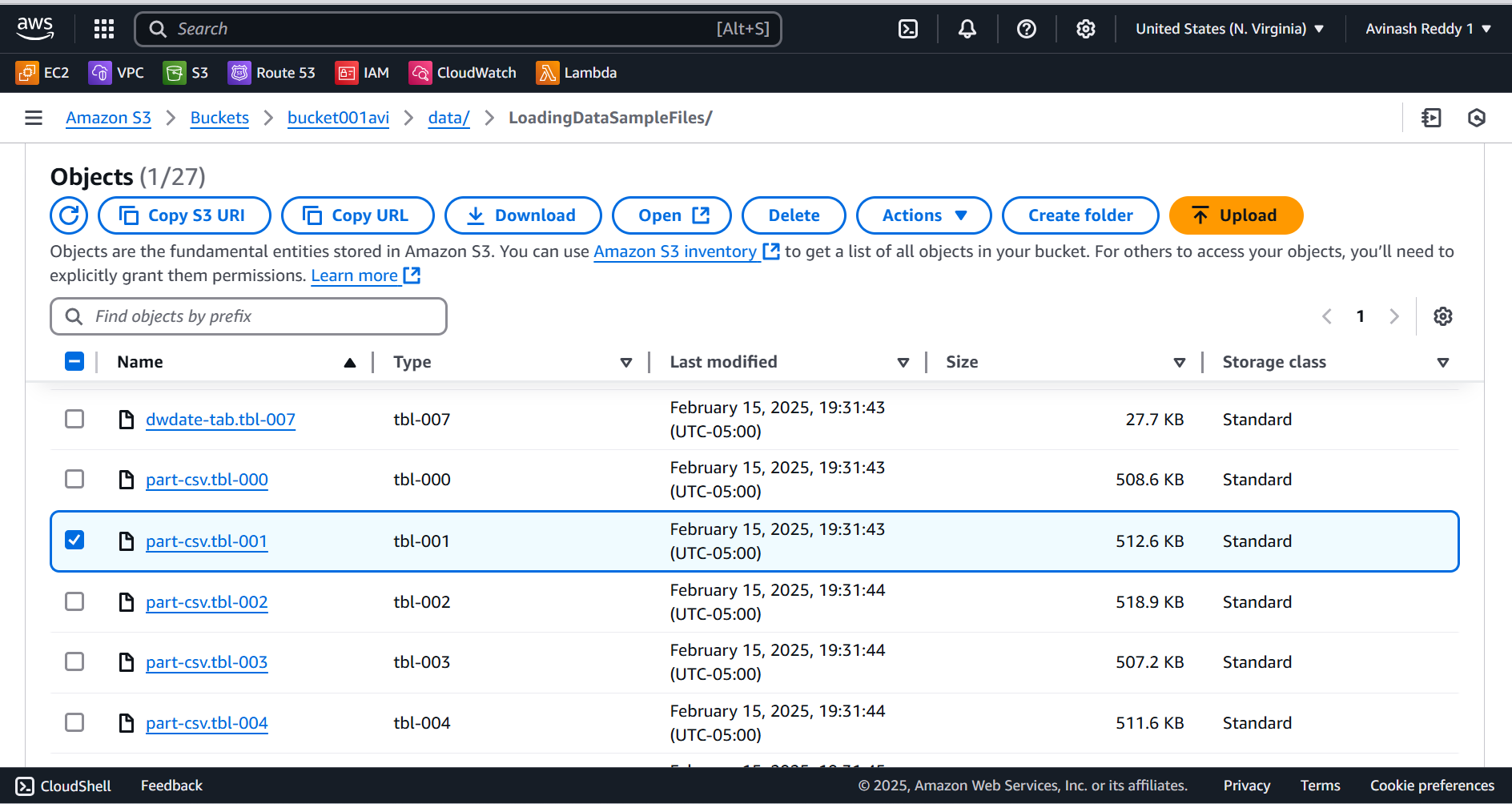
Step 5: Storing and Loading Data from Amazon S3
AWS Redshift allows us to pull large datasets from Amazon S3, making it efficient for analytics.
