linux basic CMD
 manohar sharma
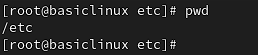
manohar sharmapwd : present working directory ==>
To check the current working directory
syntax: # pwd
****************************************************************************************************
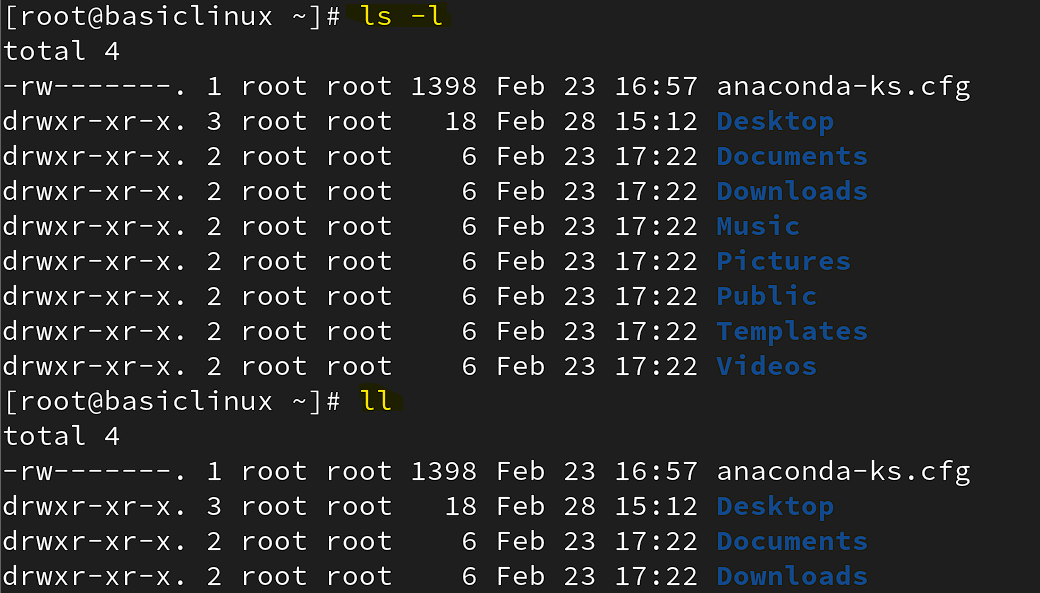
ls\= to check the file and directories of a particular location.
Listing of F&D
syntax: # ls -

option:
a= all hidden and non-hidden f&d

l= long form of f&d (aliasname = ll )
d= for directory

t= time sorting
r= recursively(ascending order)
h= human readable format
ls -d .* ==> only Hidden file and Directory (alias name = l.)
***************************************************************************************************
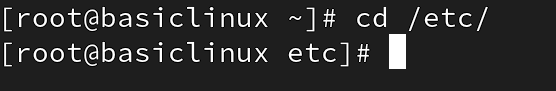
cd= (change directory)
to change one directory into another directory
syntax: # cd
cd .. = to go one step back
cd ../.. = to go two step back
cd / = to go on root directory
cd ~ = to go on home directory of user
cd = to go on home directory of user
cd . = to go on the same directory
cd - = to go previous working directory
. = It is functional directory to use as current directory
.. = It is functional directory to use as previous directory
****************************************************************************************************
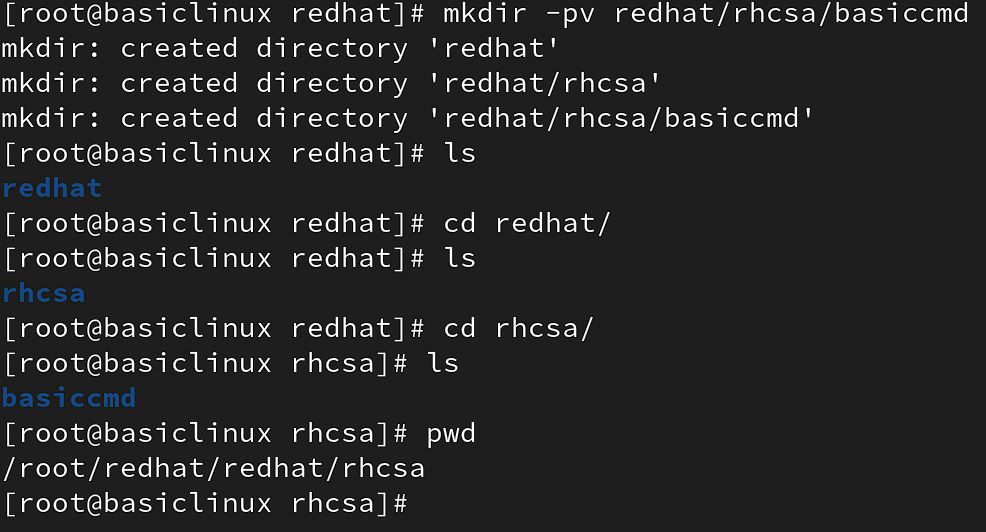
mkdir(make directory)= to create a Blank directory
syntax= # mkdir -option Directory

