Mastering Technologies Used for Real-Time Data Communication
 Shayan Danish
Shayan DanishIn the ever-evolving world of web development, real-time technologies have become essential for delivering seamless user experiences. Whether it's live chat, collaborative editing, or stock price updates, the right real-time technology can make all the difference. Here’s a deep dive into the five key real-time technologies and when to use them.
1️⃣ WebSockets → The Gold Standard for Real-Time Communication 🔥
🔹 Use Case:
Real-time chat applications (WhatsApp, Slack, Discord)
Live updates in web apps (Google Docs, Figma, TradingView)
Multiplayer gaming and collaborative tools
🔹 Why Learn It?
✅ WebSockets enable bi-directional, persistent communication between the server and client. ✅ They provide low latency, making them the best choice for highly interactive applications.
Where It’s Used?
💡 Google Docs, WhatsApp, Figma, TradingView
2️⃣ Server-Sent Events (SSE) → One-Way Data Streaming 🌟
🔹 Use Case:
Stock market price updates
Social media notifications (Facebook, Twitter feeds)
Live news and sports score updates
🔹 Why Learn It?
✅ SSE is lighter than WebSockets, ideal for real-time updates where clients only receive data (unidirectional). ✅ Works over a single HTTP connection, reducing overhead.

🔹 Where It’s Used?
💡 Facebook notifications, Twitter feeds, Stock Market apps ❌ Not suitable for two-way communication—use WebSockets instead.
3️⃣ WebRTC → The Power Behind Video, Audio, and Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Communication 🌍
🔹 Use Case:
Video & audio calls (Google Meet, Zoom, WhatsApp Calls)
Screen sharing & P2P file sharing (WebTorrent, Clubhouse)
Ultra-low latency media streaming
🔹 Why Learn It?
✅ Uses peer-to-peer (P2P) communication, eliminating the need for a central server. ✅ Built on UDP, ensuring minimal delay for real-time communication.
🔹 Where It’s Used?
💡 Google Meet, Zoom, Discord Voice, WhatsApp Video Calls ❌ Not necessary if your app doesn’t involve media streaming.
4️⃣ Long Polling → The Legacy Fallback ⚡
🔹 Use Case:
When WebSockets or SSE aren’t available (e.g., in legacy systems)
Chat applications & notifications in outdated environments
🔹 How It Works?
The client sends a request to the server.
The server holds the request open until new data is available.
Once the response is sent, the client immediately sends another request.
🔹 Why It’s NOT Ideal?
❌ Higher latency and inefficient resource usage. ❌ Consumes more server resources compared to WebSockets or SSE.

🔹 Where It’s Used?
💡 Older chat applications, outdated real-time systems.
5️⃣ Short Polling → The Last Resort 🛑
🔹 Use Case:
Basic periodic updates (e.g., checking for new messages every few seconds)
Legacy applications where real-time updates aren’t critical
🔹 How It Works?
The client makes HTTP requests at fixed intervals (e.g., every 5 seconds).
The server responds with the latest available data.
🔹 Why It’s BAD?
❌ Inefficient and wastes bandwidth. ❌ Delays updates since the client only checks periodically.
🔹 Where It’s Used?
💡 Basic notification systems, outdated APIs.
🚀 Final Takeaway: What to Use in Modern Web Apps?
