Cloud Computing: What It Is and How It's Rapidly Growin
 Stefania Gil
Stefania Gil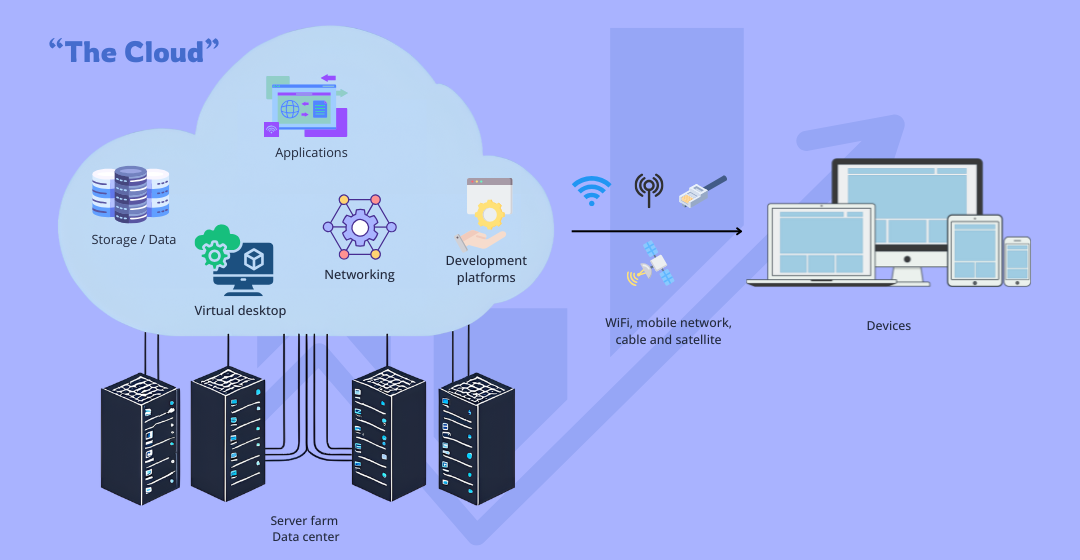
The Beginnings of Cloud Computing
When the internet was in its early days, companies used high-powered computers to host websites and store files. These computers were the first servers. Each computer could run multiple websites, and the computer's storage had all the files needed for the site stored on it.
As internet technology evolved, server farms were developed, where hundreds and then thousands of servers were networked together to share the tasks or workloads involved in delivering hundreds of websites and services.
What is the Cloud?
The cloud is an evolution of these server farms. Early internet servers were designed by computer scientists to provide websites with all the necessary services, such as storage, networking, and security, all in a single server.
Today, the cloud offers a much more advanced and flexible infrastructure, allowing businesses to access scalable computing resources, AI services, distributed databases, and highly secure storage solutions without the need to manage their own hardware.
The Role of Data Centers in Cloud Computing
Data centers are the foundation of cloud computing as they provide the necessary physical infrastructure to store, process, and distribute large volumes of data. These facilities are specifically designed to house server farms, with advanced cooling, security, and power redundancy systems to ensure uninterrupted and reliable operations.
Thanks to data centers, cloud providers can offer scalable services, run complex applications, and provide high-availability connectivity to users. They are the core where computing, storage, and network resources are managed to enable cloud computing.
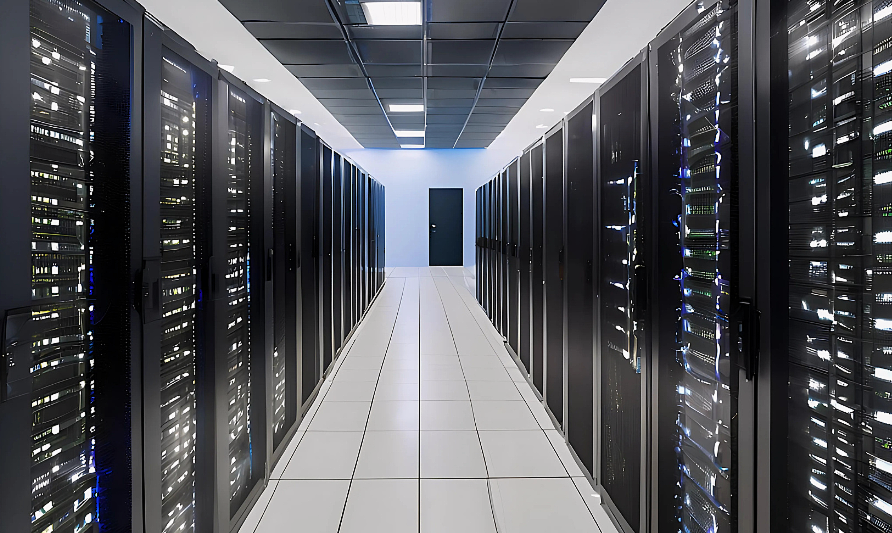

Data center (created with Canva).
Data Centers Working Together
Since cloud service providers operate globally, they distribute their data centers across different regions of the world. These facilities are designed to provide a secure and controlled environment, ensuring the reliable operation of cloud infrastructure.
Through advanced software, providers synchronize data and services across multiple data centers, enabling efficient access, continuous availability, and a consistent experience for users in any location.
An example of how cloud service providers manage their infrastructure is IBM, which has data centers spread globally. To learn more about where they are located, you can visit: IBM - Data Centers.