option:
v= verbose= to print the action
p= parent = to create multiple sub-directory into single directory
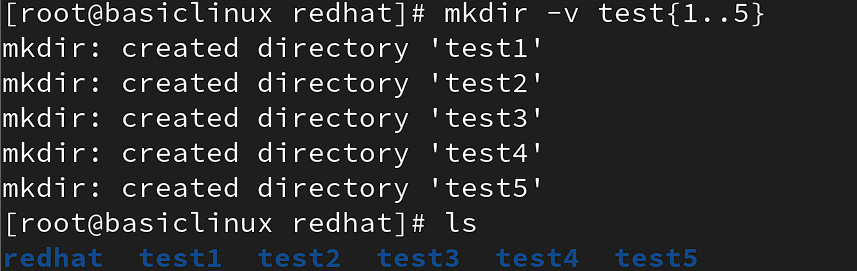
create directory in loop.
mkdir -option dirname{1..5}
with Space count directory= exp: new folder
mkdir 'New folder'

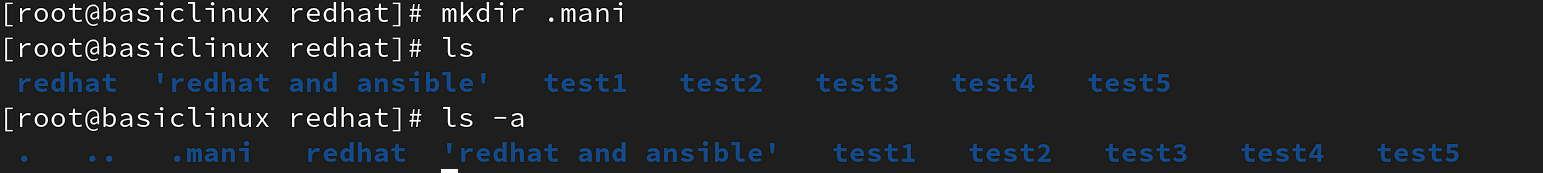
Hidden directory:
mkdir -v <.directory name>
*********************************************************************************************
Touch: to create a blank file
You can follow same as mkdir for creation of file
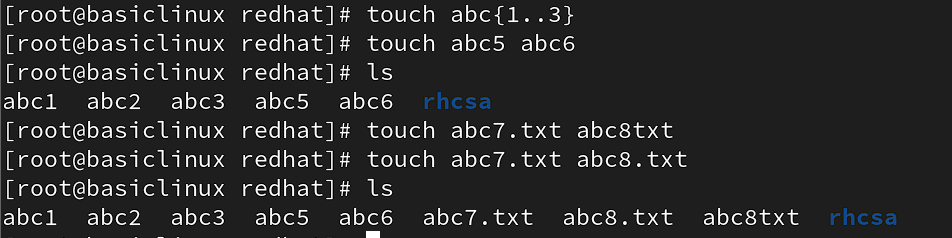
syntax= # touch filename1 filename2 filename3
touch filename{1..5}
touch filename{1..5}.txt
touch .filename ===Hidden file
touch 'file name' == for space count
*************************************************************************************************
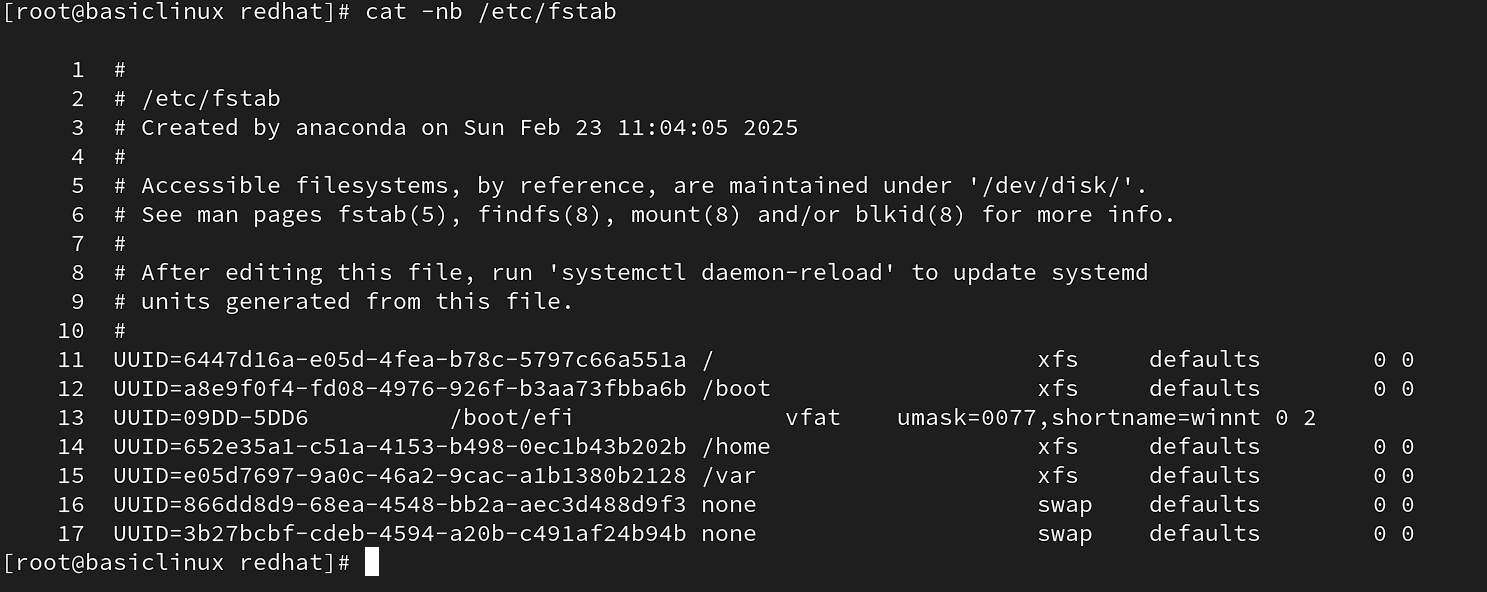
