A Comprehensive Guide to Upgrading Amazon EKS
 Saikrishna Yalamati
Saikrishna YalamatiTable of contents
- Introduction
- Things to Consider Before Upgrading EKS
- 1. AWS Release Notes and Compatibility
- 2. EKS Versioning and Upgrade Path
- 3. Cluster and Node Compatibility
- 4. Add-ons and Third-party Dependencies
- 5. Application Readiness
- 6. Backup and Rollback Strategy
- 7. Testing and Staging
- 8. Cluster Autoscaler and Scaling Policies
- 9. Security and IAM Policies
- 10. Observability and Monitoring
- 11. Cost and Performance Considerations
- EKS Upgrade Process
- Conclusion
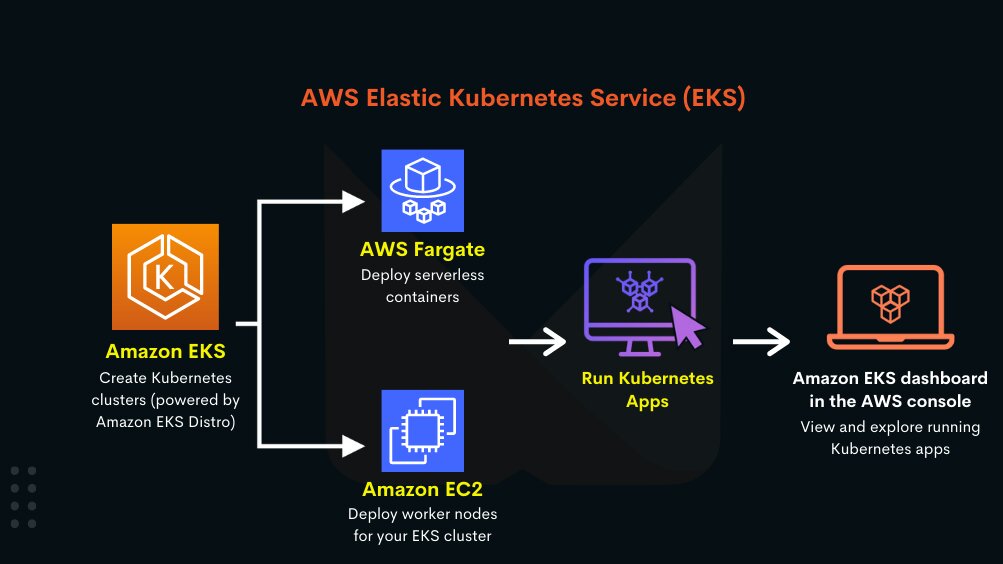
Introduction
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is a managed Kubernetes service that simplifies cluster management on AWS. However, keeping EKS up to date is crucial to ensure security, performance, and feature enhancements. Upgrading EKS involves multiple considerations and a well-defined process to minimize downtime and disruptions.
Things to Consider Before Upgrading EKS
1. AWS Release Notes and Compatibility
Review the AWS EKS Release Notes to understand changes and deprecations.
Ensure your applications, add-ons, and dependencies are compatible with the new version.
2. EKS Versioning and Upgrade Path
AWS supports only the last three Kubernetes versions.
You cannot skip versions (e.g., upgrading from 1.28 to 1.30 directly); you must go through 1.29 first.
3. Cluster and Node Compatibility
Managed node groups and self-managed nodes should be compatible with the EKS control plane.
Consider upgrading worker nodes separately to avoid disruptions.
4. Add-ons and Third-party Dependencies
Upgrade and test Kubernetes add-ons such as CoreDNS, kube-proxy, and Amazon VPC CNI.
Verify third-party applications and custom controllers remain functional.
5. Application Readiness
Ensure your applications support the API changes in the new Kubernetes version.
Use
kubectl deprecationsandkubectl api-resourcesto check for deprecated APIs.
6. Backup and Rollback Strategy
Take an EKS cluster backup using tools like Velero.
Plan for rollback in case of unexpected failures.
7. Testing and Staging
Upgrade a test cluster before production to identify potential issues.
Run integration and load tests post-upgrade.
8. Cluster Autoscaler and Scaling Policies
Ensure the Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler is compatible with the new version.
Verify scaling policies and node provisioning are working correctly post-upgrade.
9. Security and IAM Policies
Review and update IAM roles and policies associated with the EKS cluster.
Ensure network policies, security groups, and RBAC rules remain intact.
10. Observability and Monitoring
Validate monitoring tools such as Prometheus, Grafana, AWS CloudWatch, and Splunk.
Ensure logging and alerting systems are functional post-upgrade.
11. Cost and Performance Considerations
Monitor AWS resource consumption during and after the upgrade.
Optimize costs by adjusting instance types or leveraging Spot Instances where feasible.
EKS Upgrade Process
Step 1: Upgrade EKS Control Plane
Check the current version:
aws eks describe-cluster --name my-cluster --query cluster.versionUpgrade using AWS CLI:
aws eks update-cluster-version --name my-cluster --kubernetes-version 1.30Monitor the upgrade status:
aws eks describe-cluster --name my-cluster --query cluster.status
Step 2: Upgrade Managed Node Groups
Identify node groups:
aws eks list-nodegroups --cluster-name my-clusterUpgrade a node group:
aws eks update-nodegroup-version --cluster-name my-cluster --nodegroup-name my-nodegroup
Step 3: Upgrade Self-Managed Nodes (If Applicable)
Drain and cordon nodes:
kubectl drain <node-name> --ignore-daemonsets --delete-local-dataManually update the node AMI and recreate instances.
Step 4: Upgrade Kubernetes Add-ons
Upgrade CoreDNS:
kubectl edit deployment coredns -n kube-systemUpgrade Kube-Proxy:
kubectl set image daemonset/kube-proxy -n kube-system kube-proxy=602401143452.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/eks/kube-proxy:v1.30.0
Step 5: Validate the Upgrade
Check cluster nodes:
kubectl get nodesEnsure workloads are running as expected:
kubectl get pods -AMonitor logs for errors:
kubectl logs -l app=my-app
Conclusion
Upgrading Amazon EKS requires careful planning to ensure a smooth transition with minimal downtime. By considering compatibility, backups, testing, security, observability, and a step-by-step upgrade process, you can maintain a secure and high-performing Kubernetes environment.
Regular upgrades are essential to staying within the supported Kubernetes versions and avoiding technical debt.
Automating parts of the upgrade process using Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools such as Terraform can reduce manual errors.
Continuous monitoring post-upgrade ensures that performance remains optimal and unexpected issues are quickly addressed.
Educating teams and stakeholders about the upgrade process can improve collaboration and preparedness for future upgrades.
Always document the upgrade process and any issues encountered to streamline future upgrades.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Saikrishna Yalamati directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