Upload a sample dataset to an S3 bucket. (you can make use of this one)
Create an IAM Role that allows Redshift to access S3.
Attach this role to your Redshift cluster.
Also create an IAM user for access keys to connect workbench to S3.
Run the following command in Workbench from Windows instance to load data from S3:
copy part
from 's3://bucket001avi/data/LoadingDataSampleFiles/part-csv.tbl-001'
credentials 'aws_access_key_id=xxxxxxxxxx;aws_secret_access_key=xxxxxxxxx'
csv
null as '\000';
This populates the data to Workbench from S3.
Step 6: Querying the Data
Once the data is loaded, queries can be performed efficiently.
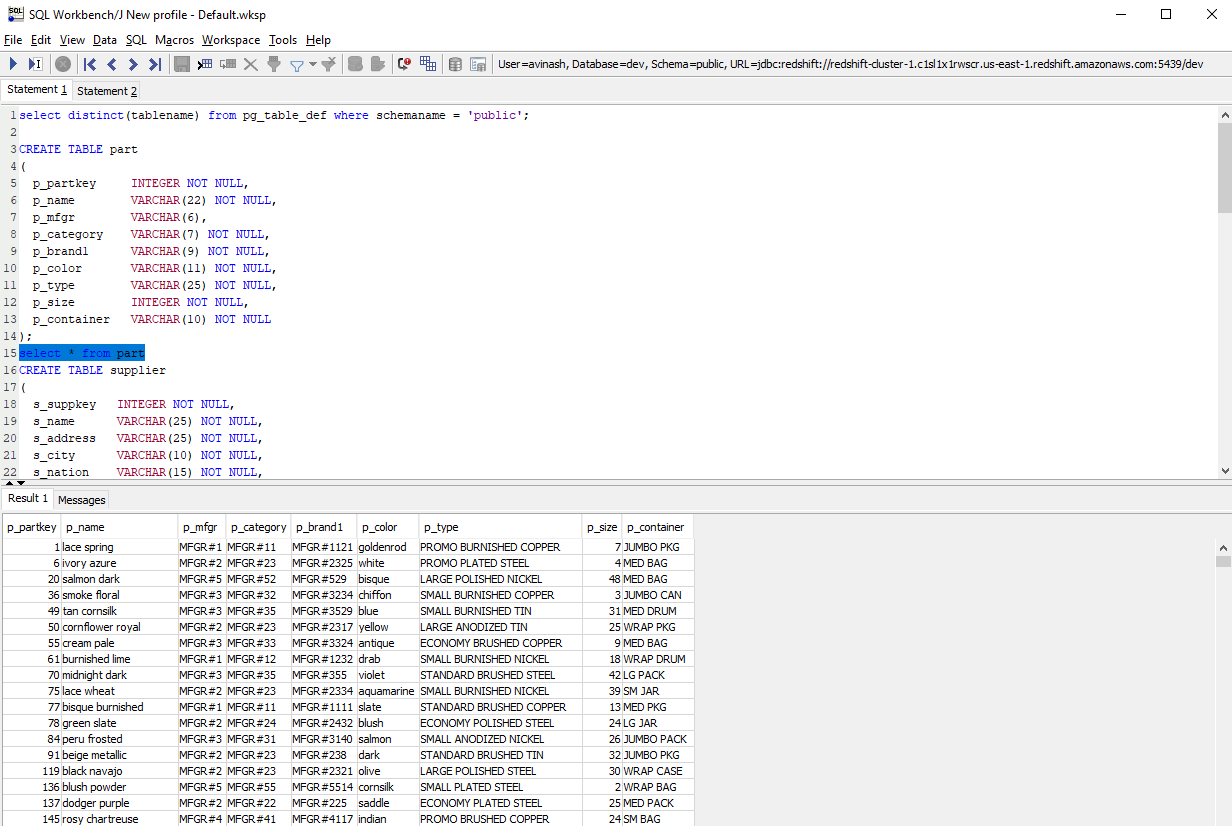
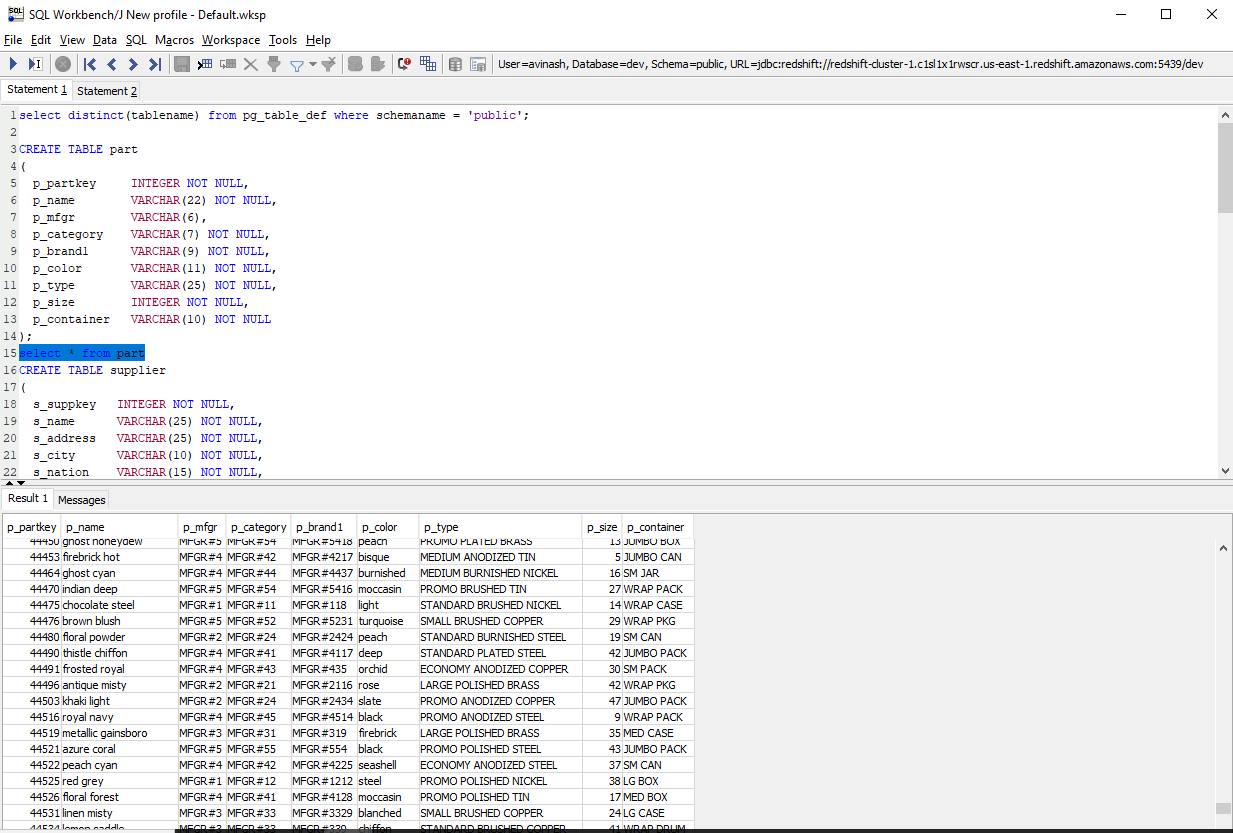
This query helps pull out details about parts in that company.
Real-time Use Cases
An e-commerce company can analyze customer purchases and browsing patterns to personalize recommendations.
A bank can monitor unusual credit card transactions in real time to flag potential fraud.
A smart city traffic system can collect and process live traffic data to optimize signal timings.
Conclusion
My POC demonstrated how AWS Redshift efficiently queries large amounts of data quickly and handles large datasets by integrating with Amazon S3 and SQL Workbench, making Redshift an excellent choice for data warehousing solutions.
Let me know your thoughts on this. Cheers!
Credits: Saikiran P. on YT
#AWS #Redshift #SQL #Data
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Avinash Reddy directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
