Article Review: Deep learning based time of flight ToF enhancement of non ToF PET scans for different radiotracers
 Aldo Yang
Aldo Yang2 min read
Objectives
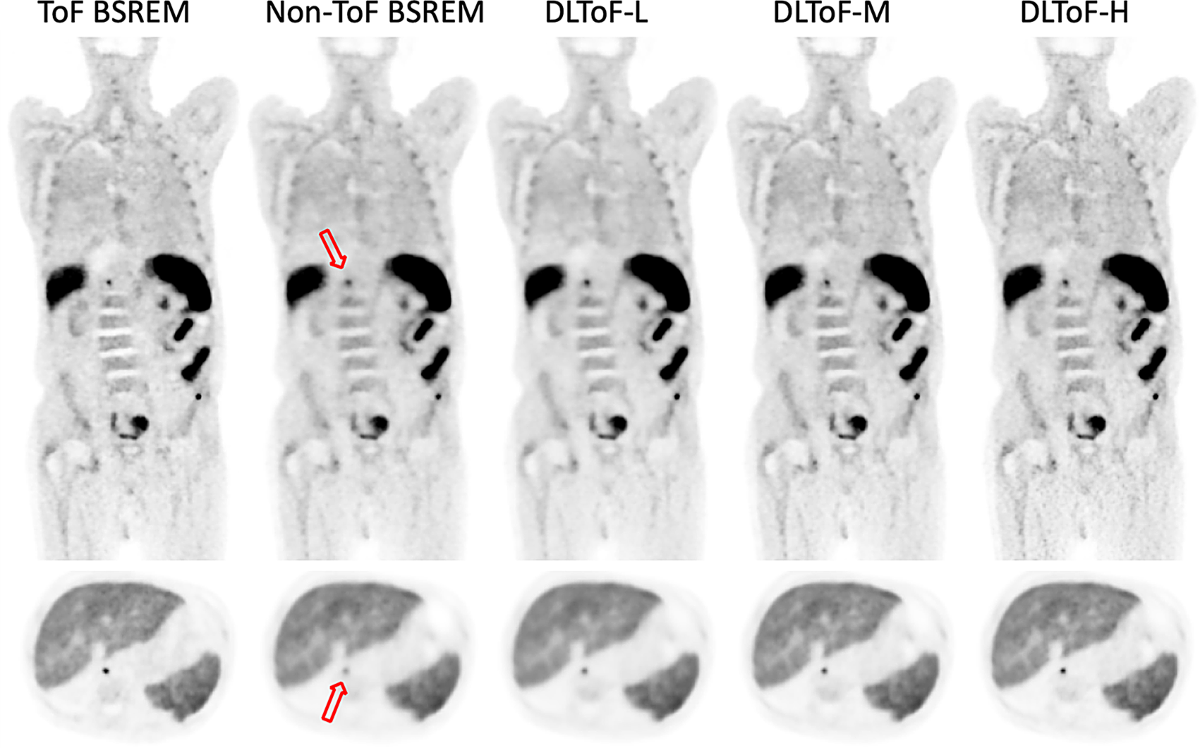
- Developed deep learning-based time-of-flight (DLToF) models to enhance non-ToF PET images, making them comparable to ToF PET images.
- Trained models with a range of radiotracers (18F-FDG, 18F-PSMA, 68Ga-PSMA, 68Ga-DOTATATE) for oncology, prostate, and neuroendocrine tumor PET imaging.
- Offered three levels of model strength (Low, Medium, High) to accommodate user preferences for contrast and noise.
- Demonstrated improved lesion detectability and quantification, particularly with the DLToF-H model.
Methodology
- Implemented a 3D U-Net network with residual and skip connections in PyTorch.
- Trained DLToF networks in a supervised session using mean squared error (MSE) loss function.
- Used the ADAM algorithm to update the networks' trainable parameters.
- Training data included 309 datasets from 11 sites, with 8 different tracers (75% FDG, 25% non-FDG).
- Adjusted the beta value of target ToF images to define the contrast and noise properties of each model (Low, Medium, High).
Results
- Quantitatively evaluated using 60 testing datasets (15 exams per 4 radiotracers).
- DLToF-H reduced non-ToF BSREM errors in lesion SUVmax:
- 18F-FDG: from -39% to -6% (38 lesions).

- 18F-PSMA: from -42% to -7% (35 lesions).
- 68Ga-PSMA: from -34% to -4% (23 lesions).
- 68Ga-DOTATATE: from -34% to -12% (32 lesions).
- 18F-FDG: from -39% to -6% (38 lesions).
- Clinical reader study (4 readers) showed DLToF-H improved lesion detectability, DLToF-L had highest image quality scores, and DLToF-M had best diagnostic confidence scores.
- Liver noise measurements showed DLToF-L had lower noise than non-ToF BSREM, and DLToF-H had noise levels similar to or slightly higher than ToF images.

Discussions
- The study demonstrates a well-designed deep learning approach for enhancing non-ToF PET images. However, the testing sets were chosen with small and low-contrast lesions, potentially biasing the results towards emphasizing the gap between ToF and non-ToF reconstructions.
- The readers were shown all 5 image series of a subject simultaneously, which might introduce bias, although it could help in identifying false positives or missing lesions.
- A data sufficiency experiment for the proportion of multi-tracer datasets was not performed. Future work should address this.
- The study lacks quantitative and clinical evaluation of the trained models on Omni Legend™ PET/CT scanners. This should be a focus of future research.




Reference: Deep learning based time of flight ToF enhancement of non ToF PET scans for different radiotracers
0
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aldo Yang directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