cat: to read the content of any file
syntax: #cat -option filename
option: n= line number including blank line
b= line number but avoid blank line
*****************************************************************************************************
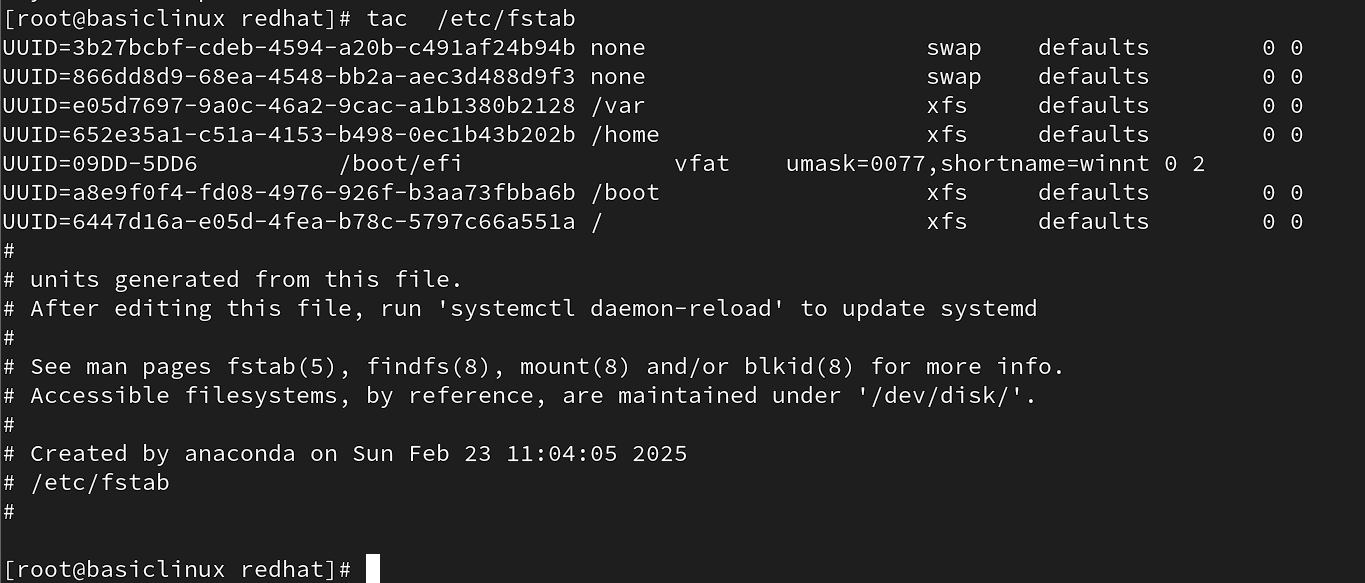
tac: To read the content of any file but in reverse form
syntax : #tac filename
***************************************************************************************************
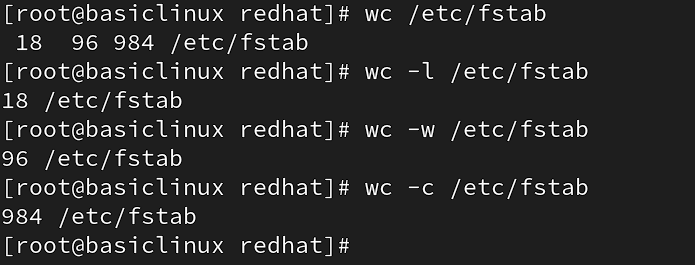
wc (word count): to count line number, word and character of any file
Syntax : #wc -option Filename
Option:
l= line number
w= word
c= character
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from manohar sharma directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