| Technology | Best For | Should You Learn It? |
| WebSockets | Real-time chat, live updates, multiplayer games, collaborative tools | ✅ Yes, Essential |
| SSE (Server-Sent Events) | Stock prices, social media feeds, live notifications | ✅ Yes, useful for one-way updates |
| WebRTC | Video calls, voice chats, P2P file transfers | ✅ Yes, if media streaming is required |
| Long Polling | Chat & real-time updates in legacy systems | ❌ Only for old systems when WebSockets aren’t available |
| Short Polling | Checking for updates at intervals | ❌ Only as a last resort (inefficient) |
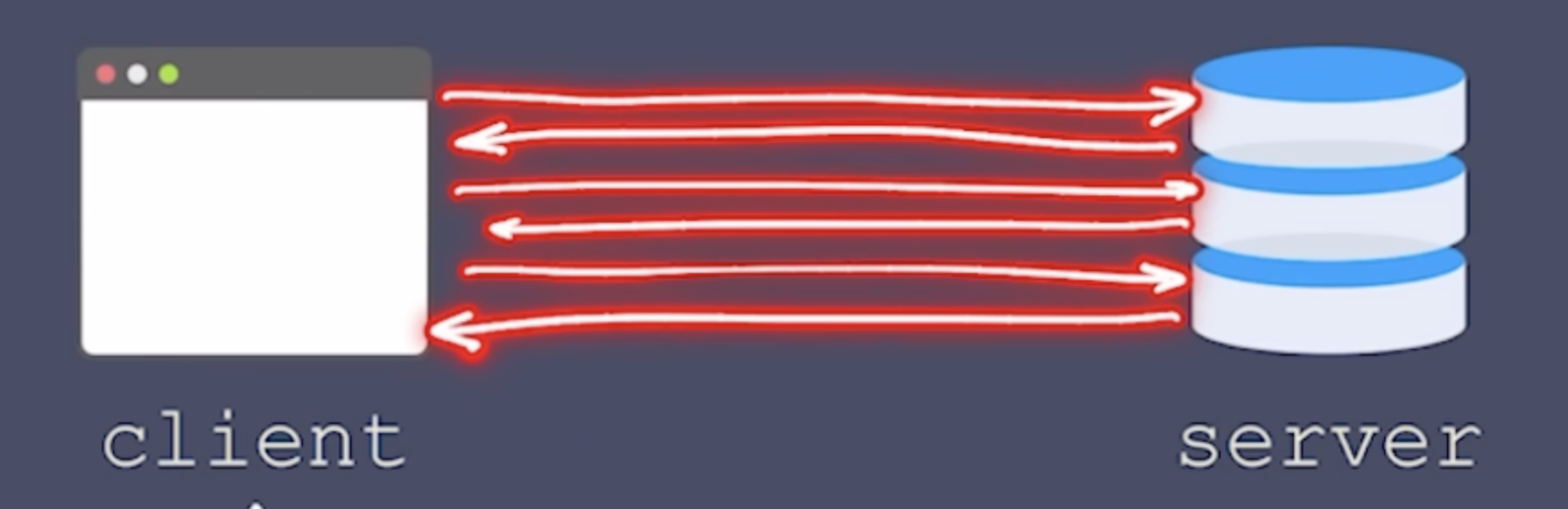
🌟 Why WebSockets Over HTTP for Real-Time Apps?
❌ HTTP is Not Built for Real-Time Systems:
HTTP is stateless and unidirectional, meaning each request-response cycle ends the TCP connection.
Every new request requires additional headers and authentication, causing unnecessary overhead.
✅ WebSockets Solve This Problem:
Persistent connection → No need to establish a new connection for every request.
Full duplex & bi-directional → Both server and client can send messages anytime, just like a phone call.
Lower latency → No need to wait for new HTTP requests.
🔹 How WebSockets Work?
1. The client sends an HTTP handshake request with an Upgrade header.
2. The server responds with a 101 Switching Protocols response.
3. A WebSocket connection is established, enabling continuous data transfer.
💡 Analogy:
HTTP is like sending emails—every message is a separate event.
WebSockets are like a phone call—both parties can speak anytime.
🎯 Conclusion
Real-time web technologies have revolutionized modern applications, making them faster and more interactive. By focusing on WebSockets, SSE, and WebRTC, you can build efficient, scalable real-time apps. Understanding the differences between these technologies will help you make informed decisions when developing web applications that rely on live updates and real-time interactions.
Which real-time technology are you using in your next project? Drop your thoughts in the comments!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Shayan Danish directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Shayan Danish
Shayan Danish
Full Stack Developer | Building Products & Crafting Solutions for Everyday Challenges