Services Hosted in the Cloud
Data Storage
Cloud storage allows users to securely store, manage, and retrieve information. Some of the most widely used services include Google Drive and AWS S3, which offer flexible and accessible solutions for storing and sharing files. Other services such as Azure Blob Storage from Microsoft, IBM Cloud Object Storage, and Google Cloud Storage efficiently handle large volumes of unstructured data. Additionally, data lakes, such as those offered by AWS Glacier and Azure Data Lake Storage, allow for long-term storage of vast amounts of data, optimizing the large-scale analysis of information.
Virtual Machines
Virtual machines provide scalable infrastructure that allows users to run operating systems and applications on remote servers. They are fundamental in IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) models such as AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine, which allow businesses to access flexible computing power without investing in physical hardware. These services offer on-demand scalability, making it easier to adjust resources as business needs change.
Applications
Cloud applications allow users to access software from any device without the need for installation. This includes popular tools like Google Workspace, which offers online productivity solutions, Dropbox, for file storage and collaboration, and Salesforce, a leading cloud-based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform.
Networking
Cloud networking ensures efficient and secure connectivity between devices and services. This includes the use of VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for secure connections, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for system integration, CDNs (Content Delivery Networks) for accelerating content delivery, SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) for network optimization, VPCs (Virtual Private Clouds) for creating private networks, and load balancers for traffic distribution. Services such as AWS Direct Connect and Azure ExpressRoute provide dedicated, high-capacity connections between on-premise infrastructure and the cloud.
Development Platforms
Development platforms offer ready-to-use environments for building and deploying software without managing infrastructure. Services like AWS Lambda, Google App Engine, and Firebase allow developers to focus on writing code, removing the need to worry about server management.
Importance of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers a key alternative to traditional IT infrastructure, which often requires significant time and money. Companies opting for on-premise systems must purchase physical servers and other resources, a provisioning process that can take months. Additionally, this infrastructure requires specialized physical space, such as a room with enough power and cooling capacity. Once the systems are installed and configured, companies need experts to manage and maintain the IT architecture.
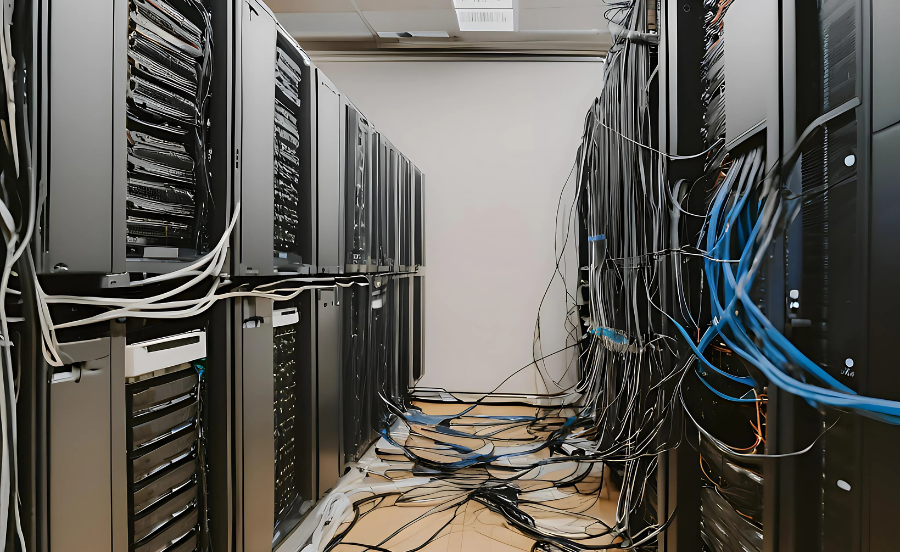

Local data center with limited space, complex and difficult to maintain (created with Canva).
This process becomes even more complex during periods of high demand or when the business is experiencing rapid growth. Often, businesses end up acquiring more resources than necessary, leading to underutilization of infrastructure.
Cloud computing solves these problems by offering scalable, on-demand services without the need for physical infrastructure. Businesses can adjust their resources based on demand, pay only for what they use, and avoid resource overload. This not only improves operational efficiency but also allows companies to focus on their strategic objectives without worrying about managing and maintaining infrastructure.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers significant advantages, such as cost-effectiveness, by eliminating the need for local infrastructure. It enhances speed and agility, providing quick access to applications without relying on hardware and software managed by IT teams. Additionally, it offers unlimited scalability, adjusting resources according to demand. It also provides improved strategic value, enabling access to innovations such as artificial intelligence, enhancing the customer experience, and freeing up teams for more strategic tasks.
Growth of Cloud Computing in Recent Years
In recent years, the adoption of cloud computing has grown significantly, transforming industries such as technology, healthcare, education, and fintech. This trend has enabled businesses to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and drive innovation in their services.
According to Computer Reseller News (CRN), a specialized tech and business media outlet, market leaders in cloud computing—Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud—have demonstrated notable revenue growth.
Google Cloud reported a 35% year-over-year revenue increase in the third quarter of 2024, rising from $8.4 billion in third-quarter 2023 to $11.4 billion.
Meanwhile, Microsoft’s Intelligent Cloud division recorded $24.1 billion in net revenue, reflecting a 20% increase from the $20 billion reported the previous year. Microsoft's server and cloud services revenue increased 23 percent year over year in the quarter, driven by 33 percent growth in Azure and other cloud services revenue.
Similarly, AWS grew its total revenue 19 percent year-over-year to $27.5 billion compared to $23 billion in the third quarter of 2024.
This consistent expansion highlights cloud computing as a fundamental driver of digital transformation, enabling companies across various industries to scale, innovate, and optimize their operations efficiently.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Stefania Gil directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
