What is Zero Copy in Kafka?
 clasnake
clasnake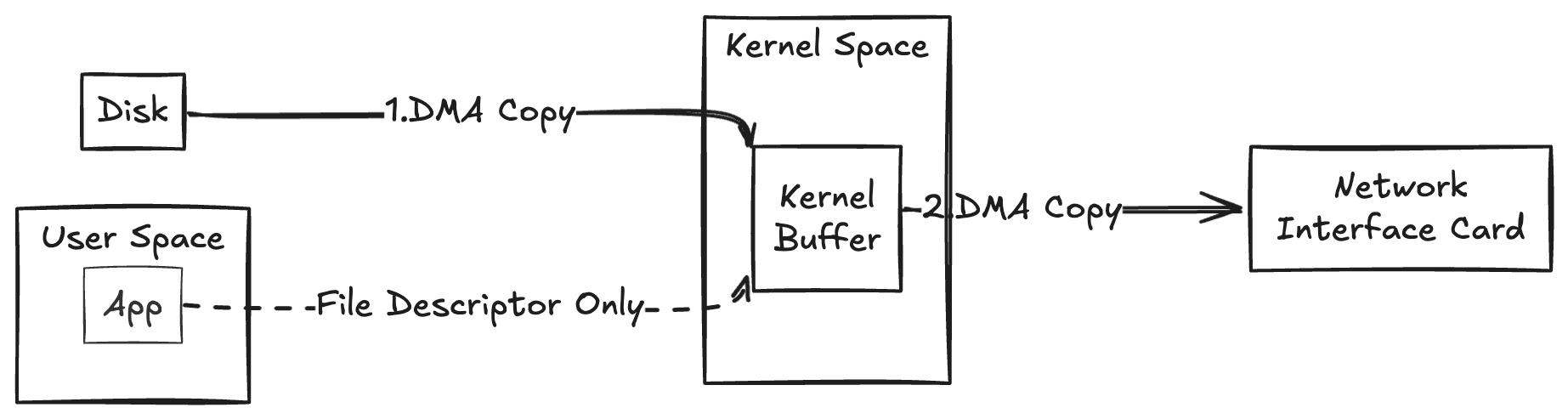
What is Zero Copy?
Zero Copy is a technique that eliminates unnecessary data copying between memory regions by the CPU. In Kafka, this technology optimizes data transfer from disk files to the network, reducing redundant data copies and improving transmission efficiency.
Traditional Copy vs. Zero Copy
Traditional Copy Process

The traditional data copy process involves 4 copies and 4 context switches:
Disk --> Kernel Buffer
Kernel Buffer --> Application Buffer
Application Buffer --> Socket Buffer
Socket Buffer --> NIC Buffer
Zero Copy Process

Zero Copy requires only 2 copies and 2 context switches:
Disk --> Kernel Buffer
Kernel Buffer --> NIC Buffer
Performance Benefits of Zero Copy
Reduced CPU Copy Operations
Decreased from 4 copies to 2
Lower CPU utilization
Fewer Context Switches
Reduced from 4 switches to 2
Decreased system call overhead
Enhanced Data Transfer Efficiency
Direct data flow from page cache to NIC
Elimination of intermediate buffers
Zero Copy Implementation in Kafka
Kafka's Zero Copy implementation relies on two key features of Java NIO: memory mapping (mmap) and the sendfile system call. These mechanisms offer different advantages for optimizing data transfer efficiency.
1. mmap (Memory Mapping)
Memory mapping allows direct access to kernel space memory from user space, eliminating the need to copy data between kernel and user space. This method is particularly effective for small file transfers.
// Implementing memory mapping using MappedByteBuffer
FileChannel fileChannel = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw").getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer buffer = fileChannel.map(
FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, fileChannel.size());
2. sendfile
Introduced in Linux 2.1, sendfile is a system call that directly transfers data between file descriptors. It's ideal for large file transfers and is implemented through FileChannel's transferTo method in Java NIO.
// Implementing Zero Copy using transferTo
public static void transferTo(String source, String dest) throws IOException {
FileChannel sourceChannel = new FileInputStream(source).getChannel();
FileChannel destChannel = new FileOutputStream(dest).getChannel();
sourceChannel.transferTo(0, sourceChannel.size(), destChannel);
}
Comparison of Implementation Methods
mmap:
Pros: Suitable for small files, supports random access
Cons: Higher memory usage, potential page faults
sendfile:
Pros: Optimal for large files, more efficient Zero Copy
Cons: No data modification support, whole-file transfer only
Applications in Kafka
1. Log File Transfer
Brokers use Zero Copy to efficiently send log files directly to consumers
Leverages sendfile for high-performance bulk log transfer
Significantly reduces memory usage and CPU overhead
2. Message Production and Consumption
Optimizes network transfer for large batch message production
Enables efficient data retrieval during batch consumption
Uses mmap for flexible access to small message batches
3. Cluster Data Synchronization
Facilitates efficient data transfer from Leader to Follower replicas
Reduces network overhead in cross-datacenter replication
Accelerates large-scale data migration processes
Best Practices
Strategic Implementation
Choose implementation based on file size: mmap for files under 1MB, sendfile for larger files
Apply appropriate methods per use case: sendfile for log transfer, mmap for random access
Balance memory usage and performance: monitor available system memory
Performance Monitoring
Track key metrics: CPU usage, memory utilization, I/O wait times
Set appropriate alerts: trigger at 70% CPU or 80% memory usage
Identify bottlenecks through I/O wait time analysis
Configuration Optimization
Tune system parameters: adjust vm.max_map_count, file descriptors
Optimize memory allocation: configure JVM heap size, reserve page cache memory
Fine-tune socket buffer sizes based on workload
Security Considerations
Monitor file descriptor leaks
Plan capacity based on growth projections
Implement robust backup strategies
Summary
Zero Copy is a fundamental technology behind Kafka's high performance. By minimizing data copies and context switches, it significantly improves data transfer efficiency. Success in implementation requires careful consideration of use cases and ongoing performance monitoring.
Related Resources:
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from clasnake directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
